|
Meyer Hardness Test
The Meyer hardness test is a hardness test based upon projected area of an impression. The hardness, H, is defined as the maximum load, P_\text divided by the projected area of the indent, A_\text. :H=\frac . This is a more fundamental measurement of hardness than other hardness tests which are based on the surface area of an indentation. The principle behind the test is that the mean pressure required to test the material is the measurement of the hardness of the material. Units of megapascals (MPa) are frequently used for reporting Meyer hardness, but any unit of pressure can be used.. The test was originally defined for spherical indenters, but can be applied to any indenter shape. It is often the definition used in nanoindentation testing. An advantage of the Meyer test is that it is less sensitive to the applied load, especially compared to the Brinell hardness test. For cold worked materials the Meyer hardness is relatively constant and independent of load, whereas for t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meyer Hardness Test Vs Brinell Hardness Test
Meyer may refer to: People *Meyer (surname), listing people so named *Meyer (name), a list of people and fictional characters with the name Companies * Meyer Burger, a Swiss mechanical engineering company * Meyer Corporation * Meyer Sound Laboratories * Meyer Turku, a Finnish shipbuilding company * Behn Meyer, a German chemical company * Fred Meyer, a American hypermarket chain and subsidiary of Kroger * Fred Meyer Jewelers Places United States * Meyer, Illinois, an unincorporated community in Adams County, Illinois * Meyer, Franklin County, Illinois, an unincorporated community in Franklin County, Illinois * Meyer, Iowa, in Mitchell County, Iowa * Myers, Montana (also spelled Meyer), an unincorporated community in Treasure County * Meyer Township, Michigan Other * Meyer House (other), multiple buildings in the U.S. * Meyer locomotive * Meyer Theatre, an historic theater in Wisconsin, U.S. * USS ''Meyer'' (DD-279), a ''Clemson''-class destroyer in the United S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hardness
In materials science, hardness (antonym: softness) is a measure of the resistance to localized plastic deformation induced by either mechanical indentation or abrasion. In general, different materials differ in their hardness; for example hard metals such as titanium and beryllium are harder than soft metals such as sodium and metallic tin, or wood and common plastics. Macroscopic hardness is generally characterized by strong intermolecular bonds, but the behavior of solid materials under force is complex; therefore, hardness can be measured in different ways, such as scratch hardness, indentation hardness, and rebound hardness. Hardness is dependent on ductility, elastic stiffness, plasticity, strain, strength, toughness, viscoelasticity, and viscosity. Common examples of hard matter are ceramics, concrete, certain metals, and superhard materials, which can be contrasted with soft matter. Measuring hardness There are three main types of hardness measurements: ''s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Projected Area
Projected area is the two dimensional area measurement of a three-dimensional object by projecting its shape on to an arbitrary plane. This is often used in mechanical engineering and architectural engineering related fields, specifically hardness testing, axial stress, wind pressures, and terminal velocity. The geometrical definition of a projected area is: "the rectilinear parallel projection In three-dimensional geometry, a parallel projection (or axonometric projection) is a projection of an object in three-dimensional space onto a fixed plane, known as the '' projection plane'' or ''image plane'', where the '' rays'', known as ' ... of a surface of any shape onto a plane". This translates into the equation: A_\text = \int_ \cos \, dA where A is the original area, and \beta is the angle between the normal to the local plane and the line of sight to the surface A. For basic shapes the results are listed in the table below. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pascal (pressure)
The pascal (symbol: Pa) is the unit of pressure in the International System of Units (SI), and is also used to quantify internal pressure, stress, Young's modulus, and ultimate tensile strength. The unit, named after Blaise Pascal, is defined as one newton per square metre and is equivalent to 10 barye (Ba) in the CGS system. The unit of measurement called standard atmosphere (atm) is defined as 101,325 Pa. Common multiple units of the pascal are the hectopascal (1 hPa = 100 Pa), which is equal to one millibar, and the kilopascal (1 kPa = 1000 Pa), which is equal to one centibar. Meteorological observations typically report atmospheric pressure in hectopascals per the recommendation of the World Meteorological Organization, thus a standard atmosphere (atm) or typical sea-level air pressure is about 1013 hPa. Reports in the United States typically use inches of mercury or millibars (hectopascals). In Canada these reports are given in kilopascals ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
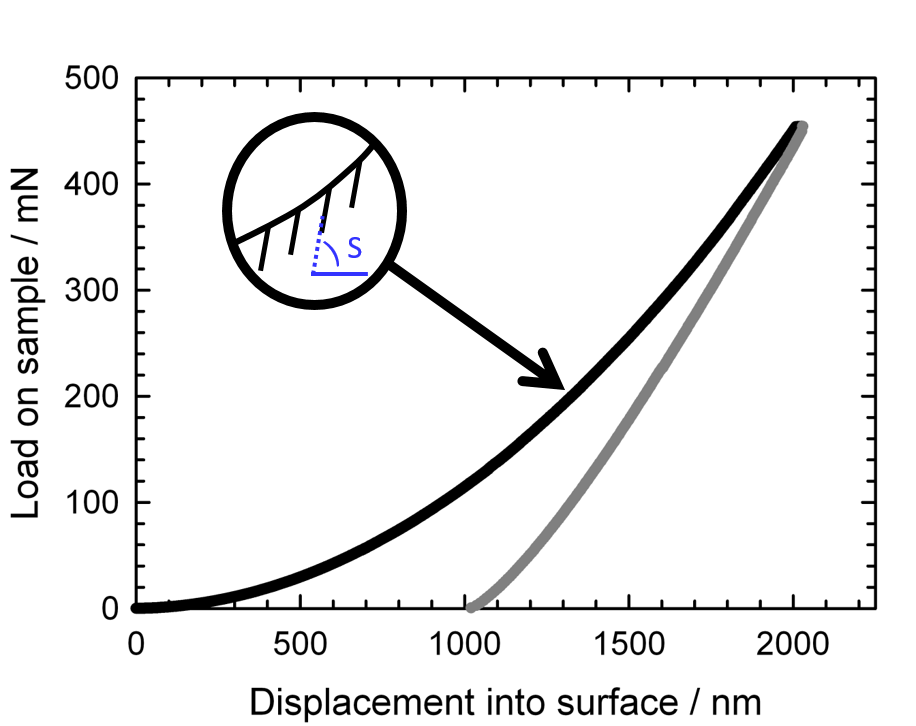
Nanoindentation
Nanoindentation, also called instrumented indentation testing, is a variety of indentation hardness tests applied to small volumes. Indentation is perhaps the most commonly applied means of testing the mechanical properties of materials. The nanoindentation technique was developed in the mid-1970s to measure the hardness of small volumes of material. Background In a traditional indentation test (macro or micro indentation), a hard tip whose mechanical properties are known (frequently made of a very hard material like diamond) is pressed into a sample whose properties are unknown. The load placed on the indenter tip is increased as the tip penetrates further into the specimen and soon reaches a user-defined value. At this point, the load may be held constant for a period or removed. The area of the residual indentation in the sample is measured and the hardness, H, is defined as the maximum load, P_, divided by the residual indentation area, A_r: :H=\frac . For most techniques, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brinell Scale
The Brinell scale characterizes the indentation hardness of materials through the scale of penetration of an indenter, loaded on a material test-piece. It is one of several definitions of hardness in materials science. History Proposed by Swedish engineer Johan August Brinell in 1900, it was the first widely used and standardised hardness test in engineering and metallurgy. The large size of indentation and possible damage to test-piece limits its usefulness. However, it also had the useful feature that the hardness value divided by two gave the approximate UTS in ksi for steels. This feature contributed to its early adoption over competing hardness tests. Test details The typical test uses a diameter steel ball as an indenter with a force. For softer materials, a smaller force is used; for harder materials, a tungsten carbide ball is substituted for the steel ball. The indentation is measured and hardness calculated as: :\operatorname=\frac where: :BHN = Brinell Hardn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cold Work
Cold is the presence of low temperature, especially in the atmosphere. In common usage, cold is often a subjective perception. A lower bound to temperature is absolute zero, defined as 0.00K on the Kelvin scale, an absolute thermodynamic temperature scale. This corresponds to on the Celsius scale, on the Fahrenheit scale, and on the Rankine scale. Since temperature relates to the thermal energy held by an object or a sample of matter, which is the kinetic energy of the random motion of the particle constituents of matter, an object will have less thermal energy when it is colder and more when it is hotter. If it were possible to cool a system to absolute zero, all motion of the particles in a sample of matter would cease and they would be at complete rest in the classical sense. The object could be described as having zero thermal energy. Microscopically in the description of quantum mechanics, however, matter still has zero-point energy even at absolute zero, because ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Annealing (metallurgy)
In metallurgy and materials science, annealing is a heat treatment that alters the physical and sometimes chemical properties of a material to increase its ductility and reduce its hardness, making it more workable. It involves heating a material above its recrystallization temperature, maintaining a suitable temperature for an appropriate amount of time and then cooling. In annealing, atoms migrate in the crystal lattice and the number of dislocations decreases, leading to a change in ductility and hardness. As the material cools it recrystallizes. For many alloys, including carbon steel, the crystal grain size and phase composition, which ultimately determine the material properties, are dependent on the heating rate and cooling rate. Hot working or cold working after the annealing process alters the metal structure, so further heat treatments may be used to achieve the properties required. With knowledge of the composition and phase diagram, heat treatment can be used t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meyer's Law
Meyer's law is an empirical relation between the size of a hardness test indentation and the load required to leave the indentation.. The formula was devised by Eugene Meyer of the Materials Testing Laboratory at the Imperial School of Technology, Charlottenburg, Germany, circa 1908. Equation It takes the form: :P\,=\,kd^n where *''P'' is the pressure in megapascals *''k'' is the resistance of the material to initial penetrationS.L. Hoyt, "The Ball Indentation Hardness Test," ''Trans. Am. Soc. Steel Treating'', 6 (1924). *''n'' is Meyer's index, a measure of the effect of the deformation on the hardness of the material *''d'' is the chordal diameter (diameter of the indentation) The index ''n'' usually lies between the values of 2, for fully strain hardened materials, and 2.5, for fully annealed materials. It is roughly related to the strain hardening coefficient in the equation for the true stress-true strain curve by adding 2. Note, however, that below approximately ''d' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charlottenburg
Charlottenburg () is a locality of Berlin within the borough of Charlottenburg-Wilmersdorf. Established as a town in 1705 and named after Sophia Charlotte of Hanover, Queen consort of Prussia, it is best known for Charlottenburg Palace, the largest surviving royal palace in Berlin, and the adjacent museums. Charlottenburg was an independent city to the west of Berlin until 1920 when it was incorporated into "Groß-Berlin" (Greater Berlin) and transformed into a borough. In the course of Berlin's 2001 administrative reform it was merged with the former borough of Wilmersdorf becoming a part of a new borough called Charlottenburg-Wilmersdorf. Later, in 2004, the new borough's districts were rearranged, dividing the former borough of Charlottenburg into the localities of Charlottenburg proper, Westend and Charlottenburg-Nord. Geography Charlottenburg is located in Berlin's inner city, west of the Großer Tiergarten park. Its historic core, the former village green of Alt L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brinelling
Brinelling {{IPAc-en, ˈ, b, r, ɪ, n, ə, l, ɪ, ŋ is the permanent indentation of a hard surface. It is named after the Brinell scale of hardness, in which a small ball is pushed against a hard surface at a preset level of force, and the depth and diameter of the mark indicates the Brinell hardness of the surface. Brinelling is permanent plastic deformation of a surface, and usually occurs while two surfaces in contact are stationary (such as rolling elements and the raceway of a bearings) and the material yield strength has been exceeded. Brinelling is undesirable, as the parts often mate with other parts in very close proximity. The very small indentations can quickly lead to improper operation, such as chattering or excess vibration, which in turn can accelerate other forms of wear, such as spalling and ultimately, failure of the bearing. Introduction Brinelling is a material surface failure caused by Hertz contact stress that exceeds the material limit. It usually occ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hardness Comparison
A variety of hardness-testing methods are available, including the Vickers, Brinell, Rockwell, Meyer and Leeb tests. Although it is impossible in many cases to give an exact conversion, it is possible to give an approximate material-specific comparison table for steels. Hardness comparison table {, class="wikitable" ! Brinell HB (10 mm Ball, 3000 kg load)!!Vickers Vickers was a British engineering company that existed from 1828 until 1999. It was formed in Sheffield as a steel foundry by Edward Vickers and his father-in-law, and soon became famous for casting church bells. The company went public i ... HV (5 kg)!! Rockwell C HRC (120 degree cone 150 kg)!!Rockwell B HRB (1/16" ball 100 kg)!! Leeb HLDH.Pollok, „Umwertung der Skalen“ (“Conversion of Scales”), Qualität und Zuverlässigkeit, Ausgabe 4/2008. , - , 800, , -, , 72, , -, , 856 , - , 780, , 1220, , 71, , -, , 850 , - , 760, , 1210, , 70, , -, , 843 , - , 745, , 1114, , 68 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.png)