|
Mittag-Lefflerbreen
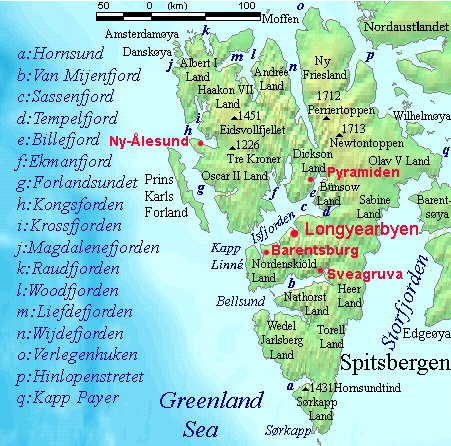
Mittag-Lefflerbreen is a glacier at Spitsbergen, Svalbard. The glacier is located in Ny-Friesland, Dickson Land and Olav V Land, and debouches into Austfjorden. It is named after mathematician Gösta Mittag-Leffler. The lower, northern part of the glacier is included in the Indre Wijdefjorden National Park Indre Wijdefjorden National Park ( no, Indre Wijdefjorden nasjonalpark) is located in a steep fjord landscape in northern Spitsbergen in Svalbard, Norway. It covers the inner part of Wijdefjorden—the longest fjord on Svalbard. The national .... References Glaciers of Spitsbergen {{spitsbergen-glacier-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indre Wijdefjorden National Park
Indre Wijdefjorden National Park ( no, Indre Wijdefjorden nasjonalpark) is located in a steep fjord landscape in northern Spitsbergen in Svalbard, Norway. It covers the inner part of Wijdefjorden—the longest fjord on Svalbard. The national park was established on 9 September 2005 and covers , of which is on land and is sea. The marine environment changes vastly from the mouth of the fjord, through a still, cold, water basin, becoming deeper before reaching the glacier Mittag-Lefflerbreen at the inner-most sections of the fjord. On both sides of Wijdefjorden there is High Arctic steppe vegetation, dominated by grasses and extremely dry, basic earth. There are some areas dominated by exposure of mineral earth. The area around the fjord has a vegetation which is unique and not preserved in other areas of Svalbard. Along with vegetation found on nesting cliffs, it is the most exclusive flora in Svalbard. There are several exclusive species in the national park, including , ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gösta Mittag-Leffler
Magnus Gustaf "Gösta" Mittag-Leffler (16 March 1846 – 7 July 1927) was a Swedish mathematician. His mathematical contributions are connected chiefly with the theory of functions, which today is called complex analysis. Biography Mittag-Leffler was born in Stockholm, son of the school principal John Olof Leffler and Gustava Wilhelmina Mittag; he later added his mother's maiden name to his paternal surname. His sister was the writer Anne Charlotte Leffler. He matriculated at Uppsala University in 1865, completed his PhD in 1872 and became docent at the university the same year. He was also curator (chairman) of the Stockholms nation (1872–1873). He next traveled to Paris, Göttingen and Berlin, studying under Weierstrass in the latter place. During this period he edited a weekly newspaper, ''Ny Illustrerad Tidning'', which was based in Stockholm. He then took up a position as professor of mathematics (as successor to Lorenz Lindelöf) at the University of Helsinki from 1877 t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glacier
A glacier (; ) is a persistent body of dense ice that is constantly moving under its own weight. A glacier forms where the accumulation of snow exceeds its Ablation#Glaciology, ablation over many years, often Century, centuries. It acquires distinguishing features, such as Crevasse, crevasses and Serac, seracs, as it slowly flows and deforms under stresses induced by its weight. As it moves, it abrades rock and debris from its substrate to create landforms such as cirques, moraines, or fjords. Although a glacier may flow into a body of water, it forms only on land and is distinct from the much thinner sea ice and lake ice that form on the surface of bodies of water. On Earth, 99% of glacial ice is contained within vast ice sheets (also known as "continental glaciers") in the polar regions, but glaciers may be found in mountain ranges on every continent other than the Australian mainland, including Oceania's high-latitude oceanic island countries such as New Zealand. Between lati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spitsbergen
Spitsbergen (; formerly known as West Spitsbergen; Norwegian: ''Vest Spitsbergen'' or ''Vestspitsbergen'' , also sometimes spelled Spitzbergen) is the largest and the only permanently populated island of the Svalbard archipelago in northern Norway. Constituting the westernmost bulk of the archipelago, it borders the Arctic Ocean, the Norwegian Sea, and the Greenland Sea. Spitsbergen covers an area of , making it the largest island in Norway and the 36th-largest in the world. The administrative centre is Longyearbyen. Other settlements, in addition to research outposts, are the Russian mining community of Barentsburg, the research community of Ny-Ålesund, and the mining outpost of Sveagruva. Spitsbergen was covered in of ice in 1999, which was approximately 58.5% of the island's total area. The island was first used as a whaling base in the 17th and 18th centuries, after which it was abandoned. Coal mining started at the end of the 19th century, and several permanent commun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Svalbard
Svalbard ( , ), also known as Spitsbergen, or Spitzbergen, is a Norwegian archipelago in the Arctic Ocean. North of mainland Europe, it is about midway between the northern coast of Norway and the North Pole. The islands of the group range from 74° to 81° north latitude, and from 10° to 35° east longitude. The largest island is Spitsbergen, followed by Nordaustlandet and . The largest settlement is Longyearbyen. The islands were first used as a base by the whalers who sailed far north in the 17th and 18th centuries, after which they were abandoned. Coal mining started at the beginning of the 20th century, and several permanent communities were established. The Svalbard Treaty of 1920 recognizes Norwegian sovereignty, and the 1925 Svalbard Act made Svalbard a full part of the Kingdom of Norway. They also established Svalbard as a free economic zone and a demilitarized zone. The Norwegian Store Norske and the Russian remain the only mining companies in place. Res ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ny-Friesland
Ny-Friesland is the land area between Wijdefjorden and Hinlopen Strait on Spitsbergen, Svalbard. The area is named after the Dutch province of Friesland Friesland (, ; official fry, Fryslân ), historically and traditionally known as Frisia, is a province of the Netherlands located in the country's northern part. It is situated west of Groningen, northwest of Drenthe and Overijssel, north of .... References Peninsulas of Spitsbergen {{Spitsbergen-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dickson Land
Dickson Land is a land area between Isfjorden and Wijdefjorden Wijdefjord is the longest fjord in Norway's Svalbard archipelago. Wijdefjord is located in the northern portion of the island of Spitsbergen, which lies in the Arctic Ocean about midway between Norway and the North Pole The North Pole, ... at Spitsbergen, Svalbard. It forms a peninsula between the Isfjorden branches Billefjorden and Dicksonfjorden. Dickson Land is named after Oscar Dickson. References Geography of Svalbard Spitsbergen {{Spitsbergen-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Olav V Land
Olav V Land is a peninsula in eastern Spitsbergen Island, Svalbard named after Olav V of Norway. It is covered by the Olav V Icefield, measuring about .''Glacier Atlas of Svalbard and Jan Mayen''. 1993. Oslo: Norsk polarinstitutt, p. 32. The only larger ice cap in the Svalbard Archipelago is Austfonna in Nordaustlandet Nordaustlandet (sometimes translated as North East Land) is the second-largest island in the archipelago of Svalbard, Norway, with an area of . It lies north east of Spitsbergen, separated by Hinlopen Strait. Much of Nordaustlandet lies under la ..., with an area of . References * http://www.ssb.no/aarbok/kart/i.html Peninsulas of Spitsbergen {{Spitsbergen-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Austfjorden (Svalbard)
Austfjorden is a fjord in Spitsbergen, Svalbard in Arctic Norway Norway, officially the Kingdom of Norway, is a Nordic country in Northern Europe, the mainland territory of which comprises the western and northernmost portion of the Scandinavian Peninsula. The remote Arctic island of Jan Mayen and the .... The fjord (East Fjord), measuring 32 kilometres (20 miles in length) is located in the east of the Indre Wijdefjorden National Park. References Fjords of Spitsbergen {{Spitsbergen-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norwegian Polar Institute
The Norwegian Polar Institute (NPI; no, Norsk Polarinstitutt) is Norway's central governmental institution for scientific research, mapping and environmental monitoring in the Arctic and the Antarctic. The NPI is a directorate under Norway's Ministry of Climate and Environment. The institute advises Norwegian authorities on matters concerning polar environmental management and is the official environmental management body for Norwegian activities in Antarctica. Activities The institute's activities are focused on environmental research and management in the polar regions. The NPI's researchers investigate biodiversity, climate and environmental toxins in the Arctic and Antarctic, and in this context the institute equips and organizes large-scale expeditions to both polar regions. The institute contributes to national and international climate work, and is an active contact point for the international scientific community. The institute collects and analyses data on the environm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |