|
Mocoso
Mocoso (or Mocoço) was the name of a 16th-century chiefdom located on the east side of Tampa Bay, Florida near the mouth of the Alafia River, of its chief town and of its chief. Mocoso was also the name of a 17th-century village in the province of Acuera, a branch of the Timucua. The people of both villages are believed to have been speakers of the Timucua language. The Mocoso of Tampa Bay lived in the area of the Safety Harbor culture. The Mocoso people were among the first inhabitants of Florida encountered by both the Narváez expedition in 1528 and the de Soto expedition in 1539. Hernando de Escalante Fontaneda, who was a captive of various tribes in Florida from about 1549 until about 1566, described Mocoso as a "kingdom by t/nowiki>self", i.e., not part of the Calusa domain. The de Soto expedition chroniclers recorded that Mocoso was subject to an inland chief named Paracoxi or Urriparacoxi, of a village of the same name. ''Paracoxi'' was a leadership title used some of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Juan Ortiz (captive)
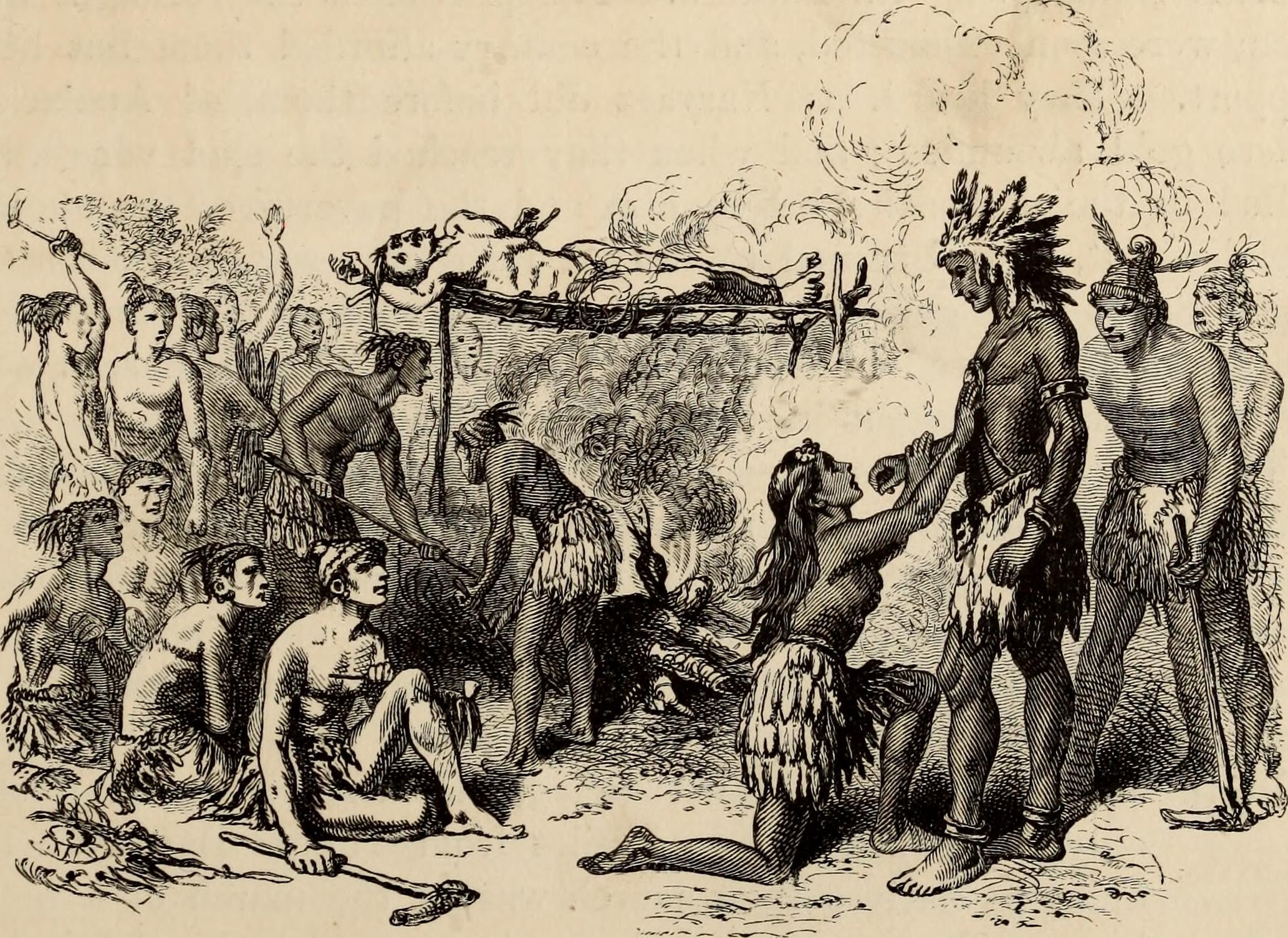
Juan Ortiz was a Spanish sailor who was held captive by Native Americans in Florida for eleven years, from 1528 until he was rescued by the Hernando de Soto expedition in 1539. Two accounts of Ortiz's eleven years as a captive, differing in details, offer a story of Ortiz being sentenced to death by a Native American chief two or three times, saved each time by the intervention of a daughter (and possibly other female relatives) of the chief, and finally escaping to a neighboring chiefdom, whose chief sheltered him. Captivity In 1528 Juan Ortiz was on a ship searching Tampa Bay for any sign of the Narváez expedition which had landed in Tampa Bay the year before. Ortiz and one or more companions were enticed on shore by some people who had what the Spanish thought was a message from Narváez. (The Spanish would not learn the fate of the Narváez expedition for another eight years, until Álvar Núñez Cabeza de Vaca and three other survivors reached a Spanish outpost in northwest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Safety Harbor Culture
The Safety Harbor culture was an archaeological culture practiced by Native Americans living on the central Gulf coast of the Florida peninsula, from about 900 CE until after 1700. The Safety Harbor culture is defined by the presence of Safety Harbor ceramics in burial mounds. The culture is named after the Safety Harbor site, which is close to the center of the culture area. The Safety Harbor site is the probable location of the chief town of the Tocobaga, the best known of the groups practicing the Safety Harbor culture. The Safety Harbor people were organized into chiefdoms and lived primarily in villages along the shoreline of Tampa Bay and the adjacent Gulf of Mexico coast. The chiefdoms may have consisted of about of shoreline, and extended about inland. Each chiefdom had a principal town or "capital" with a temple mound and central plaza. Fifteen such towns have been identified along the Florida Gulf coast from southern Pasco County to northern Sarasota County, an area ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Timucua
The Timucua were a Native American people who lived in Northeast and North Central Florida and southeast Georgia. They were the largest indigenous group in that area and consisted of about 35 chiefdoms, many leading thousands of people. The various groups of Timucua spoke several dialects of the Timucua language. At the time of European contact, Timucuan speakers occupied about in the present-day states of Florida and Georgia, with an estimated population of 200,000. Milanich notes that the population density calculated from those figures, is close to the population densities calculated by other authors for the Bahamas and for Hispaniola at the time of first European contact.Milanich 2000 The territory occupied by Timucua speakers stretched from the Altamaha River and Cumberland Island in present-day Georgia as far south as Lake George in central Florida, and from the Atlantic Ocean west to the Aucilla River in the Florida Panhandle, though it reached the Gulf of Mexico at no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acuera
Acuera was the name of both an indigenous town and a province or region in central Florida during the 16th and 17th centuries. The indigenous people of Acuera spoke a dialect of the Timucua language. In 1539 the town first encountered Europeans when it was raided by soldiers of Hernando de Soto's expedition. French colonists also knew this town during their brief tenure (1564–1565) in northern Florida. Late in the 16th century, Acuera came under Spanish influence as it expanded its settlements. Two or three Spanish missions were founded in the Acuera province in the 17th century. Location Based on distances between indigenous towns reported by Spanish explorers, anthropologists Jerald T. Milanich and Charles Hudson locate the town of Acuera in central Florida near Lake Weir and Lake Griffin, near the headwaters of the Oklawaha River, a tributary of the St. Johns River. A map produced by Jacques le Moyne, who was part of the late 16th-century French attempt to colonize Florida a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
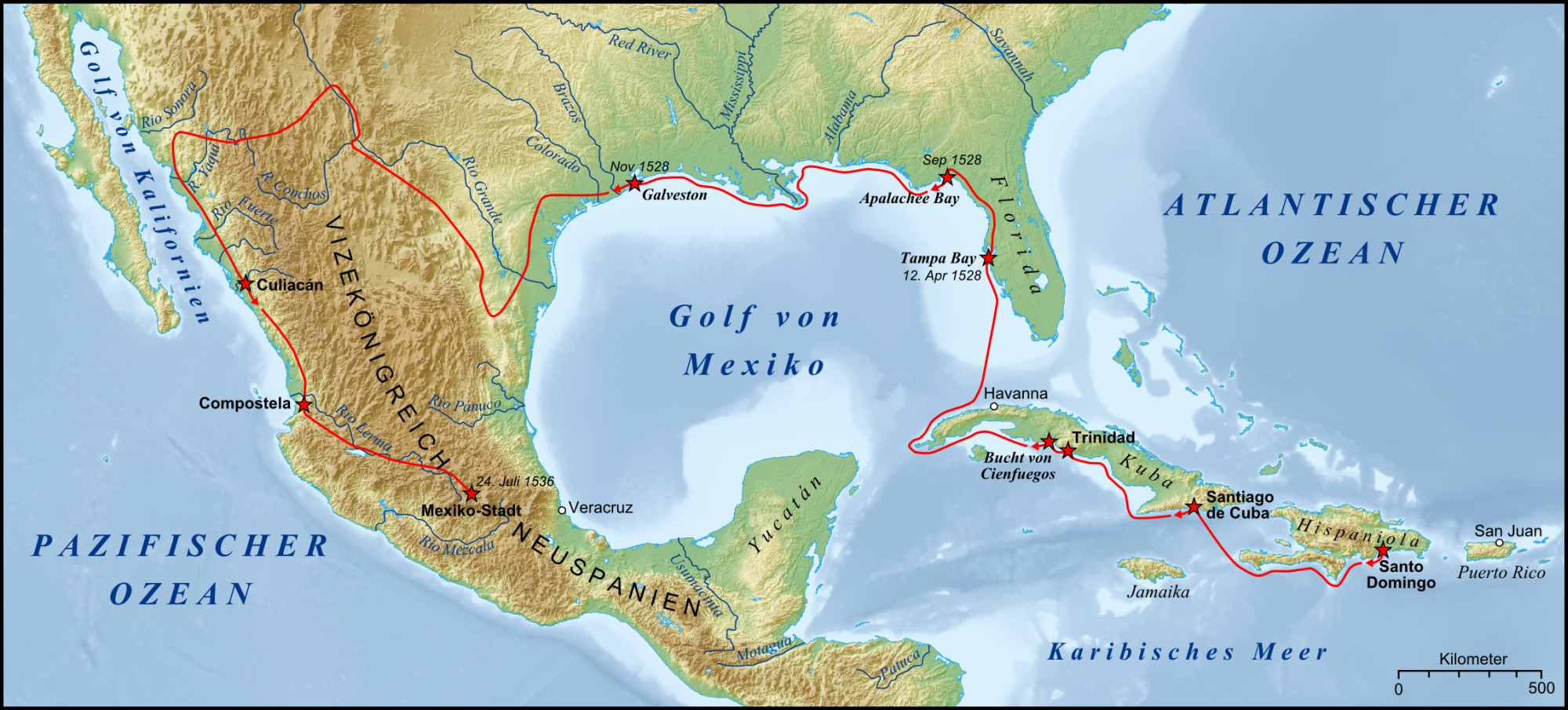
Narváez Expedition
The Narváez expedition was a Spanish journey of exploration and colonization started in 1527 that intended to establish colonial settlements and garrisons in Florida. The expedition was initially led by Pánfilo de Narváez, who died in 1528. Many more people died as the expedition traveled west along the explored Gulf Coast of the present-day United States and into the American Southwest. Only four of the expedition's original members survived, reaching Mexico City in 1536. These survivors were the first known non-Native Americans to see the Mississippi River, and to cross the Gulf of Mexico and Texas. Narváez's crew initially numbered about 600, including men from Spain, Portugal, Greece, and Italy. The expedition met with disaster almost immediately. Making stops at Hispaniola and Cuba on the way to La Florida, the fleet was devastated by a hurricane, among other storms, and lost two ships. They left Cuba in February 1528. Their intended destination was the Rio de las Palma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hernando De Soto
Hernando de Soto (; ; 1500 – 21 May, 1542) was a Spanish explorer and '' conquistador'' who was involved in expeditions in Nicaragua and the Yucatan Peninsula. He played an important role in Francisco Pizarro's conquest of the Inca Empire in Peru, but is best known for leading the first European expedition deep into the territory of the modern-day United States (through Florida, Georgia, Alabama, Mississippi, and most likely Arkansas). He is the first European documented as having crossed the Mississippi River. De Soto's North American expedition was a vast undertaking. It ranged throughout what is now the southeastern United States, both searching for gold, which had been reported by various Native American tribes and earlier coastal explorers, and for a passage to China or the Pacific coast. De Soto died in 1542 on the banks of the Mississippi River; different sources disagree on the exact location, whether it was what is now Lake Village, Arkansas, or Ferriday, Louisia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Native American Tribes In Florida
The indigenous peoples of Florida lived in what is now known as Florida for more than 12,000 years before the time of first contact with Europeans. However, the indigenous Floridians living east of the Apalachicola River had largely died out by the early 18th century. Some Apalachees migrated to Louisiana, where their descendants now live; some were taken to Cuba and Mexico by the Spanish in the 18th century, and a few may have been absorbed into the Seminole and Miccosukee tribes. Paleoindians The first people arrived in Florida before the extinction of the Pleistocene megafauna. Human remains and/or artifacts have been found in association with the remains of Pleistocene animals at a number of Florida locations. A carved bone depicting a mammoth found near the site of Vero man has been dated to 13,000 to 20,000 years ago. Artifacts recovered at the Page-Ladson site date to 12,500 to 14,500 years ago. Evidence that a giant tortoise was cooked in its shell at Little Salt Spring ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uzita (Florida)
Uzita (Uçita) was the name of a 16th-century native chiefdom, its chief town and its chiefs. Part of the Safety Harbor culture, it was located in present-day Florida on the south side of Tampa Bay. History The chief town was near the mouth of the Little Manatee River on the south side of Tampa Bay, Florida in the area of Hillsborough County that is now Ruskin, Florida. The territory of Uzita was said to extend from the Little Manatee River to Sarasota Bay. The Uzita people were part of the Safety Harbor culture. The people of Uzita were the first inhabitants of Florida to be encountered by both the Narváez expedition in 1528 and the de Soto expedition in 1539. The town of Uzita was described as consisting of the chief's house on a mound, seven or eight other houses, and a "temple" (apparently a charnel house). The houses were made of wood and palm thatch, and probably housed a large number of people each. The Uzitans used bows and arrows. The Spanish described the bows as being ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indigenous Peoples Of The Southeastern Woodlands
Indigenous peoples of the Southeastern Woodlands, Southeastern cultures, or Southeast Indians are an ethnographic classification for Native Americans who have traditionally inhabited the area now part of the Southeastern United States and the northeastern border of Mexico, that share common cultural traits. This classification is a part of the Eastern Woodlands. The concept of a southeastern cultural region was developed by anthropologists, beginning with Otis Mason and Frank Boas in 1887. The boundaries of the region are defined more by shared cultural traits than by geographic distinctions.Jackson and Fogelson 3 Because the cultures gradually instead of abruptly shift into Plains, Prairie, or Northeastern Woodlands cultures, scholars do not always agree on the exact limits of the Southeastern Woodland culture region. Shawnee, Powhatan, Waco, Tawakoni, Tonkawa, Karankawa, Quapaw, and Mosopelea are usually seen as marginally southeastern and their traditional lands represent the b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alafia River
The Alafia River is long, with a watershed of in Hillsborough County, Florida, United States, flowing into Tampa Bay. The watershed contains ten named lakes and ponds, and 29 named rivers, streams and canals. During the rainy season, excess water is pumped to the new C.W. Bill Young Regional Reservoir, which opened in 2005. The river is formed by two prongs. The north prong starts south of Mulberry and runs for 23.9 miles until it meets the south prong in Lithia. The south prong begins south of Bradley Junction and continues for 28.7 miles. The combined river then flows 24.7 miles west into Tampa Bay. History For centuries the Alafia was home to various native tribes, including the Tocobaga. From their settlement at the mouth of the river to their hunting camps upstream, the Indians left traces of their lives and activities. The Mocoso occupied the area around the mouth of the Alafia in the 16th century and were believed to speak Timucuan. In the sixteenth century, the expedit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Sites And Peoples Visited By The Hernando De Soto Expedition
This is a list of sites and peoples visited by the Hernando de Soto Expedition in the years 1539–1543. In May 1539, de Soto left Havana, Cuba, with nine ships, over 620 men and 220 surviving horses and landed at Charlotte Harbor, Florida. This began his three-year odyssey through the Southeastern North American continent, from which de Soto and a large portion of his men would not return. They met many varied Native American groups, most of them bands and chiefdoms related to the widespread Mississippian culture. Only a few of these ancestral cultures survived into the seventeenth century, or their descendants combined as historic tribes known to later Europeans. Others have been recorded only in the written historical accounts of de Soto's expedition. Florida * Uzita * Mocoso * Urriparacoxi * Timucua * Ocale * Acuera * Potano * Alachua culture * Northern Utina * Yustaga * Uzachile * Anhaica * Apalachee * Narváez expedition's "Bay of Horses" Georgia The peoples th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urriparacoxi
Urriparacoxi, or Paracoxi, was the chief of a Native American group in central Florida at the time of Hernando de Soto's expedition through what is now the southeastern United States. "Urriparacoxi" was a title, meaning "war leader". There is no known name for the people he led, or for their territory. Encounter with de Soto Hernando de Soto landed on the west coast of the peninsula of Florida in the summer of 1539 with a large contingent of men, with the intention of exploring and colonizing the country. The exact place at which de Soto landed has been controversial, but a number of historians accept Tampa Bay as the site. Soon after landing de Soto encountered Juan Ortiz, a Spanish sailor who had been held captive by local chiefs for eleven years. Ortiz told de Soto of a chief called Urriparacoxi who lived inland, who had a lot of maize, and to whom the local chiefdoms, including Mocoso and Uzita, paid tribute. De Soto sent one of his lieutenants, Baltazar de Gallegos, with bet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |