|
Military Revolutionary Council
The Military Revolutionary Council (russian: Военно-революционный Совет , VRS) was the ''de facto'' executive of the Makhnovshchina, empowered to act during the interim between sittings of the Regional Congresses. Function Its powers covered both military and civil matters in the region, although it was also subject to instant recall at the will of the Regional Congress and its activities were limited to those explicitly outlined by the Congresses themselves. At each Regional Congress, the VRS was to provide detailed reports of its activities and subjected itself to reorganization. When it came to the decisions of local soviets and assemblies, the VRS presented itself as a solely advisory board, with no power over the local bodies of self-government. The VRS also functioned as the supreme body of the Revolutionary Insurgent Army, acting in concert with its elected general staff and in consultation with insurgent detachments, thus "representing the a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Revolutionary Military Council
The Revolutionary Military Council (russian: Революционный Военный Совет, Revolyutsionny Voyenny Sovyet, Revolutionary Military Council), sometimes called the Revolutionary War CouncilBrian PearceIntroductionto Fyodor Raskolnikov s "Tales of Sub-lieutenant Ilyin." or ''Revvoyensoviet'' (), was the supreme military authority of Soviet Russia and later the Soviet Union. It was instituted on September 2, 1918 by decree of the All-Russian Central Executive Committee (VTsIK), known as the "Decree Declaring the Soviet Republic Military Camp". Prior to ''Revvoyensoviet'', the two main military authorities had been the Supreme Military Council (, ') and the operations division of the People's Commissariat on War and Navy Affairs. The decree put all fronts and military organizations under the command of the chairman of ''Revvoyensoviet'', with a commander-in-chief second-in-line to the chairman to lead strategic and military operations stateside. The chairma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
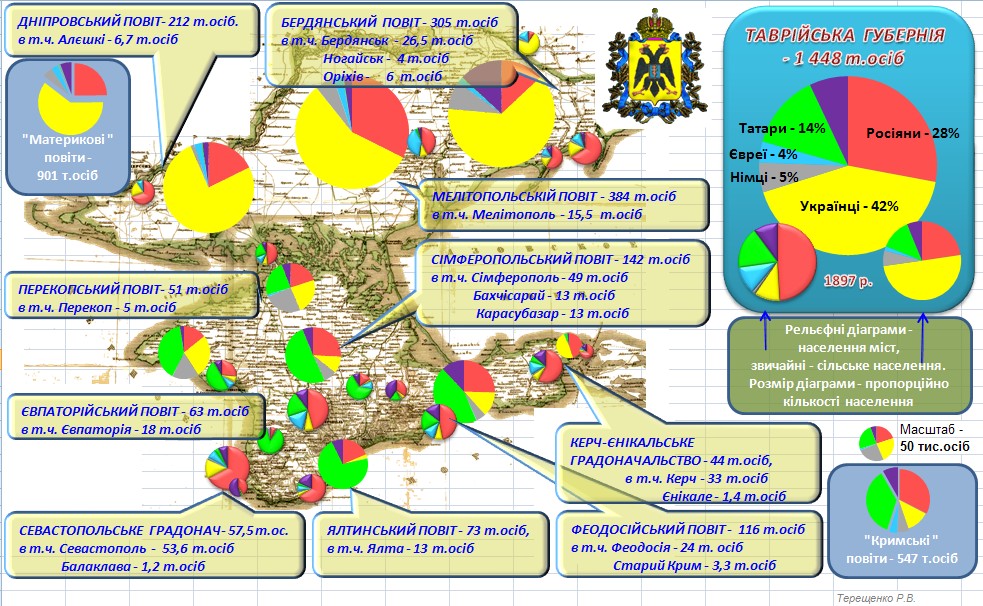
Taurida Governorate
The Taurida Governorate (russian: Тавріическая губернія, modern spelling , ; crh, script=Latn, Tavrida guberniyası, ) or the Government of Taurida, was a historical governorate of the Russian Empire. It included the Crimean Peninsula and the mainland between the lower Dnieper River and the coasts of the Black Sea and Sea of Azov. It was formed after the Taurida Oblast was abolished in 1802 in the course of Paul I's administrative reform of the southwestern territories that had been annexed from the Crimean Khanate. The governorate's centre was the city of Simferopol. The province was named after the ancient Greek name of Crimea - Taurida. Today the territory of the governorate is part of the Crimea, Kherson, and Zaporizhzhia regions of Ukraine. Administrative divisions The governorate comprised three counties (uyezds) on the mainland: * Berdyansky Uyezd, centred in Berdyansk * Dneprovsky Uyezd, Oleshky * Melitopolsky Uyezd, Melitopol and five counties pl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ukrainian Nationalism
Ukrainian nationalism refers to the promotion of the unity of Ukrainians as a people and it also refers to the promotion of the identity of Ukraine as a nation state. The nation building that arose as nationalism grew following the French Revolution and it was inspired by the ideals of people ruling themselves. Ukrainian Nationalism, while emerging in the 18th century, draws upon a single national identity of culture, ethnicity, geographic location, language, politics (or the government), religion, traditions and belief in a shared singular history, that dates back to the 9th century. The origins of modern Ukrainian nationalism emerge during the 17th-century Cossack uprising against the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth led by Bohdan Khmelnytsky. History Nationalism emerged after the French Revolution while modern day Ukraine faced external pressure from the suzerainty of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, the Tsardom of Russia and the Ottoman Empire but the National Identit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uman
Uman ( uk, Умань, ; pl, Humań; yi, אומאַן) is a city located in Cherkasy Oblast in central Ukraine, to the east of Vinnytsia. Located in the historical region of the eastern Podolia, the city rests on the banks of the Umanka River at around . Uman serves as the administrative center of Uman Raion (district). It hosts the administration of Uman urban hromada, one of the hromadas of Ukraine. Population: Among Ukrainians, Uman is known for its depiction of the Haidamak rebellions in Taras Shevchenko's longest of poems, ''Haidamaky'' ("The Haidamaks", 1843). The city is also a pilgrimage site for Breslov Hasidic Jews and a major center of gardening research containing the dendrological park Sofiyivka and the University of Gardening. Uman (Humań) was a privately owned city of Poland and the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. History Uman was first mentioned in historical documents in 1616, when it was under Polish rule. It was part of the Bracław Voivodeship of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chief Of Staff
The title chief of staff (or head of staff) identifies the leader of a complex organization such as the armed forces, institution, or body of persons and it also may identify a principal staff officer (PSO), who is the coordinator of the supporting staff or a primary aide-de-camp to an important individual, such as a president, or a senior military officer, or leader of a large organization. In general, a chief of staff provides a buffer between a chief executive and that executive's direct-reporting team. The chief of staff generally works behind the scenes to solve problems, mediate disputes, and deal with issues before they are brought to the chief executive. Often chiefs of staff act as a confidant and advisor to the chief executive, acting as a sounding board for ideas. Ultimately the actual duties depend on the position and the people involved. Civilian Government Brazil *Chief of Staff of the Presidency Canada * Chief of Staff to the Prime Minister *Principal Sec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hryhorii Makhno
Hryhorii Ivanovych Makhno ( uk, Григорій Іванович Махно; 24 January 1886 – 18 September 1919) was a Ukrainian rebel commander and brother of Nestor Makhno. Biography Hryhorii was born into a peasant family in the village of Huliaipole on 24 January 1886 to Ivan Rodionovych Mikhnenko and Evdokiia Matveevna Perederyi. His father died in 1889, leaving he and his brothers in the sole care of their mother. Hryhorii was married to a peasant woman Khristina, with whom he had two daughters: Maria and Elizabeth. In 1907, he joined the anarcho-communist Union of Poor Peasants. When his brother Nestor Makhno was arrested for participating in the group, Hryhorii visited him in prison and told him of the death of their comrade Oleksandr Semenyuta. In the same year he was drafted into the Imperial Russian Army, in which he fought during World War I. In 1918 he took part in the defense of the Donets-Krivoy Rog Soviet Republic as part of an anarcho-communist detachment, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Green Armies
The Green armies (russian: Зеленоармейцы), also known as the Green Army (Зелёная Армия) or Greens (Зелёные), were armed peasant groups which fought against all governments in the Russian Civil War from 1917 to 1922. The Green armies were semi-organized local militias that opposed the Bolsheviks, Whites, and foreign interventionists, and fought to protect their communities from requisitions or reprisals carried out by third parties. The Green armies were politically and ideologically neutral, but at times associated with the Socialist-Revolutionary Party. The Green armies had at least tacit support throughout much of Russia. However, their primary base, the peasantry, were largely reluctant to wage an active campaign during the Russian Civil War and eventually dissolved following Bolshevik victory in 1922. Background The Russian peasantry lived through two wars against the Russian state, the product of revolutions that ended with state victory: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nykyfor Hryhoriv
Nykyfor Oleksandrovych Hryhoriv (né Nychypir Servetnyk, 1884 – 27 July 1919) was a Ukrainian paramilitary leader noted for repeatedly switching sides during the Ukrainian Civil War. He was commonly known as "Otaman Hryhoriv." In some historical accounts, his first name is given as "Matvii" or "Mykola". He is sometimes misrepresented as the otaman, or leader, of the Green armies. His association with the Green armies is due to collaboration with the army of Danylo Terpylo, which fought against the Ukrainian People's Republic, Red Army, and White Army. Although he cooperated with Terpylo, this was marginal. Biography Nykyfor Servetnik was born in 1884 in the small village of , in the Novo-Ushytsia uyezd of Podolian Governorate, which was then part of the Russian Empire. Servetnik served in the cavalry of the Russian Imperial Army in the region of Kherson and participated in Russo-Japanese War in the Russian Far East serving in the Trans-Baikal Host. After his discharge he ser ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cheka
The All-Russian Extraordinary Commission ( rus, Всероссийская чрезвычайная комиссия, r=Vserossiyskaya chrezvychaynaya komissiya, p=fsʲɪrɐˈsʲijskəjə tɕrʲɪzvɨˈtɕæjnəjə kɐˈmʲisʲɪjə), abbreviated as VChK ( rus, ВЧК, p=vɛ tɕe ˈka), and commonly known as Cheka ( rus, Чека, p=tɕɪˈka; from the initialism russian: ЧК, ChK, label=none), was the first of a succession of Soviet secret-police organizations. Established on December 5 (Old Style) 1917 by the Sovnarkom, it came under the leadership of Felix Dzerzhinsky, a Polish aristocrat-turned-Bolshevik. By late 1918, hundreds of Cheka committees had sprung up in the RSFSR at the oblast, guberniya, raion, uyezd, and volost levels. Ostensibly set up to protect the revolution from reactionary forces, i.e., "class enemies" such as the bourgeoisie and members of the clergy, it soon became the repression tool against all political opponents of the communist regime. At the dir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Red Army
The Workers' and Peasants' Red Army (Russian: Рабо́че-крестья́нская Кра́сная армия),) often shortened to the Red Army, was the army and air force of the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic and, after 1922, the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. The army was established in January 1918. The Bolsheviks raised an army to oppose the military confederations (especially the various groups collectively known as the White Army) of their adversaries during the Russian Civil War. Starting in February 1946, the Red Army, along with the Soviet Navy, embodied the main component of the Soviet Armed Forces; taking the official name of "Soviet Army", until its dissolution in 1991. The Red Army provided the largest land force in the Allied victory in the European theatre of World War II, and its invasion of Manchuria assisted the unconditional surrender of Imperial Japan. During operations on the Eastern Front, it accounted for 75–80% of casual ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Authority
A Central Authority is an agency or organization that is designated to play a key facilitating role in the implementation and operation of an international treaty in public and private international law. Prior to the Hague Evidence Convention and the Hague Service Convention's of 1965 and 1970, most treaties would designate two separate agencies to, respectively, transmit and receive treaty petitions and applications with their corresponding agencies in foreign states. The Conventions of '65 and '70 consolidated these roles into a single ''Central Authority.'' Future Conventions, such as Hague Abduction Convention The Hague Convention on the Civil Aspects of International Child Abduction or Hague Abduction Convention is a multilateral treaty that provides an expeditious method to return a child internationally abducted by a parent from one member countr ... also demanded that the Central Authority in each country handle two-way communications with domestic courts, adminis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)