|
Mikhail Vasilievich Ostrogradsky
Mikhail Vasilyevich Ostrogradsky (transcribed also ''Ostrogradskiy'', Ostrogradskiń≠) (russian: –ú–ł—Ö–į–łŐĀ–Ľ –í–į—Ā–łŐĀ–Ľ—Ć–Ķ–≤–ł—á –ě—Ā—ā—Ä–ĺ–≥—Ä–įŐĀ–ī—Ā–ļ–ł–Ļ, ua, –ú–ł—Ö–įŐĀ–Ļ–Ľ–ĺ –í–į—Ā–łŐĀ–Ľ—Ć–ĺ–≤–ł—á –ě—Ā—ā—Ä–ĺ–≥—Ä–įŐĀ–ī—Ā—Ć–ļ–ł–Ļ; 24 September 1801 ‚Äď 1 January 1862) was a Ukraine, Ukrainian mathematician, mechanics, mechanician and physicist of Ukrainian Cossacks, Ukrainian Cossack ancestry. Ostrogradsky was a student of Timofei Fedorovic Osipovsky, Timofei Osipovsky and is considered to be a disciple of Leonhard Euler, who was known as one of the leading mathematicians of Imperial Russia. Life Ostrogradsky was born on 24 September 1801 in the village of Pashennaya (at the time in the Poltava Governorate, Russian Empire, today in Kremenchuk Raion, Poltava Oblast, Ukraine). From 1816 to 1820, he studied under Timofei Fedorovic Osipovsky, Timofei Osipovsky (1765‚Äď1832) and graduated from the Kharkiv University, Imperial University of Kharkov. When Osipovsky was suspend ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kozelshchyna Raion
Kozelshchyna Raion ( uk, –ö–ĺ–∑–Ķ–Ľ—Ć—Č–ł–Ĺ—Ā—Ć–ļ–ł–Ļ —Ä–į–Ļ–ĺ–Ĺ; translit.: ''Kozelshchynskyi raion'') was a raion (district) in Poltava Oblast in central Ukraine. The raion's administrative center was the urban-type settlement of Kozelshchyna Kozelschyna ( uk, –ö–ĺ–∑–Ķ–Ľ—Ć—Č–ł–Ĺ–į) is an urban-type settlement in Poltava Oblast (province) of central Ukraine, located 77 km from Poltava. It formerly served as the administrative center of Kozelshchyna Raion, but is now administrated with .... The other urban-type settlement in the raion was Nova Haleshchyna ( uk, –Ě–ĺ–≤–į –ď–į–Ľ–Ķ—Č–ł–Ĺ–į). The raion was abolished and its territory was merged into Kremenchuk Raion on 18 July 2020 as part of the administrative reform of Ukraine, which reduced the number of raions of Poltava Oblast to four. The last estimate of the raion population was Important rivers within the Kozelshchyna Raion include the Psel. Settlements References External links *Kozelshchyna Raionofficial websit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Timofei Fedorovic Osipovsky
Timofei Fyodorovich Osipovsky (russian: –Ę–ł–ľ–ĺ—Ą–Ķ–Ļ –§–Ķ–ī–ĺ—Ä–ĺ–≤–ł—á –ě—Ā–ł–Ņ–ĺ–≤—Ā–ļ–ł–Ļ; February 2, 1766, Osipovo ‚Äď June 24, 1832, Moscow) was a Russian Imperial mathematician, physicist, astronomer, and philosopher. Timofei Osipovsky graduated from the St Petersburg Teachers Seminary. He became a teacher at Imperial Kharkov University, in 1805, the year it was founded. The city of Kharkov, thanks to its educational establishments, became one of the most important cultural and educational centres of Russian Empire The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended the Great Northern War. .... In 1813 he became rector of the university. However, in 1820, Osipovsky was suspended from his post on religious grounds. Osipovsky's most famous work was the three volume book ''A Course of Mathematics'' (18 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calculus Of Variations
The calculus of variations (or Variational Calculus) is a field of mathematical analysis that uses variations, which are small changes in functions and functionals, to find maxima and minima of functionals: mappings from a set of functions to the real numbers. Functionals are often expressed as definite integrals involving functions and their derivatives. Functions that maximize or minimize functionals may be found using the Euler‚ÄďLagrange equation of the calculus of variations. A simple example of such a problem is to find the curve of shortest length connecting two points. If there are no constraints, the solution is a straight line between the points. However, if the curve is constrained to lie on a surface in space, then the solution is less obvious, and possibly many solutions may exist. Such solutions are known as ''geodesics''. A related problem is posed by Fermat's principle: light follows the path of shortest optical length connecting two points, which depends up ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coin Of Ukraine Ostrograd R
A coin is a small, flat (usually depending on the country or value), round piece of metal or plastic used primarily as a medium of exchange or legal tender. They are standardized in weight, and produced in large quantities at a mint in order to facilitate trade. They are most often issued by a government. Coins often have images, numerals, or text on them. ''Obverse'' and its opposite, ''reverse'', refer to the two flat faces of coins and medals. In this usage, ''obverse'' means the front face of the object and ''reverse'' means the back face. The obverse of a coin is commonly called ''heads'', because it often depicts the head of a prominent person, and the reverse ''tails''. Coins are usually made of metal or an alloy, or sometimes of man-made materials. They are usually disc shaped. Coins, made of valuable metal, are stored in large quantities as bullion coins. Other coins are used as money in everyday transactions, circulating alongside banknotes. Usually the highest value ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
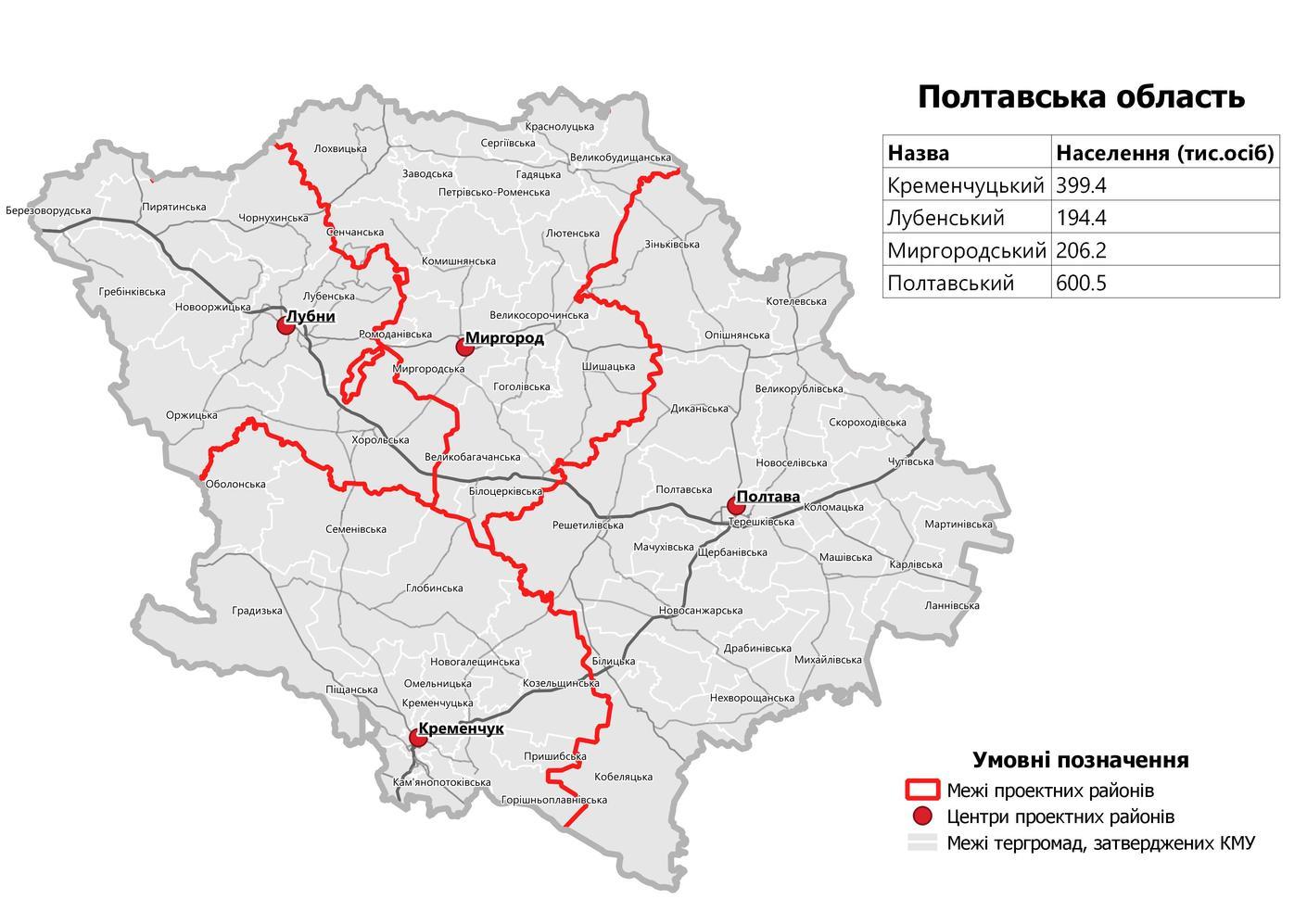
Poltava Oblast
Poltava Oblast ( uk, –ü–ĺ–Ľ—ā–įŐĀ–≤—Ā—Ć–ļ–į –ĺŐĀ–Ī–Ľ–į—Ā—ā—Ć, translit=Poltavska oblast; also referred to as Poltavshchyna ‚Äď uk, –ü–ĺ–Ľ—ā–įŐĀ–≤—Č–ł–Ĺ–į, literally 'Poltava Country') is an oblast (province) of central Ukraine. The administrative center of the oblast is the city of Poltava. Most of its territory is part of the historic Cossack Hetmanate (its southern regions: Poltava, Myrhorod, Lubny, and Hadiach). Population: Two other important cities there are Horishni Plavni and Kremenchuk. History During the 2022 Russian Invasion of Ukraine, the town of Myrhorod was bombed. However as of April 2022, there has been no ground fighting and the province remains completely under Ukrainian control. Geography Poltava Oblast is situated in the central part of Ukraine. Located on the left bank of Dnieper, Poltava region was part of the Cossack Hetmanate. It has an area of 28,800 km2. The oblast borders upon Chernihiv, Sumy, Kharkiv, Dnipropetrovsk, Kirovohrad, Cherkasy and K ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kremenchuk
Kremenchuk (; uk, –ö—Ä–Ķ–ľ–Ķ–Ĺ—á—ÉŐĀ–ļ, Kremenchuk ) is an industrial city in central Ukraine which stands on the banks of the Dnipro River. The city serves as the administrative center of the Kremenchuk Raion (district) in Poltava Oblast (province). Kremenchuk is administratively incorporated as a city of oblast significance administered by its own city council and does not form a part of the raion. Its population is approximately Along with its city-satellites Svitlovodsk and Horishni Plavni, it is an urban agglomeration and transportation hub. Although not as large as some other oblast centers and cities of regional significance, Kremenchuk has a large industrial center in Ukraine and Eastern Europe. A KrAZ truck plant, the Kremenchuk Oil Refinery of Ukrtatnafta, the Kriukiv Railway Car Building Works, and Kremenchuk Hydroelectric Power Plant, in nearby Svitlovodsk, are located in or near Kremenchuk. Highway M22 crosses the Dnieper over the dam of the power plant. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kremenchuk Mykhailo Ostrohradskyi National University
Kremenchuk Mykhailo Ostrohradskyi National University ( uk, –ö—Ä–Ķ–ľ–Ķ–Ĺ—á—É—Ü—Ć–ļ–ł–Ļ –Ĺ–į—Ü—Ė–ĺ–Ĺ–į–Ľ—Ć–Ĺ–ł–Ļ —É–Ĺ—Ė–≤–Ķ—Ä—Ā–ł—ā–Ķ—ā —Ė–ľ–Ķ–Ĺ—Ė –ú–ł—Ö–į–Ļ–Ľ–į –ě—Ā—ā—Ä–ĺ–≥—Ä–į–ī—Ā—Ć–ļ–ĺ–≥–ĺ) is a university in Kremenchuk, Ukraine, the largest university in Poltava Oblast. There are more 7 000 students studying in the university as of 2013. Its current rector is Mykhaylo Zagirnyak. History The origins of Kremenchuk Mykhailo Ostrohradskyi National University dates back to 1921. In that year the first institute of higher education was established in Kremenchuk. It offered higher educational courses with the Ukrainian language of teaching. The legal status of these courses was comparable to those offered by colleges which were considered as higher education institutions. Later, in 1925 the courses were reorganized in Kremenchuk Pedagogical College. There were day-time and evening classes where three different departments - preschool, school, and communist education - prepared ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Military Engineering-Technical University
The Saint Petersburg Military Engineering-Technical University (Nikolaevsky) (russian: –°–į–Ĺ–ļ—ā-–ü–Ķ—ā–Ķ—Ä–Ī—É—Ä–≥—Ā–ļ–ł–Ļ –í–ĺ–Ķ–Ĺ–Ĺ—č–Ļ –ł–Ĺ–∂–Ķ–Ĺ–Ķ—Ä–Ĺ–ĺ-—ā–Ķ—Ö–Ĺ–ł—á–Ķ—Ā–ļ–ł–Ļ —É–Ĺ–ł–≤–Ķ—Ä—Ā–ł—ā–Ķ—ā, VITU), previously known as the Saint Petersburg Nikolaevsky Engineering Academy, was established in 1810 under Alexander I. The university is situated in the former barracks of the Cavalier-Guard Regiment where the university was founded. Description Military Engineering-Technical University is a higher military educational institution preparing officers of engineering and building specialties for all branches of troops and navy. It is located in Saint Petersburg where the university was founded, near Engineers Castle, Summer Garden, Suvorov Museum, Tauride Palace, and Smolny Convent. Military Engineering-Technical University has six faculties preparing specialists in the following branches: * Military construction, * Military energy resource engineering, * Naval base ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russian Academy Of Science
The Russian Academy of Sciences (RAS; russian: –†–ĺ—Ā—Ā–łŐĀ–Ļ—Ā–ļ–į—Ź –į–ļ–į–ī–ĶŐĀ–ľ–ł—Ź –Ĺ–į—ÉŐĀ–ļ (–†–ź–Ě) ''Ross√≠yskaya akad√©miya na√ļk'') consists of the national academy of Russia; a network of scientific research institutes from across the Russian Federation; and additional scientific and social units such as libraries, publishing units, and hospitals. Peter the Great established the Academy (then the St. Petersburg Academy of Sciences) in 1724 with guidance from Gottfried Leibniz. From its establishment, the Academy benefitted from a slate of foreign scholars as professors; the Academy then gained its first clear set of goals from the 1747 Charter. The Academy functioned as a university and research center throughout the mid-18th century until the university was dissolved, leaving research as the main pillar of the institution. The rest of the 18th century continuing on through the 19th century consisted of many published academic works from Academy scholars and a few Ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saint Petersburg
Saint Petersburg ( rus, links=no, –°–į–Ĺ–ļ—ā-–ü–Ķ—ā–Ķ—Ä–Ī—É—Ä–≥, a=Ru-Sankt Peterburg Leningrad Petrograd Piter.ogg, r=Sankt-Peterburg, p=ňąsankt p ≤…™t ≤…™rňąburk), formerly known as Petrograd (1914‚Äď1924) and later Leningrad (1924‚Äď1991), is the second-largest city in Russia. It is situated on the Neva River, at the head of the Gulf of Finland on the Baltic Sea, with a population of roughly 5.4 million residents. Saint Petersburg is the fourth-most populous city in Europe after Istanbul, Moscow and London, the most populous city on the Baltic Sea, and the world's northernmost city of more than 1 million residents. As Russia's Imperial capital, and a historically strategic port, it is governed as a federal city. The city was founded by Tsar Peter the Great on 27 May 1703 on the site of a captured Swedish fortress, and was named after apostle Saint Peter. In Russia, Saint Petersburg is historically and culturally associated with t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paris, France
Paris () is the Capital city, capital and List of communes in France with over 20,000 inhabitants, most populous city of France, with an estimated population of 2,165,423 residents in 2019 in an area of more than 105 km² (41 sq mi), making it the List of cities proper by population density, 30th most densely populated city in the world in 2020. Since the 17th century, Paris has been one of the world's major centres of finance, diplomacy, commerce, Fashion capital, fashion, gastronomy, and science. For its leading role in the arts and sciences, as well as its very early system of street lighting, in the 19th century it became known as "the City of Light". Like London, prior to the Second World War, it was also sometimes called Caput Mundi#Paris, the capital of the world. The City of Paris is the centre of the Île-de-France Regions of France, region, or Paris Region, with an estimated population of 12,262,544 in 2019, or about 19% of the population of France, making the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |