|
Misuse Of P-values
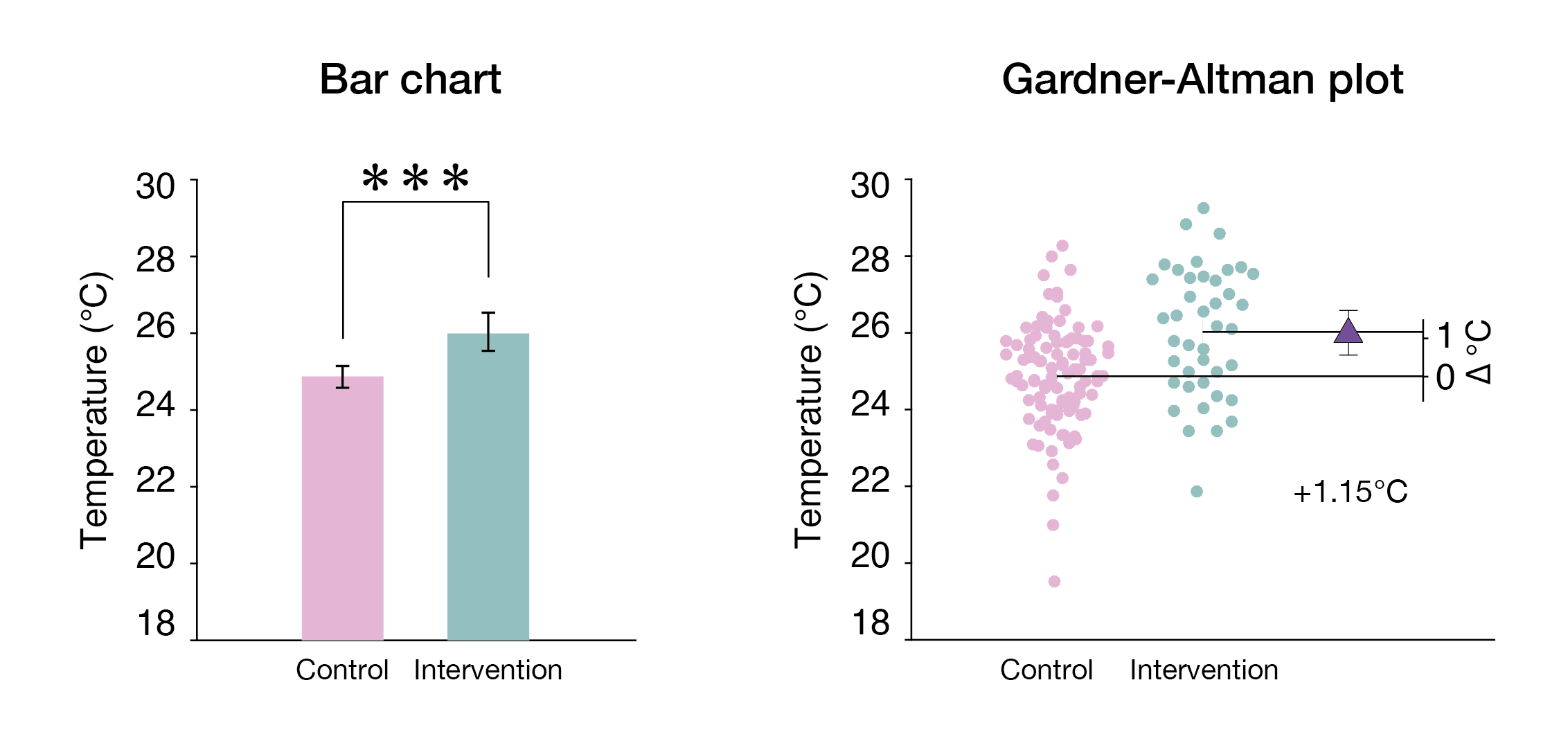
Misuse of ''p''-values is common in scientific research and scientific education. ''p''-values are often used or interpreted incorrectly; the American Statistical Association states that ''p''-values can indicate how incompatible the data are with a specified statistical model. From a Neyman–Pearson hypothesis testing approach to statistical inferences, the data obtained by comparing the ''p''-value to a significance level will yield one of two results: either the null hypothesis is rejected (which however does not prove that the null hypothesis is ''false''), or the null hypothesis ''cannot'' be rejected at that significance level (which however does not prove that the null hypothesis is ''true''). From a Fisherian statistical testing approach to statistical inferences, a low ''p''-value means ''either'' that the null hypothesis is true and a highly improbable event has occurred ''or'' that the null hypothesis is false. Clarifications about ''p''-values The following list ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Scientific Research
The scientific method is an empirical method for acquiring knowledge that has been referred to while doing science since at least the 17th century. Historically, it was developed through the centuries from the ancient and medieval world. The scientific method involves careful observation coupled with rigorous skepticism, because cognitive assumptions can distort the interpretation of the observation. Scientific inquiry includes creating a testable hypothesis through inductive reasoning, testing it through experiments and statistical analysis, and adjusting or discarding the hypothesis based on the results. Although procedures vary across fields, the underlying process is often similar. In more detail: the scientific method involves making conjectures (hypothetical explanations), predicting the logical consequences of hypothesis, then carrying out experiments or empirical observations based on those predictions. with added notes. Reprinted with previously unpublished part, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Misuse Of Statistics
Statistics, when used in a misleading fashion, can trick the casual observer into believing something other than what the data shows. That is, a misuse of statistics occurs when a statistical argument asserts a falsehood. In some cases, the misuse may be accidental. In others, it is purposeful and for the gain of the perpetrator. When the statistical reason involved is false or misapplied, this constitutes a statistical fallacy. The consequences of such misinterpretations can be quite severe. For example, in medical science, correcting a falsehood may take decades and cost lives. Misuses can be easy to fall into. Professional scientists, mathematicians and even professional statisticians, can be fooled by even some simple methods, even if they are careful to check everything. Scientists have been known to fool themselves with statistics due to lack of knowledge of probability theory and lack of standardization of their tests. Definition, limitations and context One usable d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Metascience
Metascience (also known as meta-research) is the use of scientific methodology to study science itself. Metascience seeks to increase the quality of scientific research while reducing inefficiency. It is also known as "research on research" and "the science of science", as it uses research methods to study how research is done and find where improvements can be made. Metascience concerns itself with all fields of research and has been described as "a bird's eye view of science". In the words of John Ioannidis, "Science is the best thing that has happened to human beings... but we can do it better." In 1966, an early meta-research paper examined the statistical methods of 295 papers published in ten high-profile medical journals. It found that "in almost 73% of the reports read... conclusions were drawn when the justification for these conclusions was invalid." Meta-research in the following decades found many methodological flaws, inefficiencies, and poor practices in research ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Replication Crisis
The replication crisis, also known as the reproducibility or replicability crisis, refers to the growing number of published scientific results that other researchers have been unable to reproduce or verify. Because the reproducibility of empirical results is an essential part of the scientific method, such failures undermine the credibility of theories that build on them and can call into question substantial parts of scientific knowledge. The replication crisis is frequently discussed in relation to psychology and medicine, wherein considerable efforts have been undertaken to reinvestigate the results of classic studies to determine whether they are reliable, and if they turn out not to be, the reasons for the failure. Data strongly indicate that other natural science, natural and social sciences are also affected. The phrase "replication crisis" was coined in the early 2010s as part of a growing awareness of the problem. Considerations of causes and remedies have given rise ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Estimation Statistics
Estimation statistics, or simply estimation, is a data analysis framework that uses a combination of effect sizes, confidence intervals, precision planning, and meta-analysis to plan experiments, analyze data and interpret results. It complements hypothesis testing approaches such as Statistical hypothesis testing, null hypothesis significance testing (NHST), by going beyond the question is an effect present or not, and provides information about how large an effect is. Estimation statistics is sometimes referred to as ''the new statistics''. The primary aim of estimation methods is to report an effect size (a point estimate) along with its confidence interval, the latter of which is related to the precision of the estimate. The confidence interval summarizes a range of likely values of the underlying population effect. Proponents of estimation see reporting a P-value, ''P'' value as an unhelpful distraction from the important business of reporting an effect size with its confide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Family-wise Error Rate
In statistics, family-wise error rate (FWER) is the probability of making one or more false discoveries, or type I errors when performing multiple hypotheses tests. Familywise and experimentwise error rates John Tukey developed in 1953 the concept of a familywise error rate as the probability of making a Type I error among a specified group, or "family," of tests. Based on Tukey (1953), Ryan (1959) proposed the related concept of an ''experimentwise error rate'', which is the probability of making a Type I error in a given experiment. Hence, an experimentwise error rate is a familywise error rate where the family includes all the tests that are conducted within an experiment. As Ryan (1959, Footnote 3) explained, an experiment may contain two or more families of multiple comparisons, each of which relates to a particular statistical inference and each of which has its own separate familywise error rate. Hence, familywise error rates are usually based on theoretically informative ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Expected Number
In probability theory, the expected value (also called expectation, expectancy, expectation operator, mathematical expectation, mean, expectation value, or first moment) is a generalization of the weighted average. Informally, the expected value is the mean of the possible values a random variable can take, weighted by the probability of those outcomes. Since it is obtained through arithmetic, the expected value sometimes may not even be included in the sample data set; it is not the value you would expect to get in reality. The expected value of a random variable with a finite number of outcomes is a weighted average of all possible outcomes. In the case of a continuum of possible outcomes, the expectation is defined by integration. In the axiomatic foundation for probability provided by measure theory, the expectation is given by Lebesgue integration. The expected value of a random variable is often denoted by , , or , with also often stylized as \mathbb or . History T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
No Starch Press
No Starch Press is an American publishing company, specializing in technical literature often geared towards the geek, hacker, and DIY subcultures. Popular titles include '' Hacking: The Art of Exploitation'', Andrew Huang's ''Hacking the Xbox'', and '' How Wikipedia Works''. Topics No Starch Press publishes books with a focus on networking, computer security, hacking, Linux, programming, technology for kids, Lego, math, and science. The publisher also releases educational comics like ''Super Scratch Programming Adventure'' and ''The Manga Guide to Science'' series. History No Starch Press was founded in 1994 by Bill Pollock. It is headquartered in San Francisco. The company has published titles that have received recognition in the Communication Arts Design Annual and STEP inside 100 competition, and have been awarded the Independent Publisher Book Award (the IPPYs) from Independent Publisher magazine. Availability No Starch Press titles are available online and in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
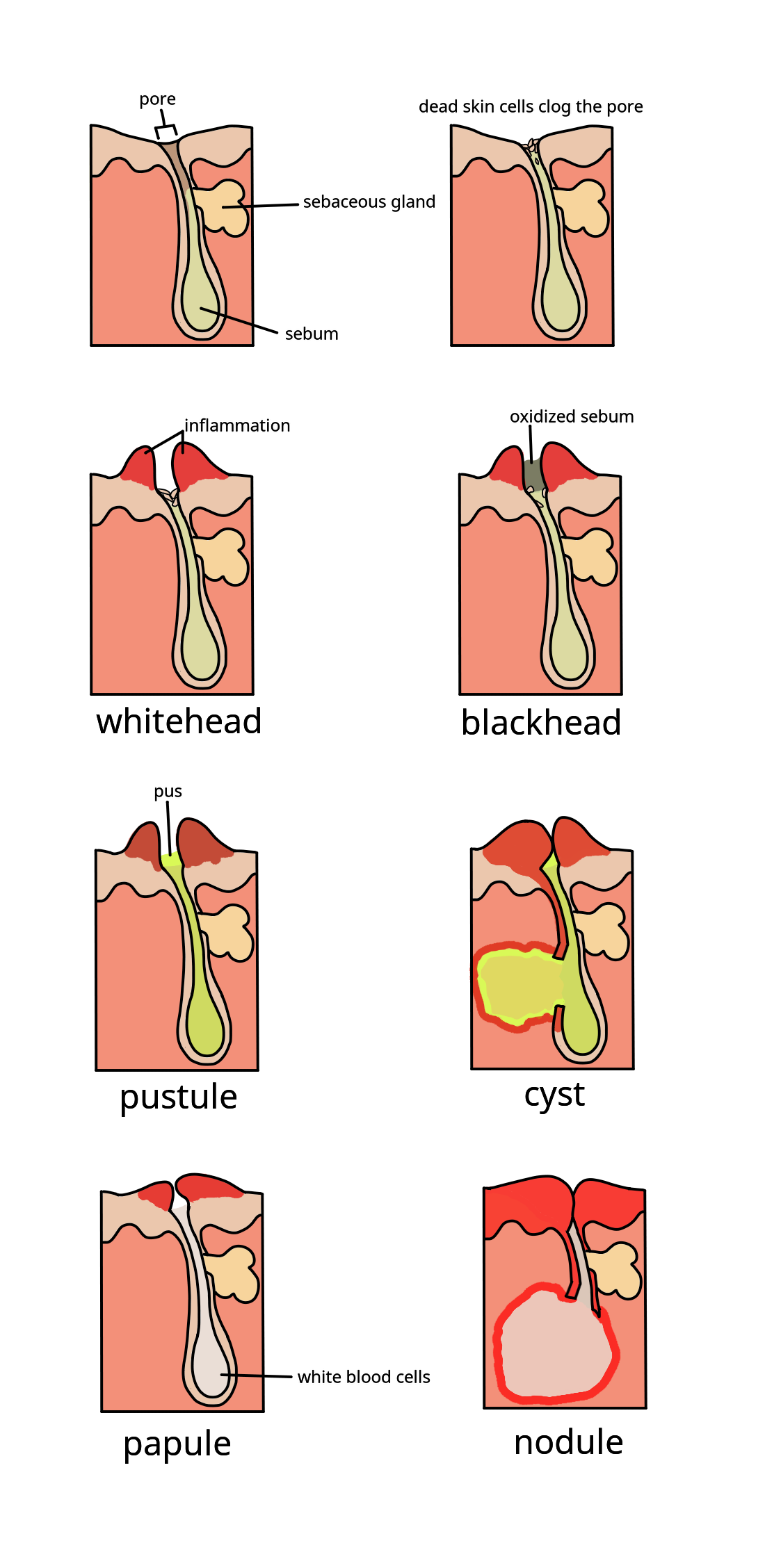
Acne
Acne ( ), also known as ''acne vulgaris'', is a long-term Cutaneous condition, skin condition that occurs when Keratinocyte, dead skin cells and Sebum, oil from the skin clog hair follicles. Typical features of the condition include comedo, blackheads or whiteheads, pimples, oily skin, and possible scarring. It primarily affects skin with a relatively high number of sebaceous gland, oil glands, including the face, upper part of the chest, and back. The resulting appearance can lead to lack of confidence, anxiety (mood), anxiety, reduced self-esteem, and, in extreme cases, clinical depression, depression or suicidal ideations, thoughts of suicide. Susceptibility to acne is primarily genetic in 80% of cases. The roles of diet and cigarette smoking in the condition are unclear, and neither hygiene, cleanliness nor exposure to sunlight are associated with acne. In both sexes, hormones called androgens appear to be part of the underlying mechanism, by causing increased production ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |