|
Missa Brevis (Britten)
The ''Missa Brevis'' in D, Op. 63, is a setting of the Latin mass completed by Benjamin Britten on Trinity Sunday, 1959.Roseberry, 11. Set for three-part treble choir and organ, it was first performed at London's Roman Catholic Westminster Cathedral on 22 July of the same year.Roseberry, 11. Britten composed the mass for George Malcolm's retirement as organist and choirmaster at Westminster:Roseberry, 11. the printed dedication reads "For George Malcolm and the boys of Westminster Cathedral Choir". It remained Britten's only liturgical setting of the mass. Malcolm's live recording, from a service at the cathedral, lasts ten minutes. Liturgy Britten's ''Missa Brevis'' contains only four movements, omitting the Credo, hence the name ''brevis'', short. The omission is notable because Mass at Westminster Cathedral would have included this movement. The piece rather seems predisposed towards the liturgy of the Church of England or the Protestant Episcopal Church of America, which of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Westminster Cathedral
Westminster Cathedral is the mother church of the Catholic Church in England and Wales. It is the largest Catholic church in the UK and the seat of the Archbishop of Westminster. The site on which the cathedral stands in the City of Westminster was purchased by the Diocese of Westminster in 1885, and construction completed in 1903. Designed by John Francis Bentley in neo-Byzantine style, and accordingly made almost entirely of brick, without steel reinforcements, Sir John Betjeman called it "a masterpiece in striped brick and stone" that shows "the good craftsman has no need of steel or concrete". History In the late 19th century, the Roman Catholic Church's hierarchy had only recently been restored in England and Wales, and it was in memory of Cardinal Wiseman (who died in 1865, and was the first Archbishop of Westminster from 1850) that the first substantial sum of money was raised for the new cathedral. The land was acquired in 1884 by Wiseman's successor, Car ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canon Law
Canon law (from grc, κανών, , a 'straight measuring rod, ruler') is a set of ordinances and regulations made by ecclesiastical authority (church leadership) for the government of a Christian organization or church and its members. It is the internal ecclesiastical law, or operational policy, governing the Catholic Church (both the Latin Church and the Eastern Catholic Churches), the Eastern Orthodox and Oriental Orthodox churches, and the individual national churches within the Anglican Communion. The way that such church law is legislated, interpreted and at times adjudicated varies widely among these four bodies of churches. In all three traditions, a canon was originally a rule adopted by a church council; these canons formed the foundation of canon law. Etymology Greek / grc, κανών, Arabic / , Hebrew / , 'straight'; a rule, code, standard, or measure; the root meaning in all these languages is 'reed'; see also the Romance-language ancestors of the Engli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bitonality
Polytonality (also polyharmony) is the musical use of more than one key simultaneously. Bitonality is the use of only two different keys at the same time. Polyvalence or polyvalency is the use of more than one harmonic function, from the same key, at the same time. Some examples of bitonality superimpose fully harmonized sections of music in different keys. History In traditional music Lithuanian traditional singing style sutartines is based on polytonality. A typical sutartines song is based on a six-bar melody, where the first three bars contains melody based on the notes of the triad of a major key (for example, in G major), and the next three bars is based on another key, always a major second higher or lower (for example, in A major). This six-bar melody is performed as a canon, and repetition starts from the fourth bar. As a result, parts are constantly singing in different tonality (key) simultaneously (in G and in A). As a traditional style, sutartines disappeared in Li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
F Major
F major (or the key of F) is a major scale based on F, with the pitches F, G, A, B, C, D, and E. Its key signature has one flat. Its relative minor is D minor and its parallel minor is F minor F minor is a minor scale based on F, consisting of the pitches F, G, A, B, C, D, and E. Its key signature consists of four flats. Its relative major is A-flat major and its parallel major is F major. Its enharmonic equivalent, E-sharp mi .... The F major scale is: : F major is the home key of the English horn, the basset horn, the French horn, horn in F, the trumpet in F and the bass Wagner tuba. Thus, music in F major for these transposing instruments is written in C major. Most of these sound a perfect fifth lower than written, with the exception of the trumpet in F which sounds a fourth higher. (The basset horn also often sounds an octave and a fifth lower.) Notable compositions in F major *Antonio Vivaldi **Twelve Trio Sonatas, Op. 1 (Vivaldi), Trio sonata Op. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Additive Rhythm
In music, the terms ''additive'' and ''divisive'' are used to distinguish two types of both rhythm and meter (music), meter: * A divisive (or, alternately, multiplicative) rhythm is a rhythm in which a larger period of time is divided into smaller rhythmic units or, conversely, some integer unit is regularly multiplied into larger, equal units. * This can be contrasted with additive rhythm, in which larger periods of time are constructed by concatenation, concatenating (joining end to end) a series of units into larger units of unequal length, such as a meter produced by the regular alternation of and . When applied to meters, the terms ''perfect'' and ''imperfect'' are sometimes used as the equivalents of ''divisive'' and ''additive'', respectively . For example, 4 may be evenly divided by 2 or reached by adding 2 + 2. In contrast, 5 is only evenly divisible by 5 and 1 and may be reached by adding 2 or 3. Thus, (or, more commonly, ) is divisive while is additive. The terms ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Officiant
An officiant is someone who officiates (i.e. leads) at a service or ceremony, such as marriage, burial, or namegiving/baptism. Religious officiants are usually ordained by a religious denomination as members of the clergy. Some officiants work within congregations in some denominations and for specified ceremonies (e.g. funerals), as non-ordained members on the clergy team. Clergy/officiants differ from chaplains in that the clergy serve the members of their congregation, while chaplains are usually employed by an institution such as the military, a hospital or other health care facility, etc. There may be more than one con-celebrant, but, even when a higher-ranking cleric is present, (save the Pope), there is only one principal celebrant. Secular officiants include civil celebrants, Humanist Society–appointed officiants, Justices of the Peace, marriage commissioners, notaries, and other persons empowered by law to perform legal marriage ceremonies. Many secular celebrant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Incipit
The incipit () of a text is the first few words of the text, employed as an identifying label. In a musical composition, an incipit is an initial sequence of notes, having the same purpose. The word ''incipit'' comes from Latin and means "it begins". Its counterpart taken from the ending of the text is the explicit. Before the development of titles, texts were often referred to by their incipits, as with for example ''Agnus Dei''. During the medieval period in Europe, incipits were often written in a different script or colour from the rest of the work of which they were a part, and "incipit pages" might be heavily decorated with illumination. Though the word ''incipit'' is Latin, the practice of the incipit predates classical antiquity by several millennia and can be found in various parts of the world. Although not always called by the name of ''incipit'' today, the practice of referring to texts by their initial words remains commonplace. Historical examples Sumerian In th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ostinato
In music, an ostinato (; derived from Italian word for ''stubborn'', compare English ''obstinate'') is a motif or phrase that persistently repeats in the same musical voice, frequently in the same pitch. Well-known ostinato-based pieces include classical compositions such as Ravel's '' Boléro'' and the ''Carol of the Bells'', and popular songs such as Donna Summer and Giorgio Moroder's "I Feel Love" (1977), Henry Mancini's theme from ''Peter Gunn'' (1959), The Who's "Baba O'Riley" (1971), and The Verve's " Bitter Sweet Symphony" (1997). Both ''ostinatos'' and ''ostinati'' are accepted English plural forms, the latter reflecting the word's Italian etymology. The repeating idea may be a rhythmic pattern, part of a tune, or a complete melody in itself. Kamien, Roger (1258). ''Music: An Appreciation'', p. 611. . Strictly speaking, ostinati should have exact repetition, but in common usage, the term covers repetition with variation and development, such as the alteration of an os ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Melodic Inversion
In music theory, an inversion is a type of change to intervals, chords, voices (in counterpoint), and melodies. In each of these cases, "inversion" has a distinct but related meaning. The concept of inversion also plays an important role in musical set theory. Intervals An interval is inverted by raising or lowering either of the notes by one or more octaves so that the positions of the notes reverse (i.e. the higher note becomes the lower note and vice versa). For example, the inversion of an interval consisting of a C with an E above it (the third measure below) is an E with a C above it – to work this out, the C may be moved up, the E may be lowered, or both may be moved. : The tables to the right show the changes in interval quality and interval number under inversion. Thus, perfect intervals remain perfect, major intervals become minor and vice versa, and augmented intervals become diminished and vice versa. (Doubly diminished intervals become doubly augmented ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
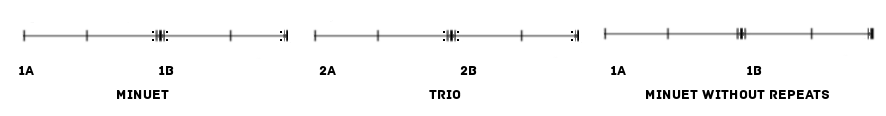
Ternary Form
Ternary form, sometimes called song form, is a three-part musical form consisting of an opening section (A), a following section (B) and then a repetition of the first section (A). It is usually schematized as A–B–A. Prominent examples include the da capo aria "The trumpet shall sound" from Handel's ''Messiah'', Chopin's Prelude in D-Flat Major "Raindrop", ( Op. 28) and the opening chorus of Bach's ''St John Passion''. Simple ternary form In ternary form each section is self-contained both thematically as well as tonally (that is, each section contains distinct and complete themes), and ends with an authentic cadence. The B section is generally in a contrasting but closely related key, usually a perfect fifth above or the parallel minor of the home key of the A section (V or i); however, in many works of the Classical period, the B section stays in tonic but has contrasting thematic material. It usually also has a contrasting character; for example section A might be stif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Key Signature
In Western musical notation, a key signature is a set of sharp (), flat (), or rarely, natural () symbols placed on the staff at the beginning of a section of music. The initial key signature in a piece is placed immediately after the clef at the beginning of the first line. If the piece contains a section in a different key, the new key signature is placed at the beginning of that section. In a key signature, a sharp or flat symbol on a line or space of the staff indicates that the note represented by that line or space is to be played a semitone higher (sharp) or lower (flat) than it would otherwise be played. This applies through the end of the piece or until another key signature is indicated. Each symbol applies to all notes in the same pitch class—for example, a flat on the third line of the treble staff (as in the diagram) indicates that all notes appearing as Bs are played as B-flats. This convention was not universal until the late Baroque and early Classical peri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)