|
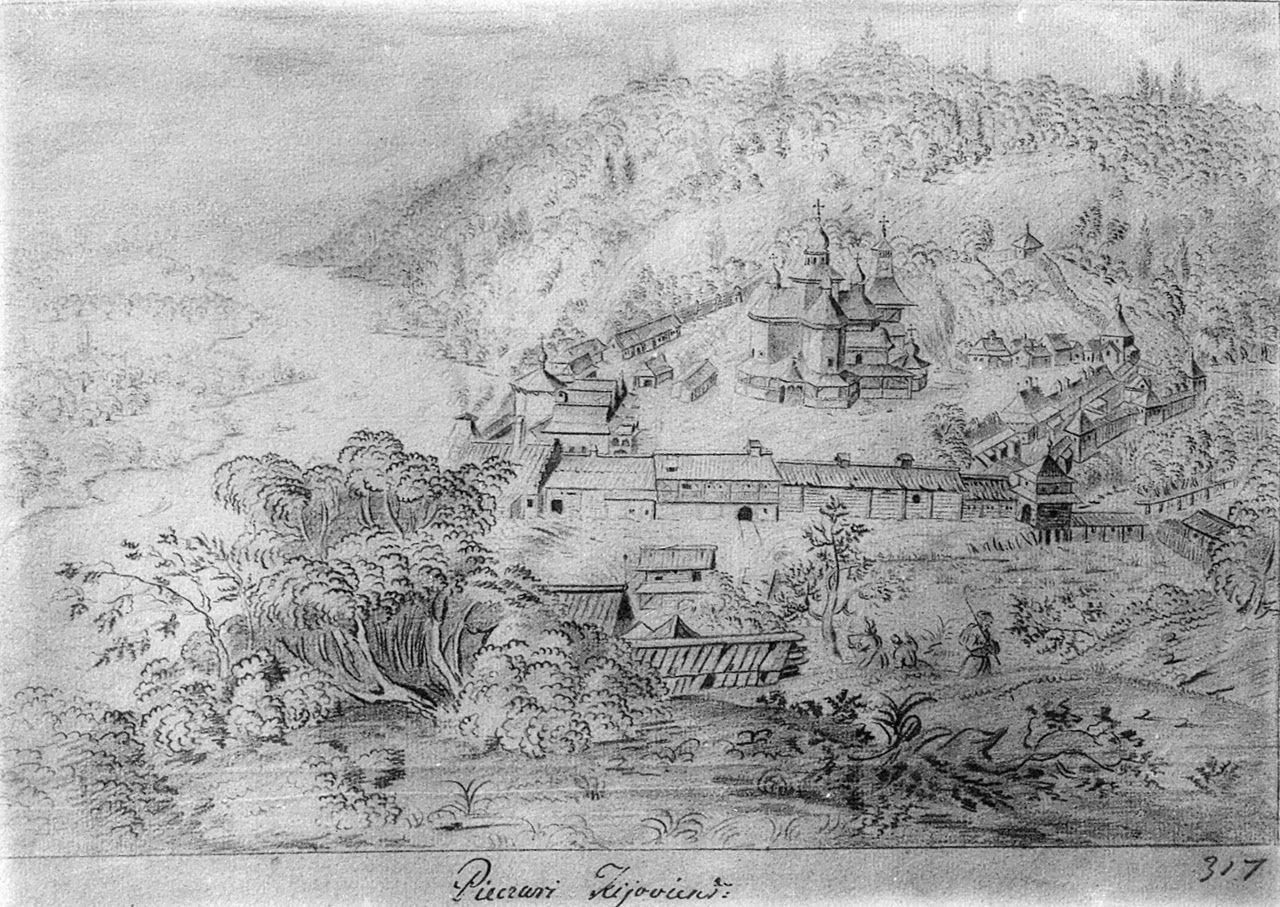
Mezhyhirya Monastery
__NOTOC__ The Mezhyhirya Savior-Transfiguration Monastery). See: , group="nb" ( uk, Межигірський Спасо-Преображенський монастир, ''Mezhyhirskyi Spaso-Preobrazhenskyi Monastyr'') was an Eastern Orthodox female monastery that was located in the neighborhood of Mezhyhiria. The monastery served as a historic Princely residency of Rurik dynasty during the Medieval times located just to the north of Vyshhorod. Today, the territory is part of the Vyshhorod Raion, Kyiv Oblast (province) in northern Ukraine. The location is situated in the Mezhyhirya ravine, on the right bank of the Dnieper River in close proximity to the Kyiv Reservoir. Founded in 988 AD, the Mezhyhirya Monastery was one of the first monasteries established in the East Slavic state of Kievan Rus'. Throughout its existence, it was destroyed, and then restored numerous times, yet it was not spared destruction by Soviet authorities in 1935. At the time of its height, the Mezhyhir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dnieper River
} The Dnieper () or Dnipro (); , ; . is one of the major transboundary rivers of Europe, rising in the Valdai Hills near Smolensk, Russia, before flowing through Belarus and Ukraine to the Black Sea. It is the longest river of Ukraine and Belarus and the fourth- longest river in Europe, after the Volga, Danube, and Ural rivers. It is approximately long, with a drainage basin of . In antiquity, the river was part of the Amber Road trade routes. During the Ruin in the later 17th century, the area was contested between the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth and Russia, dividing Ukraine into areas described by its right and left banks. During the Soviet period, the river became noted for its major hydroelectric dams and large reservoirs. The 1986 Chernobyl disaster occurred on the Pripyat, immediately above that tributary's confluence with the Dnieper. The Dnieper is an important navigable waterway for the economy of Ukraine and is connected by the Dnieper ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cossacks
The Cossacks , es, cosaco , et, Kasakad, cazacii , fi, Kasakat, cazacii , french: cosaques , hu, kozákok, cazacii , it, cosacchi , orv, коза́ки, pl, Kozacy , pt, cossacos , ro, cazaci , russian: казаки́ or , sk, kozáci , uk, козаки́ are a predominantly East Slavic Orthodox Christian people originating in the Pontic–Caspian steppe of Ukraine and southern Russia. Historically, they were a semi-nomadic and semi-militarized people, who, while under the nominal suzerainty of various Eastern European states at the time, were allowed a great degree of self-governance in exchange for military service. Although numerous linguistic and religious groups came together to form the Cossacks, most of them coalesced and became East Slavic-speaking Orthodox Christians. The Cossacks were particularly noted for holding democratic traditions. The rulers of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth and Russian Empire endowed Cossacks with certain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andrei I Bogolyubsky
Andrew I (died 28 June 1174), his Russian name in full, Andrey Yuryevich Bogolyubsky "Andrew made Vladimir the centre of the grand principality and placed a series of his relatives on the now secondary princely throne of Kiev. Later he also compelled Novgorod to accept a prince of his choice. In governing his realm, Andrew not only demanded that the subordinate princes obey him but also tried to reduce the traditional political powers of the boyars (i.e., the upper nobility) within his hereditary lands. In response, his embittered courtiers formed a conspiracy and killed him." (russian: Андрей Ю́рьевич Боголюбский, lit. Andrey Yuryevich of Bogolyubovo), was Grand prince of Vladimir-Suzdal from 1157 until his death. Andrey accompanied Yuri I Vladimirovich (Yury Dolgoruky), his father, on a conquest of Kiev, then led the devastation of the same city in 1169, and oversaw the elevation of Vladimir as the new capital of northeastern Rus'. He was canonized ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yuri Dolgoruki
Yuri I Vladimirovich ( rus, Юрий Владимирович, Yuriy Vladimirovich), commonly known as Yuri Dolgorukiy or the Long Arm ( rus, Юрий Долгорукий, Yuriy Dolgorukiy, meaning "Far-Reaching", c. 109915 May 1157) was a Rurikid prince. Noted for successfully curbing the privileges of the landowning ''boyar'' class in Rostov-Suzdal and his ambitious building programme, Yuri transformed this principality into the independent power that would evolve into early modern Muscovy. Yuri spent much of his life in internecine strife with the other Rurikid princes for suzerainty over the Kievan Rus, which had been held by his father (Vladimir Monomakh) and his elder brother before him. Although he twice managed to hold Kiev (in September 1149 - April 1151, again in March 1155 - May 1157) and rule as Grand Prince of all Rus', his autocratic rule and perceived foreigner status made him unpopular with the powerful Kievan ''boyars,'' leading to his presumed poisoning and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vladimir-Suzdal
Vladimir-Suzdal (russian: Владимирско-Су́здальская, ''Vladimirsko-Suzdal'skaya''), also Vladimir-Suzdalian Rus', formally known as the Grand Duchy of Vladimir (1157–1331) (russian: Владимиро-Су́здальское кня́жество, lit=Vladimiro-Suzdalian principality, translit=Vladimiro-Suzdal'skoye knyazhestvo; la, Volodimeriae), was one of the major principalities that succeeded Kievan Rus' in the late 12th century, centered in Vladimir-on-Klyazma. With time the principality grew into a grand duchy divided into several smaller principalities. After being conquered by the Mongol Empire, the principality became a self-governed state headed by its own nobility. A governorship of principality, however, was prescribed by a '' jarlig'' (declaration by the Khan) issued from the Golden Horde to a Rurikid sovereign. Vladimir-Suzdal is traditionally perceived as a cradle of the Great Russian language and nationality; it gradually evolved int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Byzantium
Byzantium () or Byzantion ( grc, Βυζάντιον) was an ancient Greek city in classical antiquity that became known as Constantinople in late antiquity and Istanbul today. The Greek name ''Byzantion'' and its Latinization ''Byzantium'' continued to be used as a name of Constantinople sporadically and to varying degrees during the thousand year existence of the Byzantine Empire. Byzantium was colonized by Greeks from Megara in the 7th century BC and remained primarily Greek-speaking until its conquest by the Ottoman Empire in AD 1453. Etymology The etymology of ''Byzantium'' is unknown. It has been suggested that the name is of Thracian origin. It may be derived from the Thracian personal name Byzas which means "he-goat". Ancient Greek legend refers to the Greek king Byzas, the leader of the Megarian colonists and founder of the city. The name '' Lygos'' for the city, which likely corresponds to an earlier Thracian settlement, is mentioned by Pliny the Elder in hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greece
Greece,, or , romanized: ', officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the southern tip of the Balkans, and is located at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa. Greece shares land borders with Albania to the northwest, North Macedonia and Bulgaria to the north, and Turkey to the northeast. The Aegean Sea lies to the east of the mainland, the Ionian Sea to the west, and the Sea of Crete and the Mediterranean Sea to the south. Greece has the longest coastline on the Mediterranean Basin, featuring thousands of islands. The country consists of nine traditional geographic regions, and has a population of approximately 10.4 million. Athens is the nation's capital and largest city, followed by Thessaloniki and Patras. Greece is considered the cradle of Western civilization, being the birthplace of democracy, Western philosophy, Western literature, historiography, political science, major scientific and mathematical p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Michael Of Kiev (metropolitan)
Metropolitan Michael I of Kiev (russian: Святитель Михаил Киевский и всея Руси, митрополит; uk, Митрополит Михаїл Київський; died June 15, 992) is considered to be the first Metropolitan of Kiev and All-Rus' from 988-992. He is also considered to be a saint. June 15 and September 30 are dedicated to him on the Julian Calendar. Different historical accounts state that he was either Assyrian or Bulgarian. He is traditionally accounted as founding the St. Michael's Golden-Domed Monastery in Kiev as well as the Mezhyhirskyi Monastery near Vyshhorod with Greek monks in 988 AD. His remains were originally located in the Church of the Tithes, then they were moved to the Near Caves of the Kiev Pechersk Lavra, and are now located in the Dormition Cathedral of the lavra. Michael's feast day is observed on June 15 (death day), September 30 (Translation), and formerly (with Anthony of Kiev and Theodosius of Kiev) o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metropolitan Bishop
In Christian churches with episcopal polity, the rank of metropolitan bishop, or simply metropolitan (alternative obsolete form: metropolite), pertains to the diocesan bishop or archbishop of a metropolis. Originally, the term referred to the bishop of the chief city of a historical Roman province, whose authority in relation to the other bishops of the province was recognized by the First Council of Nicaea (AD 325). The bishop of the provincial capital, the metropolitan, enjoyed certain rights over other bishops in the province, later called "suffragan bishops". The term ''metropolitan'' may refer in a similar sense to the bishop of the chief episcopal see (the "metropolitan see") of an ecclesiastical province. The head of such a metropolitan see has the rank of archbishop and is therefore called the metropolitan archbishop of the ecclesiastical province. Metropolitan (arch)bishops preside over synods of the bishops of their ecclesiastical province, and canon law and traditi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microsoft Word
Microsoft Word is a word processing software developed by Microsoft. It was first released on October 25, 1983, under the name ''Multi-Tool Word'' for Xenix systems. Subsequent versions were later written for several other platforms including: IBM PCs running DOS (1983), Apple Macintosh running the Classic Mac OS (1985), AT&T UNIX PC (1985), Atari ST (1988), OS/2 (1989), Microsoft Windows (1989), SCO Unix (1990) and macOS (2001). Using Wine, versions of Microsoft Word before 2013 can be run on Linux. Commercial versions of Word are licensed as a standalone product or as a component of Microsoft Office suite of software, which can be purchased either with a perpetual license or as part of a Microsoft 365 subscription. History Origins In 1981, Microsoft hired Charles Simonyi, the primary developer of Bravo, the first GUI word processor, which was developed at Xerox PARC. Simonyi started work on a word processor called ''Multi-Tool Word'' and soon hired Rich ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yevgeniy Bolkhovitinov
Meropolitan Eugene (russian: Митрополит Евгений, secular name: Yevfimy Alekseyevich Bolkhovitinov, russian: Евфимий Алексеевич Болховитинов; –) was the Orthodox Metropolitan of Kiev and Galicia from 1822. Best known as an antiquary and book collector, Bolkhovitinov came from a generation of learned Orthodox monks formed by the Russian Enlightenment. The son of a Voronezh priest, Bolkhovitinov attended the Slavic Greek Latin Academy and the Moscow University. As a young man he made his living by translating French books for the Novikov printing house. After his wife died, Bolkhovitinov took the tonsure in 1800 and was made a bishop 4 years later. While living in Novgorod between 1804 and 1808, he published the charter of Mstislav the Great and studied the crypt of the Yuriev Monastery. Though amateur, his archaeological and palaeographical work was highly regarded by a circle of antiquaries close to Count Nikolai Rumyantsev. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taras Bulba
''Taras Bulba'' (russian: «Тарас Бульба»; ) is a romanticized historical novella set in the first half of the 17th century, written by Nikolai Gogol (1809-1852). It features elderly Zaporozhian Cossack Taras Bulba and his sons Andriy and Ostap. The sons study at the Kiev Academy and then return home, whereupon the three men set out on a journey to the Zaporizhian Sich (the Zaporizhian Cossack headquarters, located in southern Ukraine) where they join other Cossacks and go to war against Poland. The story was initially published in 1835 as part of the ''Mirgorod'' collection of short stories, but a much expanded version appeared in 1842 with some differences in the storyline. The 1842 text has been described by as a "paragon of civic virtue and a force of patriotic edification", contrasting the rhetoric of the 1835 version with its "distinctly Cossack jingoism". Inspiration The character of Taras Bulba, the main hero of this novel, is a composite of severa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)
