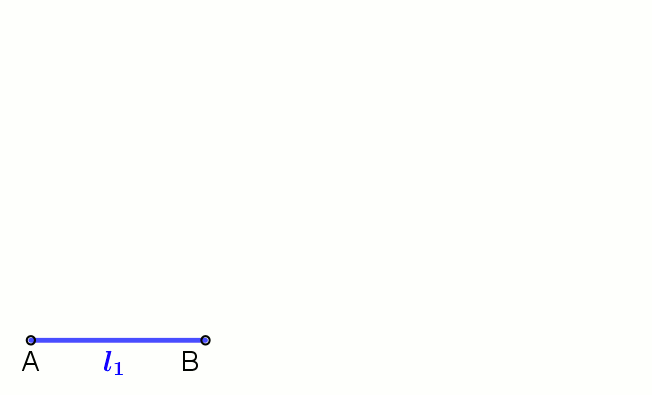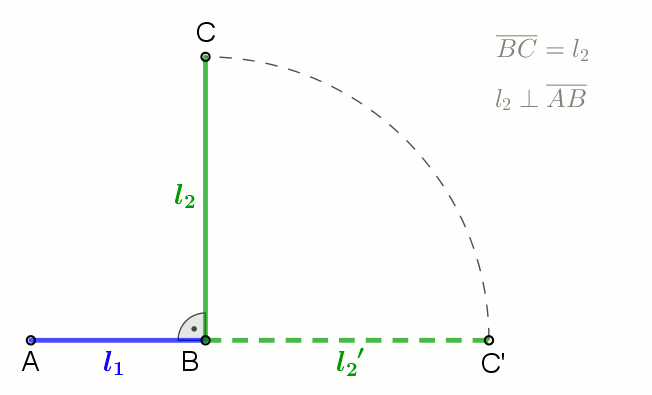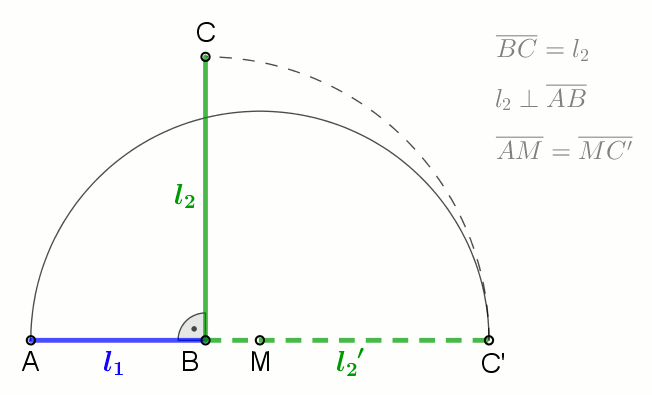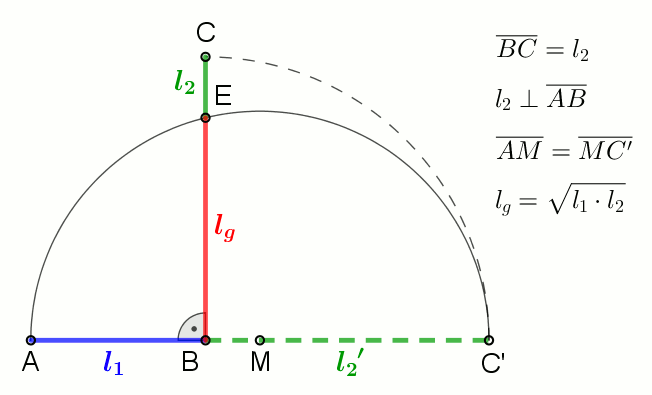|
Milankovich Cycle
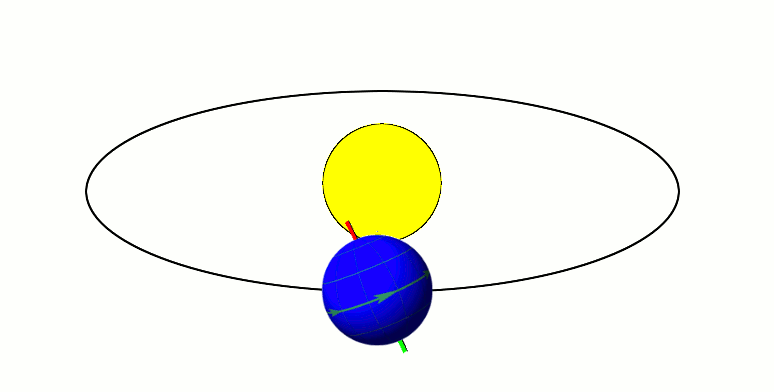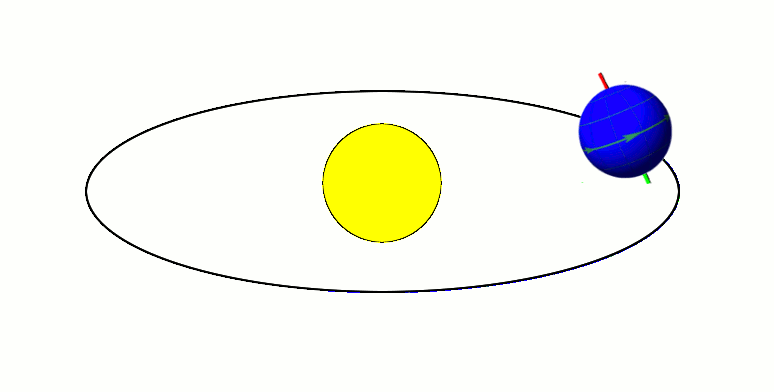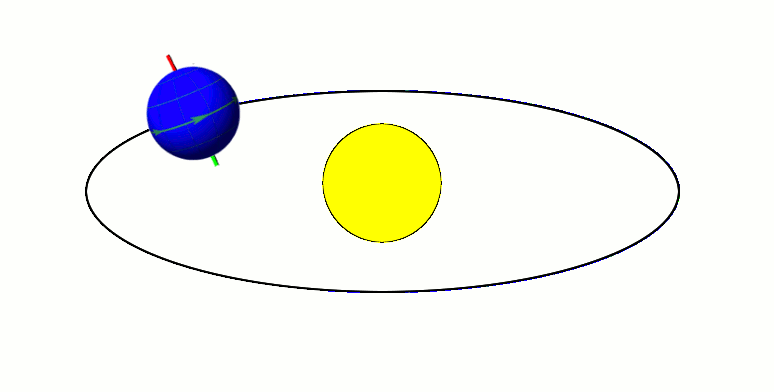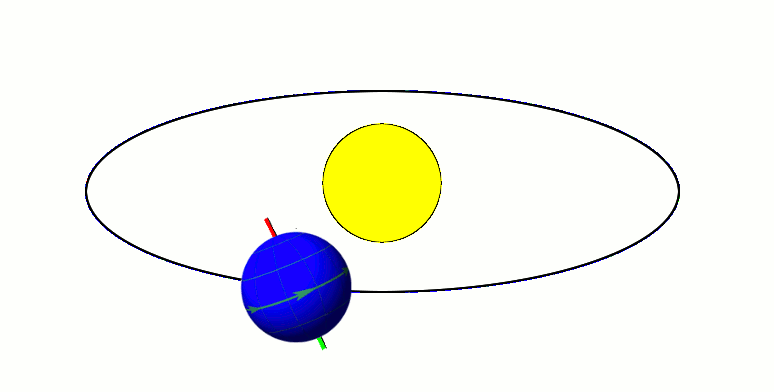
Milankovitch cycles describe the collective effects of changes in the Earth's movements on its climate over thousands of years. The term was coined and named after Serbian geophysicist and astronomer Milutin Milanković. In the 1920s, he hypothesized that variations in eccentricity, axial tilt, and precession combined to result in cyclical variations in the intra-annual and latitudinal distribution of solar radiation at the Earth's surface, and that this orbital forcing strongly influenced the Earth's climatic patterns. Earth's movements The Earth's rotation around its axis, and revolution around the Sun, evolve over time due to gravitational interactions with other bodies in the Solar System. The variations are complex, but a few cycles are dominant. The Earth's orbit varies between nearly circular and mildly elliptical (its eccentricity varies). When the orbit is more elongated, there is more variation in the distance between the Earth and the Sun, and in the amount of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Obliquity
In astronomy, axial tilt, also known as obliquity, is the angle between an object's rotational axis and its orbital axis, which is the line perpendicular to its orbital plane; equivalently, it is the angle between its equatorial plane and orbital plane. It differs from orbital inclination. At an obliquity of 0 degrees, the two axes point in the same direction; that is, the rotational axis is perpendicular to the orbital plane. The rotational axis of Earth, for example, is the imaginary line that passes through both the North Pole and South Pole, whereas the Earth's orbital axis is the line perpendicular to the imaginary plane through which the Earth moves as it revolves around the Sun; the Earth's obliquity or axial tilt is the angle between these two lines. Earth's obliquity oscillates between 22.1 and 24.5 degrees on a 41,000-year cycle. Based on a continuously updated formula (here Laskar, 1986, though since 2006 the IMCCE and the IAU recommend the P03 model), Earth's mean ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Logarithmic Mean
In mathematics, the logarithmic mean is a function of two non-negative numbers which is equal to their difference divided by the logarithm of their quotient. This calculation is applicable in engineering problems involving heat and mass transfer. Definition The logarithmic mean is defined as: :\begin M_\text(x, y) &= \lim_ \frac \\ pt &= \begin x & \textx = y ,\\ \frac & \text \end \end for the positive numbers x, y. Inequalities The logarithmic mean of two numbers is smaller than the arithmetic mean and the generalized mean with exponent one-third but larger than the geometric mean, unless the numbers are the same, in which case all three means are equal to the numbers. : \sqrt \leq \frac\leq \left(\frac2\right)^3 \leq \frac \qquad \text x > 0 \text y > 0. Toyesh Prakash Sharma generalizes the arithmetic logarithmic geometric mean inequality for any n belongs to the whole number as : \sqrt (\ln(\sqrt))^ (\ln(\sqrt)+n)\leq \frac\leq ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geometric Mean
In mathematics, the geometric mean is a mean or average which indicates a central tendency of a set of numbers by using the product of their values (as opposed to the arithmetic mean which uses their sum). The geometric mean is defined as the th root of the product of numbers, i.e., for a set of numbers , the geometric mean is defined as :\left(\prod_^n a_i\right)^\frac = \sqrt /math> or, equivalently, as the arithmetic mean in logscale: :\exp For instance, the geometric mean of two numbers, say 2 and 8, is just the square root of their product, that is, \sqrt = 4. As another example, the geometric mean of the three numbers 4, 1, and 1/32 is the cube root of their product (1/8), which is 1/2, that is, \sqrt = 1/2. The geometric mean applies only to positive numbers. The geometric mean is often used for a set of numbers whose values are meant to be multiplied together or are exponential in nature, such as a set of growth figures: values of the human population or inter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ellipse
In mathematics, an ellipse is a plane curve surrounding two focus (geometry), focal points, such that for all points on the curve, the sum of the two distances to the focal points is a constant. It generalizes a circle, which is the special type of ellipse in which the two focal points are the same. The elongation of an ellipse is measured by its eccentricity (mathematics), eccentricity e, a number ranging from e = 0 (the Limiting case (mathematics), limiting case of a circle) to e = 1 (the limiting case of infinite elongation, no longer an ellipse but a parabola). An ellipse has a simple algebraic solution for its area, but only approximations for its perimeter (also known as circumference), for which integration is required to obtain an exact solution. Analytic geometry, Analytically, the equation of a standard ellipse centered at the origin with width 2a and height 2b is: : \frac+\frac = 1 . Assuming a \ge b, the foci are (\pm c, 0) for c = \sqrt. The standard parametric e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Table Of Specific Heat Capacities
The table of specific heat capacities gives the volumetric heat capacity as well as the specific heat capacity of some substances and engineering materials, and (when applicable) the molar heat capacity. Generally, the most notable constant parameter is the volumetric heat capacity (at least for solids) which is around the value of 3 megajoule per cubic meter per kelvin: \rho c_p \simeq 3\,\text/(\text^3\text)\quad \text Note that the especially high ''molar'' values, as for paraffin, gasoline, water and ammonia, result from calculating specific heats in terms of moles of ''molecules''. If specific heat is expressed per mole of ''atoms'' for these substances, none of the constant-volume values exceed, to any large extent, the theoretical Dulong–Petit limit of 25 J⋅mol−1⋅K−1 = 3 ''R'' per mole of atoms (see the last column of this table). For example, Paraffin has very large molecules and thus a high heat capacity per mole, but as a substance it does not h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volumetric Heat Capacity
The volumetric heat capacity of a material is the heat capacity of a sample of the substance divided by the volume of the sample. It is the amount of energy that must be added, in the form of heat, to one unit of volume of the material in order to cause an increase of one unit in its temperature. The SI unit of volumetric heat capacity is joule per kelvin per cubic meter, J⋅K−1⋅m−3. The volumetric heat capacity can also be expressed as the specific heat capacity (heat capacity per unit of mass, in J⋅K−1⋅ kg−1) times the density of the substance (in kg/ L, or g/ mL). This quantity may be convenient for materials that are commonly measured by volume rather than mass, as is often the case in engineering and other technical disciplines. The volumetric heat capacity often varies with temperature, and is different for each state of matter. While the substance is undergoing a phase transition, such as melting or boiling, its volumetric heat capacity is technically in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radiative Forcing
Radiative forcing (or climate forcing) is the change in energy flux in the atmosphere caused by natural or anthropogenic factors of climate change as measured by watts / metre2. It is a scientific concept used to quantify and compare the external drivers of change to Earth's energy balance. System feedbacks and internal variability are related concepts, encompassing other factors that also influence the direction and magnitude of imbalance. Positive radiative forcing means Earth receives more incoming energy from sunlight than it radiates to space. This net gain of energy will cause warming. Conversely, negative radiative forcing means that Earth loses more energy to space than it receives from the sun, which produces cooling. A planet in radiative equilibrium with its parent star and the rest of space can be characterized by net zero radiative forcing and by a planetary equilibrium temperature. Radiative forcing on Earth is meaningfully evaluated at the tropopause and at the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Chicago Press
The University of Chicago Press is the largest and one of the oldest university presses in the United States. It is operated by the University of Chicago and publishes a wide variety of academic titles, including ''The Chicago Manual of Style'', numerous academic journals, and advanced monographs in the academic fields. One of its quasi-independent projects is the BiblioVault, a digital repository for scholarly books. The Press building is located just south of the Midway Plaisance on the University of Chicago campus. History The University of Chicago Press was founded in 1890, making it one of the oldest continuously operating university presses in the United States. Its first published book was Robert F. Harper's ''Assyrian and Babylonian Letters Belonging to the Kouyunjik Collections of the British Museum''. The book sold five copies during its first two years, but by 1900 the University of Chicago Press had published 127 books and pamphlets and 11 scholarly journals, includ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Journal Of Geology
''The Journal of Geology'' publishes research on geology, geophysics, geochemistry, sedimentology, geomorphology, petrology, plate tectonics, volcanology, structural geology, mineralogy, and planetary sciences. Its content ranges from planetary evolution to computer modeling of fossil development, making it relevant to geologists as well as other researchers working in the Earth or planetary sciences. It was established in 1893 by Thomas Chrowder Chamberlin Thomas Chrowder Chamberlin (; September 25, 1843 – November 15, 1928) was an American geologist and educator. In 1893 he founded the '' Journal of Geology'', of which he was editor for many years. Biography Chamberlin was born September 25, 18 .... References External links * English-language journals Bimonthly journals University of Chicago Press academic journals Publications established in 1893 Geology journals {{geology-journal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grove Karl Gilbert
Grove Karl Gilbert (May 6, 1843 – May 1, 1918), known by the abbreviated name G. K. Gilbert in academic literature, was an American geologist. Biography Gilbert was born in Rochester, New York and graduated from the University of Rochester. During the American Civil War, he was twice listed for the draft, but his name was drawn neither time. In 1871, he joined George M. Wheeler's geographical survey as its first geologist. Rockies geologist He then joined the Powell Survey of the Rocky Mountain Region in 1874, becoming Powell's primary assistant, and stayed with the survey until 1879. During this time he published an important monograph, ''The Geology of the Henry Mountains'' (1877). After the creation of the U.S. Geological Survey in 1879, he was appointed to the position of Senior Geologist and worked for the USGS until his death (including a term as acting director). Gilbert published a study of the former ancient Lake Bonneville in 1890 (the lake existed during the P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Season
A season is a division of the year based on changes in weather, ecology, and the number of daylight hours in a given region. On Earth, seasons are the result of the axial parallelism of Earth's tilted orbit around the Sun. In temperate and polar regions, the seasons are marked by changes in the intensity of sunlight that reaches the Earth's surface, variations of which may cause animals to undergo hibernation or to migrate, and plants to be dormant. Various cultures define the number and nature of seasons based on regional variations, and as such there are a number of both modern and historical cultures whose number of seasons varies. The Northern Hemisphere experiences most direct sunlight during May, June, and July, as the hemisphere faces the Sun. The same is true of the Southern Hemisphere in November, December, and January. It is Earth's axial tilt that causes the Sun to be higher in the sky during the summer months, which increases the solar flux. However, due to seas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |