|
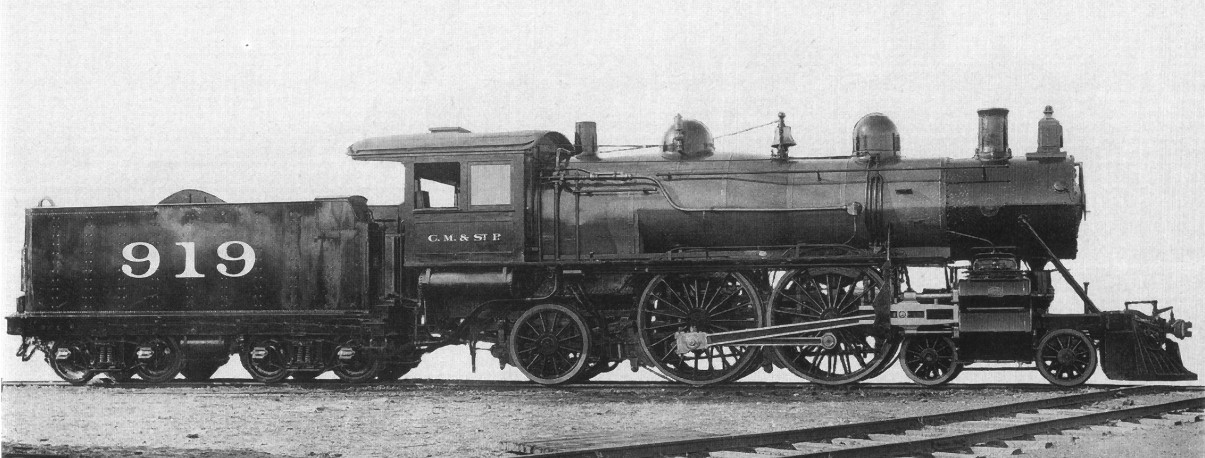
Midland Railway 990 Class
The Midland Railway 990 class was a class of 4-4-0 steam locomotive. Ten were built by the Midland Railway in 1907–1909, with simple expansion, to compare with the 1000 class compounds, with which they shared many features. Initially built as saturated, from 1910 to 1914, they were equipped with superheated boilers. These locomotives were well known for their work North of Leeds, over the demanding Settle and Carlisle route. Accidents and incidents : *On 2 September 1913, locomotive No. 993 was hauling a stalled express passenger train that was involved in a collision with another express at Ais Gill, Westmorland due to the latter passing signals at danger. Sixteen people were killed and 38 were injured.* Withdrawal They passed to the London, Midland and Scottish Railway The London, Midland and Scottish Railway (LMSIt has been argued that the initials LMSR should be used to be consistent with LNER, GWR and SR. The London, Midland and Scottish Railway's corporate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photographic Grey
Photographic grey, also known as works grey, was a paint scheme commonly applied to steam locomotives during the period before colour photography became commonplace. It was applied to allow sharper, more detailed images of the locomotive to be recorded. The first photographs of railways and their locomotives were made by private individuals, but by the 1860s the railway companies themselves were keen to create official photographs of the highest quality possible of their latest designs, which led to the adoption of photographic grey in railway photography. Use Railway companies wished to record their latest locomotives for use in publicity material and advertisements, and as a technical record of their work. This was especially the case in the United Kingdom, where all but the smallest of the 'pre-grouping' companies owned their own locomotive works and designed and built their own railway engines. For the numerous private locomotive builders it was especially important to hav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Superheater
A superheater is a device used to convert saturated steam or wet steam into superheated steam or dry steam. Superheated steam is used in steam turbines for electricity generation, steam engines, and in processes such as steam reforming. There are three types of superheaters: radiant, convection, and separately fired. A superheater can vary in size from a few tens of feet to several hundred feet (a few metres to some hundred metres). Types * A radiant superheater is placed directly in radiant zone of the combustion chamber near the water wall so as to absorb heat by radiation. * A convection superheater is located in the convective zone of the furnace usually ahead of economizer (in the path of the hot flue gases). These are also called primary superheaters. * A separately fired superheater is a superheater that is placed outside the main boiler, which has its own separate combustion system. This superheater design incorporates additional burners in the area of superheater pipes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Standard Gauge Steam Locomotives Of Great Britain
Standard may refer to: Symbols * Colours, standards and guidons, kinds of military signs * Standard (emblem), a type of a large symbol or emblem used for identification Norms, conventions or requirements * Standard (metrology), an object that bears a defined relationship to a unit of measure used for calibration of measuring devices * Standard (timber unit), an obsolete measure of timber used in trade * Breed standard (also called bench standard), in animal fancy and animal husbandry * BioCompute Standard, a standard for next generation sequencing * ''De facto'' standard, product or system with market dominance * Gold standard, a monetary system based on gold; also used metaphorically for the best of several options, against which the others are measured * Internet Standard, a specification ratified as an open standard by the Internet Engineering Task Force * Learning standards, standards applied to education content * Standard displacement, a naval term describing the weig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Railway Locomotives Introduced In 1908
Rail transport (also known as train transport) is a means of transport that transfers passengers and goods on wheeled vehicles running on rails, which are incorporated in tracks. In contrast to road transport, where the vehicles run on a prepared flat surface, rail vehicles (rolling stock) are directionally guided by the tracks on which they run. Tracks usually consist of steel rails, installed on sleepers (ties) set in ballast, on which the rolling stock, usually fitted with metal wheels, moves. Other variations are also possible, such as "slab track", in which the rails are fastened to a concrete foundation resting on a prepared subsurface. Rolling stock in a rail transport system generally encounters lower frictional resistance than rubber-tyred road vehicles, so passenger and freight cars (carriages and wagons) can be coupled into longer trains. The operation is carried out by a railway company, providing transport between train stations or freight customer facilit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Midland Railway Locomotives
Midland may refer to: Places Australia * Midland, Western Australia Canada * Midland, Albert County, New Brunswick * Midland, Kings County, New Brunswick * Midland, Newfoundland and Labrador * Midland, Ontario India * Midland Ward, Kohima, Nagaland Ireland * Midland Region, Ireland United States * Midland, Arkansas * Midland, California * Midoil, California, formerly Midland * Midland, Georgia * Midland, Indiana * Midland, Kentucky * Midland, Louisiana * Midland, Maryland * Midland, Michigan * Midland, Missouri * Midland, North Carolina * Midlands of South Carolina * Midland, Ohio * Midland, Oregon * Midland, Pennsylvania * Midland, South Dakota * Midland, Tennessee * Midland, Texas * Midland, Virginia * Midland, Washington * Midland City, Alabama Railways * Buenos Aires Midland Railway, a former British-owned railway company in Argentina * Colorado Midland Railway, US * Florida Midland Railroad (other), US * Midland Railroad (Massachusetts), US * Midland Railway, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Locomotives Of The Midland Railway
The Locomotives of the Midland Railway (which it always referred to as engines), followed its small engine policy. The policy was later adopted by the London, Midland and Scottish Railway, and contrasted with the London and North Western Railway's policy. The small engine policy was partly the consequence of a difference in the background of senior managers. In most railway companies, the elite position was the design, construction and maintenance of locomotives. Bigger engines brought more prestige and allowed longer trains. In the Midland, the marketing department was paramount. They recognised that people wanted more frequent, shorter trains rather than an infrequent service. It concentrated on very light, very fast and frequent trains. Overview The small engine policy was, perhaps, carried on too long, giving rise to the derisive poem: ''M is for Midland with engines galore'' ''Two on each train and asking for more'' Prior to around 1900 the Midland's locomotives were not ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Signal Passed At Danger
A signal passed at danger (SPAD), known in the United States as a stop signal overrun and in Canada as passing a stop signal, is an event on a railway where a train passes a stop railway signal, signal without authority. In the United States and Canada, this may be known colloquially as ''wikt:run a red light, running a red'', though this idiom principally refers to automobiles passing red traffic signals. The name derives from red Railway_signal#Colour_light_signals, colour light signals and horizontal Railway semaphore signal, semaphore signals in the United Kingdom, which are said to be ''at danger'' when they indicate that trains must stop (also known as the signal being ''on''). This terminology is not used in North America where not all red signals indicate stop. In the UK, the alternative description signal passed at red (S.P.A.R.) is used where a signal changes to red in front of a train due to either a technical fault or in an emergency, such that the train is unable t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Westmorland
Westmorland (, formerly also spelt ''Westmoreland'';R. Wilkinson The British Isles, Sheet The British IslesVision of Britain/ref> is a historic county in North West England spanning the southern Lake District and the northern Dales. It had an administrative function from the 12th century until 1974. Between 1974 and 2023 Westmorland lay within the administrative county of Cumbria. In April 2023, Cumbria County Council will be abolished and replaced with two unitary authorities, one of which, Westmorland and Furness, will cover all of Westmorland (as well as other areas), thereby restoring the Westmorland name to a top-tier administrative entity. The people of Westmorland are known as Westmerians. Early history Background At the beginning of the 10th century a large part of modern day Cumbria was part of the Kingdom of Strathclyde, and was known as '' "Scottish Cumberland" ''. The Rere Cross was ordered by Edmund I (r.939-946) to serve as a boundary marker between England an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ais Gill
Aisgill is the southernmost of the hamlets that form the parish of Mallerstang in the English county of Cumbria. It is on the B6259 road, at the head of Mallerstang dale, just before the boundary between Cumbria and North Yorkshire. The highest waterfall on the River Eden, Hellgill Force, with a drop of about 9.75 metres (according to recent measurements) is just to the north, at . The river itself rises (at first as Red Gill beck, later becoming Hell Gill beck) below Hugh Seat in the peat bogs above here. It finally becomes the river Eden after merging with the Ais Gill beck, which flows down from Wild Boar Fell. Aisgill is at both a county and a natural geographical boundary. It is at the watershed (sometimes called "the watershed of England") from which the Eden flows north towards the Irish Sea via the Solway Firth, while the River Ure flows south towards Wensleydale, and eventually into the North Sea. Swarth Fell frames the western side of the head of Mallerstang dale, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Compound Locomotive
A compound locomotive is a steam locomotive which is powered by a compound engine, a type of steam engine where steam is expanded in two or more stages. The locomotive was only one application of compounding. Two and three stages were used in ships, for example. Compounding became popular for railway locomotives from the early 1880s and by the 1890s were becoming common. Large numbers were constructed, mostly two- and four-cylinder compounds, in France, Germany, Austria, Hungary, and the United States. It declined in popularity due to maintenance issues and because superheating provided similar efficiencies at lower cost. Nonetheless, compound Mallets were built by the Norfolk and Western Railway right up to 1952. Introduction In the usual arrangement for a compound engine the steam is first expanded in one or two high-pressure ''(HP)'' cylinders, then having given up some heat and lost some pressure, it exhausts into a larger-volume low-pressure ''(LP)'' cylinder, (or two, - or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Richard Deeley
Richard Mountford Deeley (24 October 1855 – 19 June 1944) was an English engineer, chiefly noted for his five years as Chief Mechanical Engineer (CME) of the Midland Railway. Richard Deeley is recorded as being born in Derby His father had been an accountant with the Midland Railway and Richard attended grammar school in Chester. Career In 1873 he became a pupil of B. Ellington at the Hydraulic Engineering Co in Chester, and two years later he became a pupil of Samuel Waite Johnson at Derby Works. In March 1890 he became chief of the testing department at Derby, then progressed to the position of Inspector of Boilers, Engines and Machinery (March 1893), and to Derby Works Manager in January 1902, adding the post of Electrical Engineer a year later. In July 1903 he also became Assistant Locomotive Superintendent, subsequently replacing Johnson as Locomotive Superintendent on 1 January 1904. Compound locomotives He made significant contributions to compounding, adopting Smi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |