|
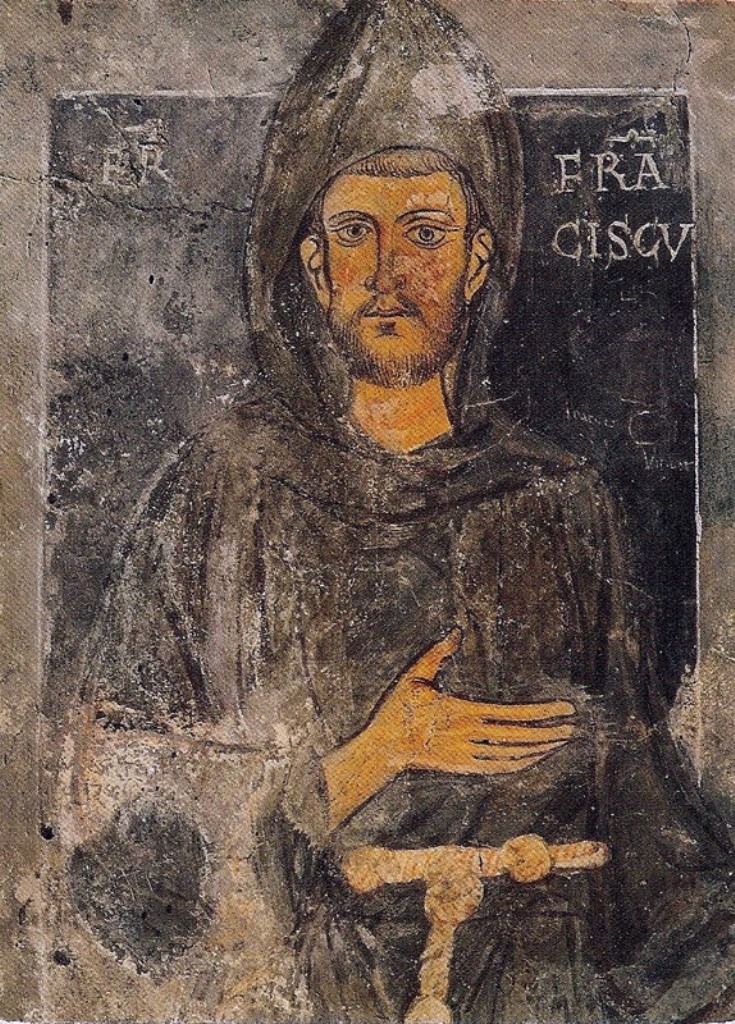
Michael Shiell
Michael Shiell OFM, Guardian of Killeigh, fl. 1693–98. Shiell was a member of the Ó Siadhail family of Kingdom of Uí Failghe, who were prominent County Offaly and County Laois in the late medieval/early modern era. Shiell was a member of the Franciscan order, and became the guardian of the Franciscan friary at Killeigh, County Offaly, in 1693. In 1698, eight individuals signed a document acknowledging that they had received chalices, pyxes, cups, an oil box, ciborium, a bell and vestments of the friary for safekeeping. Michael Shiell was one of the eight signatories, as was one William Shiell, who received at least three of the items. Krasnodebska-D'Aughton states that "both were probably members of the Ó Siadhail family, who had long associations with the Franciscans in the midlands." See also * Mícheál Ó Cléirigh * Feardorcha Ó Mealláin Feardorcha Ó Mealláin was an Irish poet the reputed author of '' An Díbirt go Connachta''. He is said to have been a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Franciscan
The Franciscans are a group of related Mendicant orders, mendicant Christianity, Christian Catholic religious order, religious orders within the Catholic Church. Founded in 1209 by Italian Catholic friar Francis of Assisi, these orders include three independent orders for men (the Order of Friars Minor being the largest contemporary male order), orders for women religious such as the Order of Saint Clare, and the Third Order of Saint Francis open to male and female members. They adhere to the teachings and spiritual disciplines of the founder and of his main associates and followers, such as Clare of Assisi, Anthony of Padua, and Elizabeth of Hungary. Several smaller Franciscan spirituality in Protestantism, Protestant Franciscan orders exist as well, notably in the Anglican and Lutheran traditions (e.g. the Community of Francis and Clare). Francis began preaching around 1207 and traveled to Rome to seek approval from Pope Innocent III in 1209 to form a new religious order. The o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Custos (Franciscans)
Custos ( en, guardian) means a religious superior or an official in the Franciscan Order. The precise meaning has differed over time, and among the Friars Minor, Conventuals, and Capuchins. Description Francis of Assisi sometimes applied the word to any superior in the Order - Guardians, Ministers Provincial, and even to the Minister General. Sometimes he restricts it to officials presiding over a certain number of friaries in the larger provinces of the Order with restricted powers and subject to their respective Ministers Provincial. It is in this latter sense that he refers to the ''custodes'' as having power, conjointly with the Provincials, to elect and to depose the Minister General. The friaries over which a ''custos'' (in this latter sense) presided were collectively called a custody ( la, custodia). The number of custodies in a province varied according to its size. Already at an early period it was deemed expedient that only one of the several ''custodes'' of a province s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ó Siadhail
Ó Siadhail / uaSiadhail / uaSiadgail is a Gaelic-Irish surname. Overview There were at least three families of this name in Gaelic Ireland. * Ó Siadhail of Ui Maine, now east County Galway. * Ó Siadhail of Uí Failghe, now County Offaly and County Laois. * Ó Siadhail of Tír Chonaill, now County Donegal. Little is recorded of the Ui Maine family. Those of Uí Failghe and Tír Chonaill were ollamhs of medicine, hereditary physicians to the ruling families in the respectives kingdoms and environs. It is not clear if the two were branches of the one family, or unrelated families who happened to bear the same surname. Current forms The surname is now generally anglicised as O'Shiel, Shiel, Sheil, Sheils, Sheals, Sheal and Sheilds (or Shiels and Shields), but the original form, Ó Siadhail, is used by persons who are Gaelic and conscious of their genealogy. Famous bearers Notable people named Ó Siadhail or one of its variants include: * Eoghan Carrach Ó Siadhail, po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Uí Failghe
The kingdom of Uí Fháilghe, ''Uí Failge'' (early spelling) or ''Uíbh Fhailí'' (modern spelling) () was a Gaelic-Irish kingdom which existed to 1550, the name of which (though not the territory) is preserved in the name of County Offaly (Irish: Contae Uíbh Fhailí), Ireland. County Offaly was constructed from elements of a number of ancient Irish Kingdoms of which Uí Failghe was one amongst such as Mide (present day west Offaly) and Munster (present day south Offaly). In modern territorial boundaries the kingdom today would correspond with County Offaly east of Tullamore, western parts of Kildare and parts of north east Laois. The name was also retained in the names of two baronies in County Kildare that formed part of the kingdom, Offaly (Ophaley) East and Offaly (Ophaley) West. Background Uí Failghe may have existed as a kingdom from the early historic era. It takes its name from the legendary king Failge Berraide (''fl.'' AD 507–514). It successfully fought o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
County Offaly
County Offaly (; ga, Contae Uíbh Fhailí) is a county in Ireland. It is part of the Eastern and Midland Region and the province of Leinster. It is named after the ancient Kingdom of Uí Failghe. It was formerly known as King's County, in honour of Philip II of Spain. Offaly County Council is the local authority for the county. The county population was 82,668 at the 2022 census. Central Statistics Office figures Geography and political subdivisions Offaly is the 18th largest of Ireland's 32 counties by area and the 24th largest in terms of population. It is the fifth largest of Leinster's 12 counties by size and the 10th largest by population.Physical geography [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
County Laois
County Laois ( ; gle, Contae Laoise) is a county in Ireland. It is part of the Eastern and Midland Region and in the province of Leinster. It was known as Queen's County from 1556 to 1922. The modern county takes its name from Loígis, a medieval kingdom. Historically, it has also been known as County Leix. Laois County Council is the local authority for the county. At the 2022 census, the population of the county was 91,657, an increase of 56% since the 2002 census. History Prehistoric The first people in Laois were bands of hunters and gatherers who passed through the county about 8,500 years ago. They hunted in the forests that covered Laois and fished in its rivers, gathering nuts and berries to supplement their diets. Next came Ireland's first farmers. These people of the Neolithic period (4000 to 2500 BC) cleared forests and planted crops. Their burial mounds remain in Clonaslee and Cuffsborough. Starting around 2500 BC, the people of the Bronze Age lived in Laois. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Friary
A monastery is a building or complex of buildings comprising the domestic quarters and workplaces of monastics, monks or nuns, whether living in communities or alone (hermits). A monastery generally includes a place reserved for prayer which may be a chapel, church, or temple, and may also serve as an oratory, or in the case of communities anything from a single building housing only one senior and two or three junior monks or nuns, to vast complexes and estates housing tens or hundreds. A monastery complex typically comprises a number of buildings which include a church, dormitory, cloister, refectory, library, balneary and infirmary, and outlying granges. Depending on the location, the monastic order and the occupation of its inhabitants, the complex may also include a wide range of buildings that facilitate self-sufficiency and service to the community. These may include a hospice, a school, and a range of agricultural and manufacturing buildings such as a barn, a forge, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
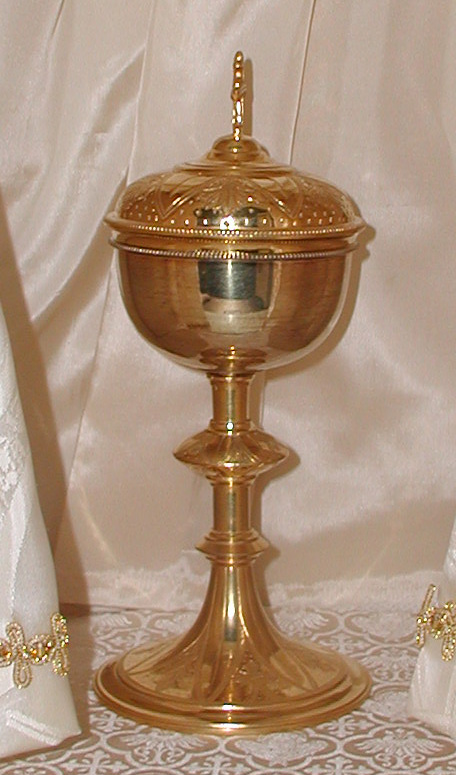
Chalice
A chalice (from Latin 'mug', borrowed from Ancient Greek () 'cup') or goblet is a footed cup intended to hold a drink. In religious practice, a chalice is often used for drinking during a ceremony or may carry a certain symbolic meaning. Religious use Christian The ancient Roman ''calix'' was a drinking vessel consisting of a bowl fixed atop a stand, and was in common use at banquets. In Roman Catholicism, Eastern Orthodox Church, Oriental Orthodoxy, Anglicanism, Lutheranism and some other Christian denominations, a chalice is a standing cup used to hold sacramental wine during the Eucharist (also called the Lord's Supper or Holy Communion). Chalices are often made of precious metal, and they are sometimes richly enamelled and jewelled. The gold goblet was symbolic for family and tradition. Chalices have been used since the early church. Because of Jesus' command to his disciples to "Do this in remembrance of me." (), and Paul's account of the Eucharistic rite in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ciborium (container)
A ciborium (plural ciboria; Medieval Latin ''ciborium'' (drinking cup), from the Ancient Greek κιβώριον ''kibōrion'', a type of drinking-cupOED.) is a vessel, normally in metal. It was originally a particular shape of drinking cup in Ancient Greece and Rome, but the word later came to refer to a large covered cup designed to hold hosts for, and after, the Eucharist, thus the counterpart (for the bread) of the chalice (for the wine). The word is also used for a large canopy over the altar of a church, which was a common feature of Early Medieval church architecture, now relatively rare. History The ancient Greek word referred to the cup-shaped seed vessel of the Egyptian water-lily '' nelumbium speciosum'' and came to describe a drinking cup made from that seed casing, or in a similar shape. These vessels were particularly common in ancient Egypt and the Greek East. The word "'ciborium'" was also used in classical Latin to describe such cups, although the only example ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mícheál Ó Cléirigh
Mícheál Ó Cléirigh (), sometimes known as Michael O'Clery, was an Irish chronicler, scribe and antiquary and chief author of the ''Annals of the Four Masters,'' assisted by Cú Choigcríche Ó Cléirigh, Fearfeasa Ó Maol Chonaire, and Peregrinus Ó Duibhgeannain. He was a member of the O'Cleric Bardic family and compiled with others the ''Annála Ríoghachta Éireann'' (Annals of the Kingdom of Ireland) at Bundrowse in County Leitrim on 10 August 1636. He also wrote the Martyrology of Donegal in the 17th Century. Background and early life Grandson of Tuathal Ó Cléirigh, a chief of the sept of Uí Chléirigh in Donegal, he was born in Kilbarron near Creevy, between Rossnowlagh and Ballyshannon on Donegal Bay. He was baptised Tadhg Ó Cléirigh and was known by the nickname Tadhg an tSléibhe (meaning Tadhg of the mountain), but took the name of Mícheál when he became a Franciscan friar. He was the youngest of four sons of Donnchadh Ó Cléirigh and his mother was Onór ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Feardorcha Ó Mealláin
Feardorcha Ó Mealláin was an Irish poet the reputed author of '' An Díbirt go Connachta''. He is said to have been a Franciscan, possibly from County Down, but both of these claims are in doubt. It is suggested that his name may be a 'pet-name' for two of his kinsmen, Henry Ó Mealláin or Tarlach Ó Mealláin, who may also be its author. See also * Aodh Buidhe Mac an Bhaird * Michael Shiell * Luke Wadding Luke Wadding, O.F.M. (16 October 158818 November 1657), was an Irish Franciscan friar and historian. Life Early life Wadding was born on 16 October 1588 in Waterford to Walter Wadding of Waterford, a wealthy merchant, and his wife, Anastasia ... * Henry Ó Mealláin References * Charles Dillon, ''Cín Lae Uí Mhealláin'', pp. 337–95 ''Tyrone:History and Society.'' * Diarmaid Ó Doibhlin (2000) ''Tyrone's Gaelic Literary Legacy'', pp. 414–17, op.cit. {{DEFAULTSORT:O Meallain, Feardorcha 17th-century Irish writers Irish-language poets Irish po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aodh Mac Cathmhaoil
Aodh Mac Cathmhaoil, O.F.M. ( la, Hugo Cavellus; anglicised: Hugh MacCaghwell; 1571 – 22 September 1626), was an Irish Franciscan theologian and Archbishop of Armagh. He was known by Irish speakers at Leuven (Louvain) by the honorary name '' Aodh Mac Aingil'' (''"Mac Aingil"'' is Irish for "Son of an Angel"), and it was under this title that he published the Irish work ''Scáthán Shacramuinte na hAthridhe''. Life Mac Cathmhaoil was born at Saul, County Down, and received his earliest education in his native place, trained at one of the bardic schools still operating in Ulster.''The Catholics of Ulster: A History'' by Marianne Elliot (pages 75-76) He next studied at a famous school in the Isle of Man. On his return to Ireland, he was hired by Hugh O'Neill, The O'Neill, 2nd Earl of Tyrone, as a tutor to his sons Henry and Hugh. Mac Cathmhaoil was sent by the Earl as special messenger to the Court of Spain to solicit aid for the Ulster forces. During his stay at Salamanca, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |