|
Modal Meinongianism
Noneism, also known in philosophy as modal Meinongianism (named after Alexius Meinong), names both a philosophical theory and an unrelated religious trend. In a philosophical and metaphysical context, the theory suggests that some things do not exist. That definition was first conceptualized by Richard Sylvan in 1980 and then later expanded on by Graham Priest in 2005. In a religious context, noneism is the practice of spirituality without an affiliation to organized religion. Philosophical context Noneism, in this context, holds that some things do not exist or have no being. There are a few controversial entities in philosophy that, according to noneism philosophy, do not exist: past and future entities, which entails any entity that no longer exists or will exist in the future; people or living things that are deceased; unactualized possibila, which are objects that have the potential to exist but do not yet exist; universals, being characteristics shared by a multiplicity ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Alexius Meinong
Alexius Meinong von Handschuchsheim (; 17 July 1853 – 27 November 1920) was an Austrian philosopher, a realist known for his unique ontology and theory of objects. He also made contributions to philosophy of mind and theory of value. Life Alexius Meinong's father was officer Anton von Meinong (1799–1870), who was granted the hereditary title of Ritter in 1851 and reached the rank of Major General in 1858 before retiring in 1859. From 1868 to 1870, Meinong studied at the Akademisches Gymnasium, Vienna. In 1870, he entered the University of Vienna law school where he was drawn to Carl Menger's lectures on economics. In summer 1874, he earned a doctorate in history by writing a thesis on Arnold of Brescia. It was during the winter term (1874–1875) that he began to focus on history and philosophy. Meinong became a pupil of Franz Brentano, who was then a recent addition to the philosophical faculty. Meinong would later claim that his mentor did not directly influence ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Gandalf
Gandalf is a protagonist in J. R. R. Tolkien's novels ''The Hobbit'' and ''The Lord of the Rings''. He is a Wizards (Middle-earth), wizard, one of the Istari order, and the leader of the Company of the Ring. Tolkien took the name "Gandalf" from the Old Norse Dvergatal, "Catalogue of Dwarves" (''Dvergatal'') in the ''Völuspá''. As a wizard and the bearer of one of the Three Rings, Gandalf has great power, but works mostly by encouraging and persuading. He sets out as Gandalf the Grey, possessing great knowledge and travelling continually. Gandalf is focused on the mission to counter the Dark Lord Sauron by destroying the One Ring. He is associated with fire; his ring of power is Narya, the Ring of Fire. As such, he delights in fireworks to entertain the hobbits of the Shire, while in great need he uses fire as a weapon. As one of the Maiar, he is an immortal spirit from Valinor, but his physical body can be killed. In ''The Hobbit'', Gandalf assists the 13 dwarves and the h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Meinong's Jungle
In metaphysics and ontology, nonexistent objects are a concept advanced by Austrian philosopher Alexius Meinong in the 19th and 20th centuries within a " theory of objects". He was interested in intentional states which are directed at nonexistent objects. Starting with the "principle of intentionality", mental phenomena are intentionally directed towards an object. People may imagine, desire or fear something that does not exist. Other philosophers concluded that intentionality is not a real relation and therefore does not require the existence of an object, while Meinong concluded there is an object for every mental state whatsoever—if not an existent then at least a nonexistent one. Round square copula The round square copula is a common example of the dual copula strategy used in reference to the "problem of nonexistent objects" as well as their relation to problems in modern philosophy of language. The issue arose, most notably, between the theories of contemporary phil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Abstract Object Theory
Abstract object theory (AOT) is a branch of metaphysics regarding abstract objects. Originally devised by metaphysician Edward Zalta in 1981, the theory was an expansion of mathematical Platonism. Overview ''Abstract Objects: An Introduction to Axiomatic Metaphysics'' (1983) is the title of a publication by Edward Zalta that outlines abstract object theory. AOT is a dual predication approach (also known as "dual copula strategy") to abstract objectsDale Jacquette, ''Meinongian Logic: The Semantics of Existence and Nonexistence'', Walter de Gruyter, 1996, p. 17. influenced by the contributions of Alexius Meinong and his student Ernst Mally. On Zalta's account, there are two modes of Predicate (mathematical logic), predication: some objects (the ordinary Abstract and concrete, concrete ones around us, like tables and chairs) ''exemplify'' properties, while others (abstract objects like numbers, and what others would call "nonexistent objects", like the Round square copula, round ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Ritual
A ritual is a repeated, structured sequence of actions or behaviors that alters the internal or external state of an individual, group, or environment, regardless of conscious understanding, emotional context, or symbolic meaning. Traditionally associated with gestures, words, or revered objects, rituals also occur in non-human species, such as elephant mourning or corvid object-leaving. They may be prescribed by tradition, including religious practices, and are often characterized by formalism, traditionalism, rule-governance, and performance. Rituals are a feature of all known human societies. They include not only the worship rites and sacraments of organized religions and cults, but also rites of passage, atonement and ritual purification, purification rites, oaths of allegiance, dedication ceremonies, coronations and presidential inaugurations, marriages, funerals and more. Even common actions like handshake, hand-shaking and saying "hello" may be termed as ''rituals''. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
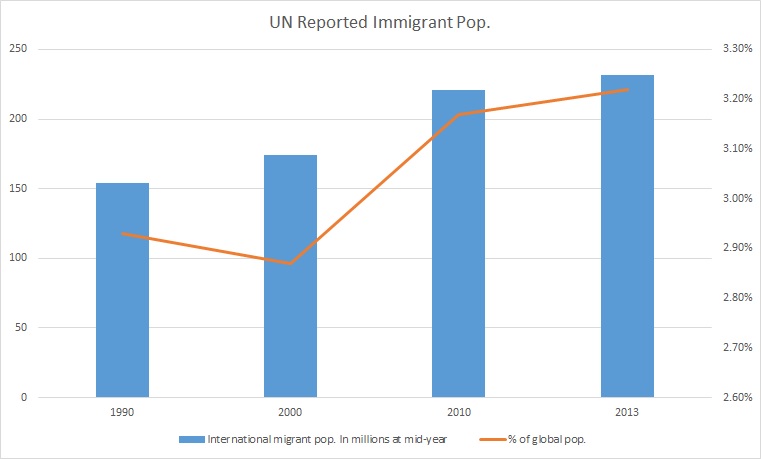
Immigrants
Immigration is the international movement of people to a destination country of which they are not usual residents or where they do not possess nationality in order to settle as permanent residents. Commuters, tourists, and other short-term stays in a destination country do not fall under the definition of immigration or migration; seasonal labour immigration is sometimes included, however. Economically, research suggests that migration can be beneficial both to the receiving and sending countries. The academic literature provides mixed findings for the relationship between immigration and crime worldwide. Research shows that country of origin matters for speed and depth of immigrant assimilation, but that there is considerable assimilation overall for both first- and second-generation immigrants. Discrimination based on nationality is legal in most countries. Extensive evidence of discrimination against foreign-born persons in criminal justice, business, the economy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 contiguous states border Canada to the north and Mexico to the south, with the semi-exclave of Alaska in the northwest and the archipelago of Hawaii in the Pacific Ocean. The United States asserts sovereignty over five Territories of the United States, major island territories and United States Minor Outlying Islands, various uninhabited islands in Oceania and the Caribbean. It is a megadiverse country, with the world's List of countries and dependencies by area, third-largest land area and List of countries and dependencies by population, third-largest population, exceeding 340 million. Its three Metropolitan statistical areas by population, largest metropolitan areas are New York metropolitan area, New York, Greater Los Angeles, Los Angel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Pacific Northwest
The Pacific Northwest (PNW; ) is a geographic region in Western North America bounded by its coastal waters of the Pacific Ocean to the west and, loosely, by the Rocky Mountains to the east. Though no official boundary exists, the most common conception includes the U.S. states of Oregon, Washington (state), Washington, Idaho, and the Canadian province of British Columbia. Some broader conceptions reach north into Alaska and Yukon, south into Northern California, and east into western Montana. Other conceptions may be limited to the coastal areas west of the Cascade Mountains, Cascade and Coast Mountains, Coast mountains. The Northwest Coast is the coastal region of the Pacific Northwest, and the Northwest Plateau (also commonly known as "British Columbia Interior, the Interior" in British Columbia), is the inland region. The term "Pacific Northwest" should not be confused with the Northwest Territory (also known as the Great Northwest, a historical term in the United States) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Religion
Religion is a range of social system, social-cultural systems, including designated religious behaviour, behaviors and practices, morals, beliefs, worldviews, religious text, texts, sanctified places, prophecies, ethics in religion, ethics, or religious organization, organizations, that generally relate humanity to supernatural, transcendence (religion), transcendental, and spirituality, spiritual elements—although there is no scholarly consensus over what precisely constitutes a religion. It is an essentially contested concept. Different religions may or may not contain various elements ranging from the divine, sacredness, faith,Tillich, P. (1957) ''Dynamics of faith''. Harper Perennial; (p. 1). and a supernatural being or beings. The origin of religious belief is an open question, with possible explanations including awareness of individual death, a sense of community, and dreams. Religions have sacred histories, narratives, and mythologies, preserved in oral traditions, sac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Agnosticism
Agnosticism is the view or belief that the existence of God, the divine, or the supernatural is either unknowable in principle or unknown in fact. (page 56 in 1967 edition) It can also mean an apathy towards such religious belief and refer to personal limitations rather than a worldview. Another definition is the view that "human reason is incapable of providing sufficient rational grounds to justify either the belief that God exists or the belief that God does not exist." The English biologist Thomas Henry Huxley said that he originally coined the word ''agnostic'' in 1869 "to denote people who, like imself confess themselves to be hopelessly ignorant concerning a variety of matters ncluding the matter of God's existence about which metaphysicians and theologians, both orthodox and heterodox, dogmatise with the utmost confidence." Earlier thinkers had written works that promoted agnostic points of view, such as Sanjaya Belatthiputta, a 5th-century BCE Indian philosophe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Atheism
Atheism, in the broadest sense, is an absence of belief in the Existence of God, existence of Deity, deities. Less broadly, atheism is a rejection of the belief that any deities exist. In an even narrower sense, atheism is specifically the position that there no deities. Atheism is contrasted with theism, which is the belief that at least one deity exists. Historically, evidence of atheistic viewpoints can be traced back to classical antiquity and Nāstika, early Indian philosophy. In the Western world, atheism declined after Christianity gained prominence. The 16th century and the Age of Enlightenment marked the resurgence of atheistic thought in Europe. Atheism achieved a significant position worldwide in the 20th century. Estimates of those who have an absence of belief in a god range from 500 million to 1.1 billion people. Atheist organizations have defended the autonomy of science, freedom of thought, secularism, and secular ethics. Arguments for atheism range from p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Religious Movement
Various sociological classifications of religious movements have been proposed by scholars. In the sociology of religion, the most widely used classification is the church-sect typology. The typology is differently construed by different sociologists, and various distinctive features have been proposed to characterise churches and sects. On most accounts, the following features are deemed relevant: * The church is a compulsory organisation into which people are born, while the sect is a voluntary organisation to which people usually convert. * The church is an inclusive organisation to which all kinds of people may belong, while the sect is an exclusive organisation of religiously qualified people. * The church is an established organisation that is well integrated into the larger society and usually inclined to seek for an alliance with the political power, while the sect is a splinter group from a larger religion: it is often in tension with current societal values, rejects an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |