|
Mişär-Tatars
The Mishar Tatars (endonyms: мишәрләр, мишәр татарлары, mişärlär, mişär tatarları) form a subgroup of the Volga Tatars, indigenous to Mordovia, Tatarstan, Bashkortostan, and Chuvashia in the Russian Federation. They also live in the Penza Oblast, Penza, Ulyanovsk Oblast, Ulyanovsk, Orenburg Oblast, Orenburg, Nizhny Novgorod Oblast, Nizhny Novgorod, Samara Oblast, Samara, Volgograd Oblast, Volgograd, and Saratov Oblasts of Russia and as an immigrant minority in Estonia, Latvia, and Finland (Mishar Tatars comprise the majority of Finnish Tatars and Tatars living in other Nordic countries, Nordic and Baltic states, Baltic countries). The Mishar Tatar dialect is one of the two Tatar language, Volga Tatar dialects. History Friar Julian describes Eastern Hungarians he found in Bashkortostan, Bashkiria in 1235. They spoke to him Hungarian language, Hungarian and their language remained mutually intelligible. Some scientists of the 19th and 20th centuries, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volga Tatars
The Volga Tatars or simply Tatars ( tt-Cyrl, татарлар, tatarlar) are a Turkic ethnic group native to the Volga-Ural region of Russia. They are subdivided into various subgroups. Volga Tatars are Russia's second-largest ethnicity after the Russians. They compose 53% of the population of Tatarstan and 25% of the population of Bashkortostan. The Volga Tatars are by far the largest group amongst the Tatars. History Tatars inhabiting the Republic of Tatarstan, a federal subject of Russia, constitute one third of all Tatars, while the other two thirds reside outside Tatarstan. Some of the communities residing outside Tatarstan developed before the Russian Revolution of 1917, as Tatars were specialized in trading. During the 14th century, Sunni Islam was adopted by many of the Tatars. Tatars became subjects of Russia after the Siege of Kazan in 1552. Russians were using the Tatar ethnonym during the 18th and 19th centuries to denote all Turkic inhabitants of the Russian Empi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volgograd Oblast
Volgograd Oblast (russian: Волгогра́дская о́бласть, ''Volgogradskaya oblast'') is a federal subjects of Russia, federal subject (an oblast) of Russia, located in the Volga region, Volga region of Southern Russia. Its administrative center is Volgograd. The population of the oblast was 2,610,161 in the Russian Census (2010), 2010 Census. Formerly known as Stalingrad Oblast, it was given its present name in 1961, when the city of Stalingrad was renamed Volgograd as part of de-Stalinization. Volgograd Oblast borders Rostov Oblast in the southwest, Voronezh Oblast in the northwest, Saratov Oblast in the north, Astrakhan Oblast and the Republic of Kalmykia in the southeast, and has an Kazakhstan–Russia border, international border with Kazakhstan in the east. The two main rivers in European Russia, the Don River (Russia), Don and the Volga River, Volga, run through the oblast and are connected by the Volga–Don Canal. Volgograd Oblast's strategic waterway ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turkic People
The Turkic peoples are a collection of diverse ethnic groups of West Asia, West, Central Asia, Central, East Asia, East, and North Asia as well as parts of Europe, who speak Turkic languages.. "Turkic peoples, any of various peoples whose members speak languages belonging to the Turkic subfamily...". "The Turkic peoples represent a diverse collection of ethnic groups defined by the Turkic languages." According to historians and linguists, the Proto-Turkic language originated in Central-East Asia region, potentially in Mongolia or Tuva. Initially, Proto-Turkic speakers were potentially both hunter-gatherers and farmers, but later became nomadic Pastoralism, pastoralists. Early and Post-classical history, medieval Turkic groups exhibited a wide range of both East Asian and West-Eurasian physical appearances and genetic origins, in part through long-term contact with neighboring peoples such as Iranian peoples, Iranian, Mongolic peoples, Mongolic, Tocharians, Yeniseian people, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chuvash Language
Chuvash ( , ; , , ) is a Turkic language spoken in European Russia, primarily in the Chuvash Republic and adjacent areas. It is the only surviving member of the Oghur branch of Turkic languages, one of the two principal branches of the Turkic family. The writing system for the Chuvash language is based on the Cyrillic script, employing all of the letters used in the Russian alphabet and adding four letters of its own: Ӑ, Ӗ, Ҫ and Ӳ. Usage Chuvash is the native language of the Chuvash people and an official language of Chuvashia. It is spoken by 1,640,000 persons in Russia and another 34,000 in other countries. 86% of ethnic Chuvash and 8% of the people of other ethnicities living in Chuvashia claimed knowledge of Chuvash language during the 2002 census. Despite that and although Chuvash is taught at schools and sometimes used in the media, it is considered endangered, because Russian dominates in most spheres of life and few children learning the language are li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mordvinic Languages
The Mordvinic languages, also known as the Mordvin, Mordovian or Mordvinian languages (russian: мордовские языки, ''mordovskiye yazyki''), are a subgroup of the Uralic languages, comprising the closely related Erzya language and Moksha language, both spoken in Mordovia. Previously considered a single "Mordvin language", it is now treated as a small language grouping. Due to differences in phonology, lexicon, and grammar, Erzya and Moksha are not mutually intelligible. The two Mordvinic languages also have separate literary forms. The Erzya literary language was created in 1922 and the Mokshan in 1923. Phonological differences between the two languages include: * Moksha retains a distinction between the vowels while in Erzya, both have merged as . * In unstressed syllables, Erzya features vowel harmony like many other Uralic languages, using in front-vocalic words and in back-vocalic words. Moksha has a simple schwa in their place. * Word-initially, Erzya has a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kazan
Kazan ( ; rus, Казань, p=kɐˈzanʲ; tt-Cyrl, Казан, ''Qazan'', IPA: ɑzan is the capital and largest city of the Republic of Tatarstan in Russia. The city lies at the confluence of the Volga and the Kazanka rivers, covering an area of , with a population of over 1.2 million residents, up to roughly 1.6 million residents in the urban agglomeration. Kazan is the fifth-largest city in Russia, and the most populous city on the Volga, as well as the Volga Federal District. Kazan became the capital of the Khanate of Kazan and was conquered by Ivan the Terrible in the 16th century, becoming a part of Russia. The city was seized and largely destroyed during Pugachev's Rebellion of 1773–1775, but was later rebuilt during the reign of Catherine the Great. In the following centuries, Kazan grew to become a major industrial, cultural and religious centre of Russia. In 1920, after the Russian SFSR became a part of the Soviet Union, Kazan became the capital of the Tat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mirfatyh Zakiev
, birth_date = , birth_place = Zaipy, Yutazinsky District, Tatar ASSR , alma_mater = Kazan State University , nationality = Russian , occupation = Linguist, university teacher and public figure , discipline = Turkologist , title = Doctor of Linguistics. Professor , awards = Honored Scientist of the Russian Federation (1976) and of the Tatarstan Republic (1970), Laureate of the Tatarstan Republic State Premium in Science and Technology , notable_works = The predicate in a modern Tatar literary language (1954); Syntactic Structure of the Tatar language (1963) , workplaces = Rector of Kazan State Pedagogical Institute, Dean of Tatar Language Faculty of Kazan State University , boards = Full member, and member of Presidium at Academy of Sciences of Tatarstan Republic (AN/RT) , thesis_title = Syntactic Structure of the Tatar language , thesis_year = 1963 , main_interests = Syntaxis of Tatar language, History of Tatar linguistics, Development of Tatar language Mirfatyh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hungarian Language
Hungarian () is an Uralic language spoken in Hungary and parts of several neighbouring countries. It is the official language of Hungary and one of the 24 official languages of the European Union. Outside Hungary, it is also spoken by Hungarian communities in southern Slovakia, western Ukraine ( Subcarpathia), central and western Romania (Transylvania), northern Serbia (Vojvodina), northern Croatia, northeastern Slovenia (Prekmurje), and eastern Austria. It is also spoken by Hungarian diaspora communities worldwide, especially in North America (particularly the United States and Canada) and Israel. With 17 million speakers, it is the Uralic family's largest member by number of speakers. Classification Hungarian is a member of the Uralic language family. Linguistic connections between Hungarian and other Uralic languages were noticed in the 1670s, and the family itself (then called Finno-Ugric) was established in 1717. Hungarian has traditionally been assigned to the Ugric alo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastern Hungarians
The term Eastern Hungarians ( hu, Keleti magyarok; or "Eastern Magyars") is used in scholarship to refer to peoples related to the Proto-Hungarians, that is, theoretically parts of the ancient community that remained in the vicinity of the Ural Mountains (at the European– Asian border) during the Migration Period and as such did not participate in the Hungarian conquest of the Carpathian Basin. The possible locations of the remnants of Hungarians Yugra Yugra ( gr, Οὔγγροι) has been believed by some to have been the Hungarian ''Urheimat'' (homeland), which is today inhabited by the Mansi and Khanty, two related ethnic groups. Magna Hungaria The term "Eastern Hungarians" is also used in relation to the ''Magna Hungaria'' of Friar Julian ( 1235), located at Bashkortostan (the land of the Bashkirs), where Julian was able to communicate with the locals in his Hungarian language. Savard Hungarians According to Hungarian scholarship, there was a group of "Savard Hungari ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Friar Julian
Friar Julian ( hu, Julianus barát) was one of a group of Hungarian Dominican friars who, in 1235, left Hungary in order to find those Magyars who — according to the chronicles — remained in the eastern homeland. After travelling a great distance, Friar Julian reached the capital of Volga Bulgaria, where he was told that the Magyars lived only two days' travel away. Julian found them, and despite the gap of at least 300–400 years since the split between the Magyars that invaded and settled in Pannonia and those that were found in Bashkiria, their language remained mutually intelligible, and they were able to communicate. Julian named the old country Magna Hungaria or Great Hungary. He became aware of stories about the Tatars, who were the enemies of the eastern Magyars and Bulgars. Two years after the original journey, Julian returned to Magna Hungaria, only to find it had been devastated by the Mongol Tatars. He returned to his kingdom with news of mortal danger ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
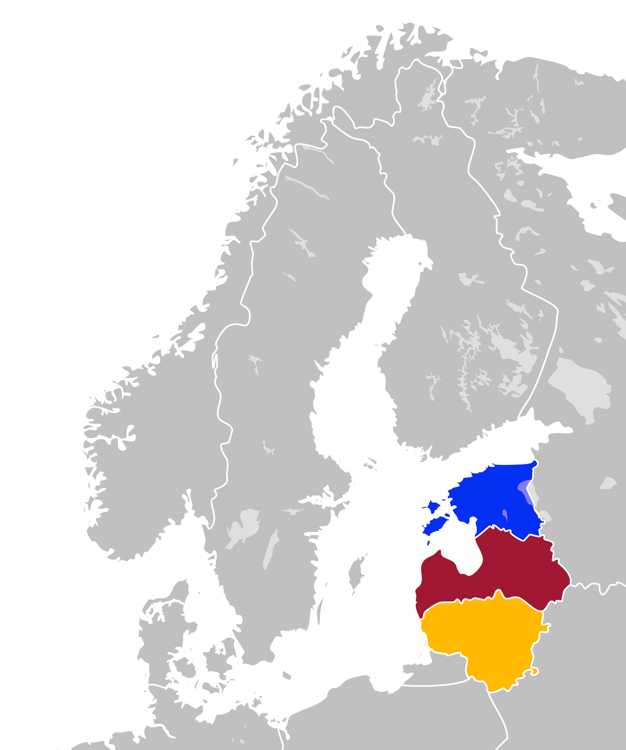
Baltic States
The Baltic states, et, Balti riigid or the Baltic countries is a geopolitical term, which currently is used to group three countries: Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania. All three countries are members of NATO, the European Union, the Eurozone, and the OECD. The three sovereign states on the eastern coast of the Baltic Sea are sometimes referred to as the "Baltic nations", less often and in historical circumstances also as the "Baltic republics", the "Baltic lands", or simply the Baltics. All three Baltic countries are classified as high-income economies by the World Bank and maintain a very high Human Development Index. The three governments engage in intergovernmental and parliamentary cooperation. There is also frequent cooperation in foreign and security policy, defence, energy, and transportation. The term "Baltic states" ("countries", "nations", or similar) cannot be used unambiguously in the context of cultural areas, national identity, or language. While the majority ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nordic Countries
The Nordic countries (also known as the Nordics or ''Norden''; literal translation, lit. 'the North') are a geographical and cultural region in Northern Europe and the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic. It includes the sovereign states of Denmark, Finland, Iceland, Norway and Sweden; the autonomous administrative division, autonomous territories of the Faroe Islands and Greenland; and the autonomous region of Åland. The Nordic countries have much in common in their way of life, History of Scandinavia, history, religion and Nordic model, social structure. They have a long history of political unions and other close relations but do not form a singular entity today. The Scandinavism, Scandinavist movement sought to unite Denmark, Norway and Sweden into one country in the 19th century. With the dissolution of the union between Norway and Sweden (Norwegian independence), the independence of Finland in the early 20th century and the 1944 Icelandic constitutional referendum, this move ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)