|
Mighty Mouse Rocket
The Mk 4 Folding-Fin Aerial Rocket (FFAR), also known as "Mighty Mouse", was an unguided rocket used by United States military aircraft. It was 2.75 inches (70 mm) in diameter. Designed as an air-to-air weapon for interceptor aircraft to shoot down enemy bombers, it primarily saw service as an air-to-surface weapon. The FFAR has been developed into the modern Hydra 70 series, which is still in service. History The advent of jet engines for fighters and bombers posed new problems for interceptors. With closing speeds of 1,500 ft/s (457 m/s) or more for head-on interceptions, the time available for a fighter pilot to successfully target an enemy aircraft and inflict sufficient damage to bring it down was increasingly small. Wartime experience had shown that .50 caliber (12.7 mm) machine guns were not powerful enough to reliably down a bomber, certainly not in a single volley, and heavy autocannons did not have the range or rate of fire to ensure a hit. Ung ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Steven F
Stephen or Steven is a common English given name, first name. It is particularly significant to Christianity, Christians, as it belonged to Saint Stephen ( grc-gre, Στέφανος ), an early disciple and deacon who, according to the Book of Acts, was stoned to death; he is widely regarded as the first martyr (or "protomartyr") of the Christian Church. In English, Stephen is most commonly pronounced as ' (). The name, in both the forms Stephen and Steven, is often shortened to Steve or Stevie (given name), Stevie. The spelling as Stephen can also be pronounced which is from the Greek original version, Stephanos. In English, the female version of the name is Stephanie. Many surnames are derived from the first name, including Template:Stephen-surname, Stephens, Stevens, Stephenson, and Stevenson, all of which mean "Stephen's (son)". In modern times the name has sometimes been given with intentionally non-standard spelling, such as Stevan or Stevon. A common variant of the name ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kiel
Kiel () is the capital and most populous city in the northern Germany, German state of Schleswig-Holstein, with a population of 246,243 (2021). Kiel lies approximately north of Hamburg. Due to its geographic location in the southeast of the Jutland peninsula on the southwestern shore of the Baltic Sea, Kiel has become one of Germany's major maritime centres, known for a variety of international sailing events, including the annual Kiel Week, which is the biggest sailing event in the world. Kiel is also known for the Kiel mutiny, Kiel Mutiny, when sailors refused to board their vessels in protest against Germany's further participation in World War I, resulting in the abdication of the Wilhelm II, German Emperor, Kaiser and the formation of the Weimar Republic. The Olympic sailing competitions of the 1936 Summer Olympics, 1936 and the 1972 Summer Olympics#Venues, 1972 Summer Olympics were held in the Bay of Kiel. Kiel has also been one of the traditional homes of the German Nav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bulova Watch Company
Bulova is an American timepiece manufacturing company that was founded in 1875 and has been owned by Japanese multinational conglomerate Citizen Watch Co. since 2008. The company makes watches, clocks and accessories, and it is based in New York City. History Founding Bulova was founded and incorporated as the J. Bulova Company in 1875 by Bohemian immigrant Joseph Bulova. It was reincorporated under the name Bulova Watch Company in 1923, and became part of the Loews Corporation in 1979 and sold to Citizen at the end of 2007. In 1912, Joseph Bulova launched his first plant dedicated entirely to the production of watches. Manufacturing watches at their factory in Biel (Switzerland), he began a standardized mass production new to watchmaking. In 1919, Bulova offered the first complete range of watches for women and men in 1924. The visual style of his first popular advertising made its watches popular with the American public. But beyond the original style, precision and technol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
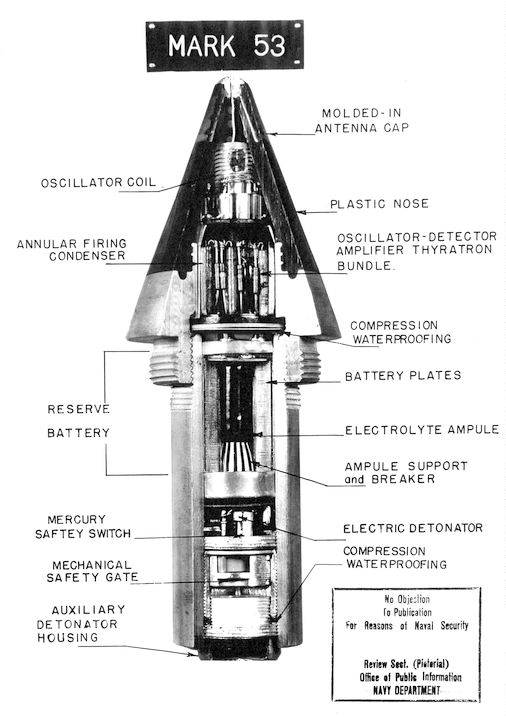
Fuze (explosives)
In military munitions, a fuze (sometimes fuse) is the part of the device that initiates function. In some applications, such as torpedoes, a fuze may be identified by function as the exploder. The relative complexity of even the earliest fuze designs can be seen in cutaway diagrams. A fuze is a device that detonates a munition's explosive material under specified conditions. In addition, a fuze will have safety and arming mechanisms that protect users from premature or accidental detonation. For example, an artillery fuze's battery is activated by the high acceleration of cannon launch, and the fuze must be spinning rapidly before it will function. "Complete bore safety" can be achieved with mechanical shutters that isolate the detonator from the main charge until the shell is fired. A fuze may contain only the electronic or mechanical elements necessary to signal or actuate the detonator, but some fuzes contain a small amount of primary explosive to initiate the detonation. Fu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flight International
''Flight International'' is a monthly magazine focused on aerospace. Published in the United Kingdom and founded in 1909 as "A Journal devoted to the Interests, Practice, and Progress of Aerial Locomotion and Transport", it is the world's oldest continuously published aviation news magazine. ''Flight International'' is published by DVV Media Group. Competitors include Jane's Information Group and ''Aviation Week''. Former editors of, and contributors include H. F. King, Bill Gunston, John W. R. Taylor and David Learmount. History The founder and first editor of ''Flight'' was Stanley Spooner. He was also the creator and editor of ''The Automotor Journal'', originally titled ''The Automotor Journal and Horseless Vehicle''.Guide To British Industrial History: Biographies: ''Stan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bridgeport Brass Company
The Bridgeport Brass Company is a former company located in Bridgeport, Connecticut that spun the wire for the first telephone line which ran from New York City to Boston Boston (), officially the City of Boston, is the state capital and most populous city of the Commonwealth of Massachusetts, as well as the cultural and financial center of the New England region of the United States. It is the 24th- mo .... History In January 1985, the company's employees signed an agreement to buyout the company from its owners to prevent its closure. By this point, the mill was 107 years old and in dire need of repairs and improvements. References Companies based in Bridgeport, Connecticut {{Connecticut-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermador
Thermador is part of BSH Home Appliances Corporation, a fully owned subsidiary of BSH Hausgeräte GmbH, the second largest appliance manufacturer in the world. The Thermador brand specializes in cooking appliance equipment such as ovens, ranges, cooktops, refrigerators and dishwashers. History Thermador invented the first wall oven and cooktop, and introduced stainless steel to home appliances. By 1948, Thermador introduced the first "Pro Range" for residential use. Patterned after commercial restaurant equipment, Thermador developed the first home version warming drawer in 1952, a kitchen appliance that warmed dishes and foods while the oven was in use. Thermador continued to improve on kitchen appliances with the first self-cleaning oven in 1963. During the 1970s, Thermador continued to innovate,. In 1970, the company released the first "smooth top" cooktop using material developed by Corning Incorporated. Julia Child used a Thermador oven in her critically acclaimed PBS TV ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North American Aviation
North American Aviation (NAA) was a major American aerospace manufacturer that designed and built several notable aircraft and spacecraft. Its products included: the T-6 Texan trainer, the P-51 Mustang fighter, the B-25 Mitchell bomber, the F-86 Sabre jet fighter, the X-15 rocket plane, the XB-70, the B-1 Lancer, the Apollo command and service module, the second stage of the Saturn V rocket, and the Space Shuttle orbiter. Through a series of mergers and sales, North American Aviation became part of North American Rockwell, which later became Rockwell International, and is now part of Boeing. History Early years On December 6, 1928, Clement Melville Keys founded North American as a holding company that bought and sold interests in various airlines and aviation-related companies. However, the Air Mail Act of 1934 forced the breakup of such holding companies. North American became a manufacturing company, run by James H. Kindelberger, James H. "Dutch" Kindelberger, who had bee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naval Air Weapons Station China Lake
Naval Air Weapons Station (NAWS) China Lake is a large military installation in California that supports the research, testing and evaluation programs of the United States Navy. It is part of Navy Region Southwest under Commander, Navy Installations Command, and was originally known as Naval Ordnance Test Station (NOTS). The installation is located in the Western Mojave Desert region of California, approximately north of Los Angeles. Occupying land in three counties – Kern, San Bernardino, and Inyo – the installation's closest neighbors are the city of Ridgecrest and the communities of Inyokern, Trona, and Darwin. China Lake is the United States Navy's largest single landholding, representing 85% of the Navy's land for weapons and armaments research, development, acquisition, testing and evaluation (RDAT&E) use and 38% of the Navy's land holdings worldwide. In total, its two ranges and main site cover more than , an area larger than the state of Rhode Island. As of 2010, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
US Navy
The United States Navy (USN) is the maritime service branch of the United States Armed Forces and one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. It is the largest and most powerful navy in the world, with the estimated tonnage of its active battle fleet alone exceeding the next 13 navies combined, including 11 allies or partner nations of the United States as of 2015. It has the highest combined battle fleet tonnage (4,635,628 tonnes as of 2019) and the world's largest aircraft carrier fleet, with eleven in service, two new carriers under construction, and five other carriers planned. With 336,978 personnel on active duty and 101,583 in the Ready Reserve, the United States Navy is the third largest of the United States military service branches in terms of personnel. It has 290 deployable combat vessels and more than 2,623 operational aircraft . The United States Navy traces its origins to the Continental Navy, which was established during the American Revolut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
USAAF
The United States Army Air Forces (USAAF or AAF) was the major land-based aerial warfare service component of the United States Army and ''de facto'' aerial warfare service branch of the United States during and immediately after World War II (1941–1945). It was created on 20 June 1941 as successor to the previous United States Army Air Corps and is the direct predecessor of the United States Air Force, today one of the six armed forces of the United States. The AAF was a component of the United States Army, which on 2 March 1942 was divided functionally by executive order into three autonomous forces: the Army Ground Forces, the United States Army Services of Supply (which in 1943 became the Army Service Forces), and the Army Air Forces. Each of these forces had a commanding general who reported directly to the Army Chief of Staff. The AAF administered all parts of military aviation formerly distributed among the Air Corps, General Headquarters Air Force, and the ground ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bomber Destroyer
Bomber destroyers were World War II interceptor aircraft intended to destroy enemy bomber aircraft. Bomber destroyers were typically larger and heavier than general interceptors, designed to mount more powerful armament, and often having twin engines. They differed from night fighters largely in that they were designed for day use. The United States Army Air Corps considered powerfully armed destroyers, like the Bell YFM-1 Airacuda prototype, to counter a potential attack of high-performance bombers. The Lockheed P-38 Lightning and Bell P-39 Airacobra were also initially specified to carry very heavy armament based on a central 37 mm cannon, specified as interceptor aircraft working in the anti-bomber role. Great Britain, by contrast, favored specialized "turret fighters", such as the Boulton Paul Defiant, which mounted heavy armament in a rotating turret. The P-38, a small, single-crewed example of the bomber destroyer type, was eventually outfitted with a 20 mm canno ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |






.jpg)