|
Military Orbital Development System
The Military Orbital Development System was created by the US Air Force Space System Division (SSD) in June 1962. It was to begin plans to use Gemini hardware as the first step in a new US Air Force man-in-space program called MODS (Manned Orbital Development System), a type of military space station that used Gemini spacecraft as ferry vehicles. The term Blue Gemini first appeared in August 1962 as part of a proposal to fly six Gemini missions with Air Force pilots in a preliminary orientation and training phase of MODS. MODS was effectively superseded when the Manned Orbital Laboratory The Manned Orbiting Laboratory (MOL) was part of the United States Air Force (USAF) human spaceflight program in the 1960s. The project was developed from early USAF concepts of crewed space stations as reconnaissance satellites, and was a succ ... was announced in December 1963. References NASA History Office on Blue Gemini Human spaceflight programs Project Gemini Crewed spacecraft< ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Space System Division
Space is the boundless three-dimensional extent in which objects and events have relative position and direction. In classical physics, physical space is often conceived in three linear dimensions, although modern physicists usually consider it, with time, to be part of a boundless four-dimensional continuum known as spacetime. The concept of space is considered to be of fundamental importance to an understanding of the physical universe. However, disagreement continues between philosophers over whether it is itself an entity, a relationship between entities, or part of a conceptual framework. Debates concerning the nature, essence and the mode of existence of space date back to antiquity; namely, to treatises like the ''Timaeus'' of Plato, or Socrates in his reflections on what the Greeks called ''khôra'' (i.e. "space"), or in the ''Physics'' of Aristotle (Book IV, Delta) in the definition of ''topos'' (i.e. place), or in the later "geometrical conception of place" as "spac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
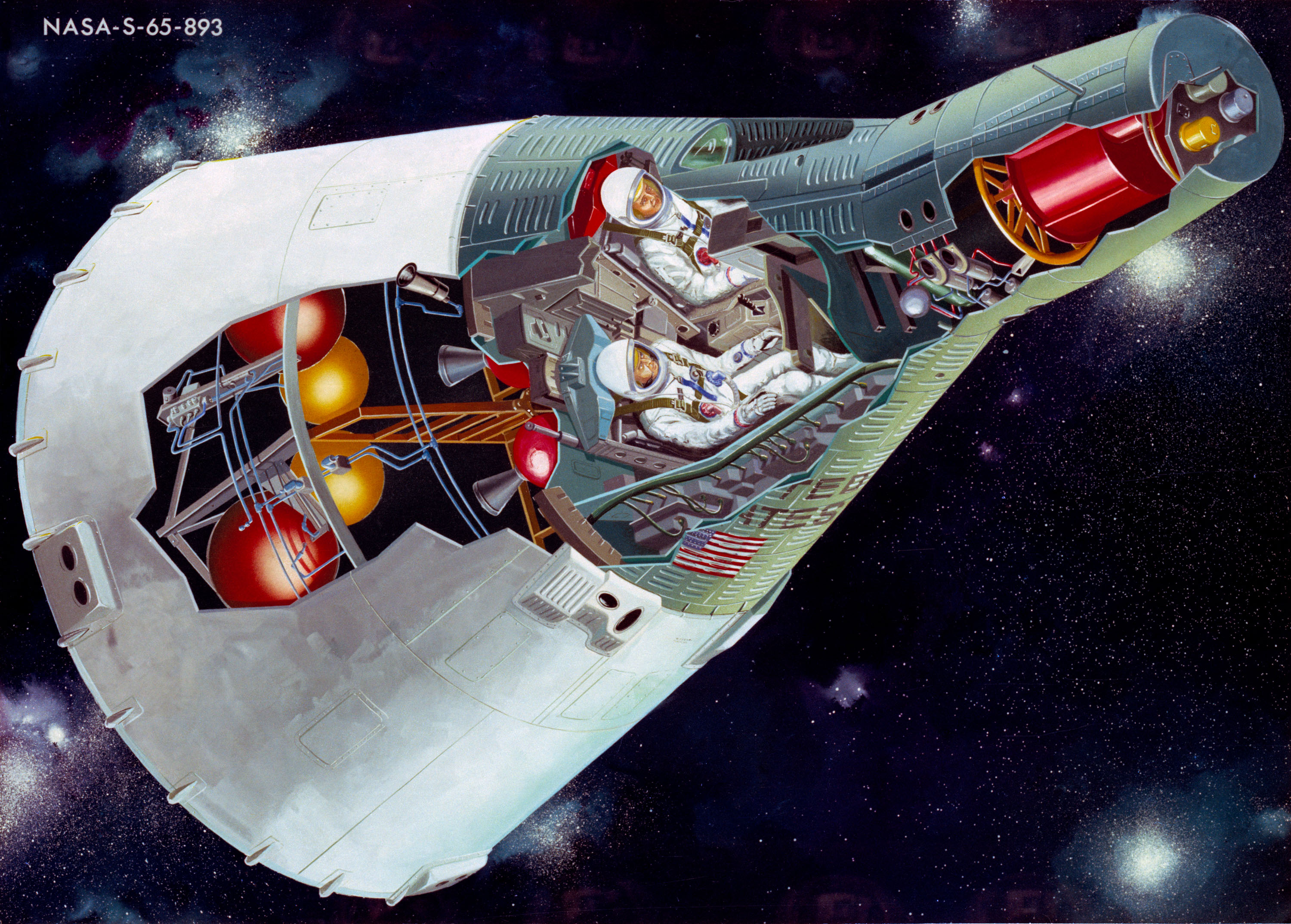
Project Gemini
Project Gemini () was NASA's second human spaceflight program. Conducted between projects Mercury and Apollo, Gemini started in 1961 and concluded in 1966. The Gemini spacecraft carried a two-astronaut crew. Ten Gemini crews and 16 individual astronauts flew low Earth orbit (LEO) missions during 1965 and 1966. Gemini's objective was the development of space travel techniques to support the Apollo mission to land astronauts on the Moon. In doing so, it allowed the United States to catch up and overcome the lead in human spaceflight capability the Soviet Union had obtained in the early years of the Space Race, by demonstrating: mission endurance up to just under 14 days, longer than the eight days required for a round trip to the Moon; methods of performing extra-vehicular activity (EVA) without tiring; and the orbital maneuvers necessary to achieve rendezvous and docking with another spacecraft. This left Apollo free to pursue its prime mission without spending time develop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
USAF
The United States Air Force (USAF) is the air service branch of the United States Armed Forces, and is one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. Originally created on 1 August 1907, as a part of the United States Army Signal Corps, the USAF was established as a separate branch of the United States Armed Forces in 1947 with the enactment of the National Security Act of 1947. It is the second youngest branch of the United States Armed Forces and the fourth in order of precedence. The United States Air Force articulates its core missions as air supremacy, global integrated intelligence, surveillance and reconnaissance, rapid global mobility, global strike, and command and control. The United States Air Force is a military service branch organized within the Department of the Air Force, one of the three military departments of the Department of Defense. The Air Force through the Department of the Air Force is headed by the civilian Secretary of the Air For ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gemini Spacecraft
Project Gemini () was NASA's second human spaceflight program. Conducted between projects Mercury and Apollo, Gemini started in 1961 and concluded in 1966. The Gemini spacecraft carried a two-astronaut crew. Ten Gemini crews and 16 individual astronauts flew low Earth orbit (LEO) missions during 1965 and 1966. Gemini's objective was the development of space travel techniques to support the Apollo mission to land astronauts on the Moon. In doing so, it allowed the United States to catch up and overcome the lead in human spaceflight capability the Soviet Union had obtained in the early years of the Space Race, by demonstrating: mission endurance up to just under 14 days, longer than the eight days required for a round trip to the Moon; methods of performing extra-vehicular activity (EVA) without tiring; and the orbital maneuvers necessary to achieve rendezvous and docking with another spacecraft. This left Apollo free to pursue its prime mission without spending time devel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blue Gemini
Blue Gemini was a United States Air Force (USAF) project first proposed in August 1962 for a series of seven flights of Gemini spacecraft to enable the Air Force to gain manned spaceflight experience prior to the launch of the Manned Orbital Development System, or MODS. The plan was to use off-the-shelf Gemini spacecraft. History Blue Gemini would consist of two National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) missions which would include a USAF co-pilot and would accomplish NASA objectives. These would be followed by two more NASA missions that would have USAF crews. Those missions would be devoted to NASA goals, but would include USAF experiments if possible. The final phase of Blue Gemini would consist of three dedicated USAF missions. One of these would be an Agena Target Vehicle rendezvous mission. It was possible that some of these later missions would carry only a single crew member, the other seat being occupied by experimental equipment. Possible payloads included ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manned Orbital Laboratory
The Manned Orbiting Laboratory (MOL) was part of the United States Air Force (USAF) human spaceflight program in the 1960s. The project was developed from early USAF concepts of crewed space stations as reconnaissance satellites, and was a successor to the canceled Boeing X-20 Dyna-Soar military reconnaissance space plane. Plans for the MOL evolved into a single-use laboratory, for which crews would be launched on 30-day missions, and return to Earth using a Gemini B spacecraft derived from NASA's Gemini spacecraft and launched with the laboratory. The MOL program was announced to the public on 10 December 1963 as an inhabited platform to demonstrate the utility of putting people in space for military missions; its reconnaissance satellite mission was a secret black project. Seventeen astronauts were selected for the program, including Major Robert H. Lawrence Jr., the first African-American astronaut. The prime contractor for the spacecraft was McDonnell Aircraft Corporation; ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Spaceflight Programs
Human spaceflight programs have been conducted, started, or planned by multiple countries and companies. Until the 21st century, human spaceflight programs were sponsored exclusively by governments, through either the military or civilian space agencies. With the launch of the privately funded SpaceShipOne in 2004, a new category of human spaceflight programs – commercial human spaceflight – arrived. , three countries (Soviet Union/Russia, United States and China) and one private company (SpaceX) have launched humans to Earth orbit, and two private companies (Scaled Composites and Blue Origin) have launched humans on a suborbital trajectory. The criteria for what constitutes human spaceflight vary. The Fédération Aéronautique Internationale defines spaceflight as any flight over . In the United States professional, military, and commercial astronauts who travel above an altitude of are awarded the United States Astronaut Badge. This article follows the FAI definition of s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)
