|
Metschnikowia Pulcherrima
''Metschnikowia pulcherrima'' is a ubiquitous species of yeast, with numerous strains, belonging to the family Metschnikowiaceae, and found on grapes, cherries, flowers, spoiled fruit and consequently carried by fruit flies. It is a non-''Saccharomyces'' yeast and plays an important role in the vinification of wine when it is present on grapes or winery equipment, and has historically seen use in South Africa’s wine industry. It is also being studied at the University of Bath as a possible alternative to the use of Palm oil, and early results show promise. ''M. pulcherrima'' is ovoid to ellipsoidal in shape and reproduces by budding. Its cells are globose and thick-walled, holding a single, large oil droplet of high refractive index. As the result of incomplete budding where cells remain attached after division, pseudohyphae may form under anaerobic conditions. The strains of ''M. pulcherrima'' show strong biocontrol activity against various microorganisms. Its value to the win ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fungus
A fungus ( : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, separately from the other eukaryotic kingdoms, which by one traditional classification include Plantae, Animalia, Protozoa, and Chromista. A characteristic that places fungi in a different kingdom from plants, bacteria, and some protists is chitin in their cell walls. Fungi, like animals, are heterotrophs; they acquire their food by absorbing dissolved molecules, typically by secreting digestive enzymes into their environment. Fungi do not photosynthesize. Growth is their means of mobility, except for spores (a few of which are flagellated), which may travel through the air or water. Fungi are the principal decomposers in ecological systems. These and other differences place fungi in a single group of related organisms, named the ''Eumycota'' (''true f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Torulaspora
''Torulaspora'' is a genus of ascomycetous yeasts in the family Saccharomycetaceae. See also *Yeast in winemaking The role of yeast in winemaking is the most important element that distinguishes wine from fruit juice. In the :wikt:anaerobic, absence of oxygen, yeast converts the sugar in wine, sugars of the fruit into ethanol, alcohol and carbon dioxide throu ... References External links Saccharomycetaceae Yeasts Yeasts used in brewing Ascomycota genera {{yeast-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
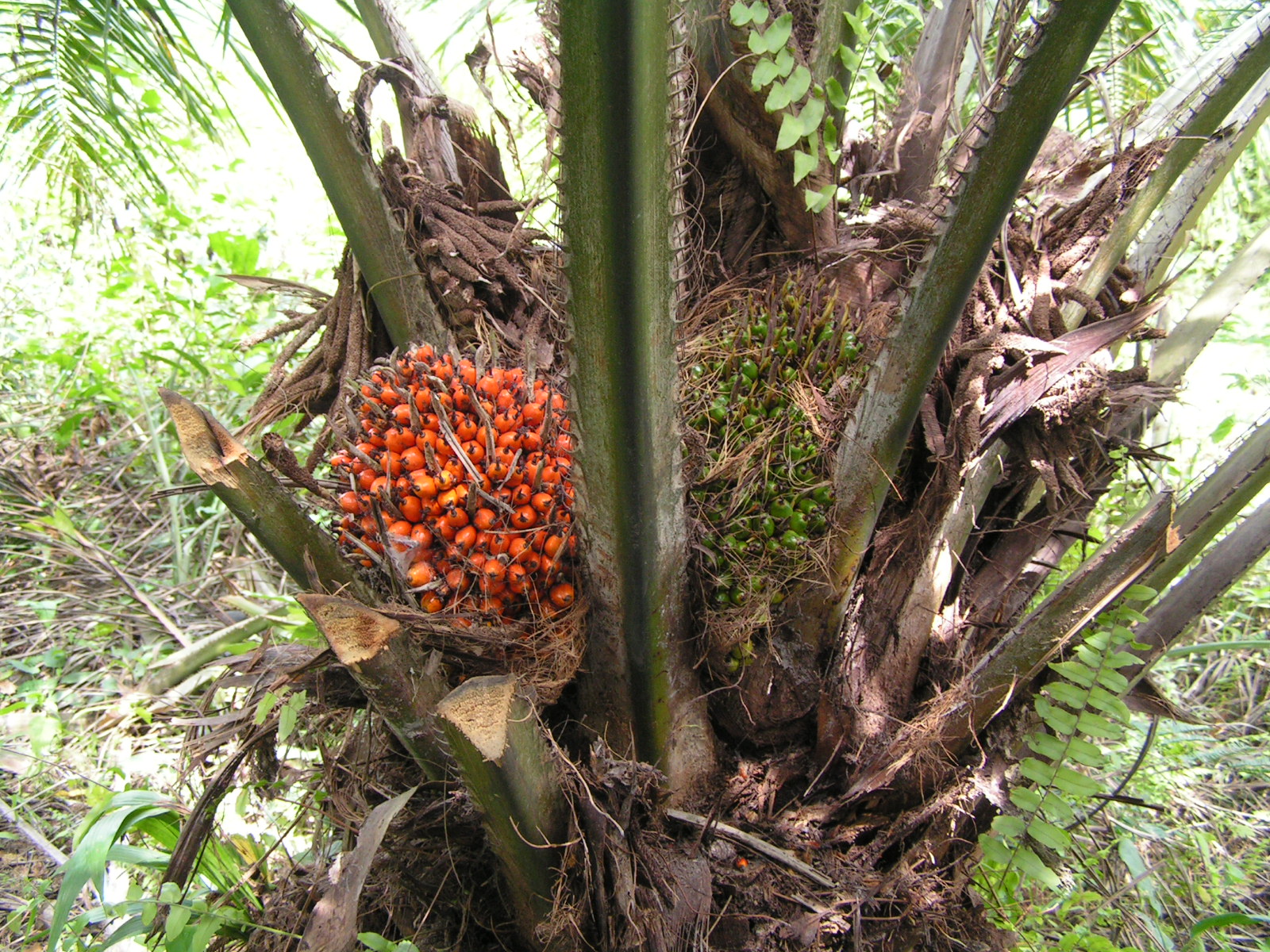
Elaeis Guineensis
''Elaeis guineensis'' is a species of palm commonly just called oil palm but also sometimes African oil palm or macaw-fat. It is the principal source of palm oil. It is native to west and southwest Africa, specifically the area between Angola and the Gambia; the species name, ''guineensis'', refers to the name for the area, Guinea, and not the modern country now bearing that name. The species is also now naturalised in Madagascar, Sri Lanka, Malaysia, Indonesia, Central America, Cambodia, the West Indies, and several islands in the Indian and Pacific Oceans. The closely related American oil palm ''Elaeis oleifera'' and a more distantly related palm, ''Attalea maripa'', are also used to produce palm oil. ''E. guineensis'' was domesticated in West Africa along the south-facing Atlantic coast. There is insufficient documentation and insufficient research to make any guesses as to when this occurred. Human use of oil palms may date as far back as 5,000 years in Egypt; in the late ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chardonnay
Chardonnay (, , ) is a green-skinned grape variety used in the production of white wine. The variety originated in the Burgundy wine region of eastern French wine, France, but is now grown wherever wine is produced, from English wine, England to New Zealand wine, New Zealand. For new and developing wine regions, growing Chardonnay is seen as a 'rite of passage' and an easy entry into the international wine market. The Chardonnay grape itself is neutral, with many of the flavors commonly associated with the wine being derived from such influences as ''terroir'' and oak (wine), oak.Robinson, 2006, pp. 154–56. It is vinified in many different styles, from the lean, crisply mineral wines of Chablis, France, to New World wines with oak and tropical fruit flavors. In cool climates (such as Chablis and the Carneros AVA of California (wine), California), Chardonnay wine tends to be medium to light body with noticeable acidity (wine), acidity and flavors of green plum, apple, and pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shirazi Wine
Shiraz wine refers to two different wines. Historically, the name refers to the wine produced around the city of Shiraz in present-day Iran.Entry on ''"Persia"'' in J. Robinson (ed), ''"The Oxford Companion to Wine"'', Third Edition, p. 512-513, Oxford University Press 2006, Hugh Johnson, ''"The Story of Wine"'', New Illustrated Edition, p. 58 & p. 131, Mitchell Beazley 2004, In the current era, "Shiraz" is an alternative name for the Syrah grape, mostly used in Australia and South Africa. The modern "Shiraz" grape is identical to Syrah and originated in southeast France with no established connection to the city of Shiraz. History By the ninth century, the city of Shiraz had established a reputation for producing the finest wine in the world, and was Iran's wine capital. The export of Shiraz wine by European merchants in the 17th century has been documented. As described by enthusiastic English and French travellers to the region in the 17th to 19th centuries, the wine grown cl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saccharomyces Uvarum
''Saccharomyces uvarum'' is a species of yeast that is commonly found in fermented beverages, particularly those fermented at colder temperatures. It was originally described by Martinus Willem Beijerinck in 1898, but was long considered identical to '' S. bayanus''. In 2000 and 2005, genetic investigations of various ''Saccharomyces'' species indicated that ''S. uvarum'' is genetically distinct from ''S. bayanus'' and should be considered a unique species. It is a bottom-fermenting yeast, so-called because it does not form the foam on top of the wort that top-fermenting yeast Yeasts are eukaryotic, single-celled microorganisms classified as members of the fungus kingdom. The first yeast originated hundreds of millions of years ago, and at least 1,500 species are currently recognized. They are estimated to constitut ... does. References uvarum Yeasts Yeasts used in brewing {{yeast-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aspergillus Niger
''Aspergillus niger'' is a mold classified within the ''Nigri'' section of the ''Aspergillus'' genus. The ''Aspergillus'' genus consists of common molds found throughout the environment within soil and water, on vegetation, in fecal matter, on decomposing matter, and suspended in the air. Species within this genus often grow quickly and can sporulate within a few days of germination. A combination of characteristics unique to ''A. niger'' makes the microbe invaluable to the production of many acids, proteins and bioactive compounds. Characteristics including extensive metabolic diversity, high production yield, secretion capability, and the ability to conduct post-translational modifications are responsible for ''A. niger's'' robust production of secondary metabolites. ''A. niger's'' capability to withstand extremely acidic conditions makes it especially important to the industrial production of citric acid. ''A. niger'' causes a disease known as "black mold" on certain fruits an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fusarium
''Fusarium'' is a large genus of filamentous fungi, part of a group often referred to as hyphomycetes, widely distributed in soil and associated with plants. Most species are harmless saprobes, and are relatively abundant members of the soil microbial community. Some species produce mycotoxins in cereal crops that can affect human and animal health if they enter the food chain. The main toxins produced by these ''Fusarium'' species are fumonisins and trichothecenes. Despite most species apparently being harmless (some existing on the skin as commensal members of the skin flora), some ''Fusarium'' species and subspecific groups are among the most important fungal pathogens of plants and animals. The name of ''Fusarium'' comes from Latin ''fusus'', meaning a spindle. Taxonomy The taxonomy of the genus is complex. A number of different schemes have been used, and up to 1,000 species have been identified at times, with approaches varying between wide and narrow concepts of speci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aspergillus Oryzae
''Aspergillus oryzae'', also known as , is a filamentous fungus (a mold) used in East Asia to saccharify rice, sweet potato, and barley in the making of alcoholic beverages such as ''sake'' and '' shōchū'', and also to ferment soybeans for making soy sauce and ''miso''. However, in the production of fermented foods of soybeans such as soy sauce and ''miso'', '' Aspergillus sojae'' is sometimes used instead of ''A. oryzae''. Incidentally, in China and Korea, the fungi used for fermented foods for a long time in the production of traditional alcoholic beverages were not ''A. oryzae'' but fungi belonging to ''Rhizopus'' and ''Mucor''. '' A. oryzae'' is also used for the production of rice vinegars. Barley ''kōji'' (麦麹) or rice ''kōji'' (米麹) are made by fermenting the grains with ''A. oryzae'' hyphae. Genomic analysis has led some scholars to believe that the Japanese domesticated the ''Aspergillus flavus'' that had mutated and ceased to produce toxic aflatoxins, givi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Penicillium Expansum
''Penicillium expansum'' is a psychrophilic blue mold that is common throughout the world in soil. It causes Blue Mold of apples, one of the most prevalent and economically damaging post-harvest diseases of apples. Though primarily known as a disease of apples, this plant pathogen can infect a wide range of hosts, including pears, strawberries, tomatoes, corn, and rice. ''Penicillium expansum'' produces the carcinogenic metabolite patulin, a neurotoxin that is harmful when consumed. Patulin is produced by the fungus as a virulence factor as it infects the host. Patulin levels in foods are regulated by the governments of many developed countries. Patulin is a particular health concern for young children, who are often heavy consumers of apple products. The fungus can also produce the mycotoxin citrinin. Hosts and disease development ''Penicillium expansum'' has a wide host range, causing similar symptoms on fruits which include apples, pears, cherries, and citrus . Initial infecti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Penicillium Italicum
''Penicillium italicum'' is a plant pathogen. It is a common post harvest disease commonly associated with citrus fruits. Management Inoculation of healthy fruit can be diminished and controlled by careful picking, handling, and packaging of the citrus so that the rinds are not damaged. Without chance of injury inflicted on the fruit, the conidia are unable to gain access, and thus unable to germinate into infectious pathogens. References External links USDA ARS Fungal Database Fungi described in 1894 Fungal citrus diseases italicum {{fungus-fruit-disease-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Penicillium Roqueforti
''Penicillium roqueforti'' is a common saprotrophic fungus in the genus ''Penicillium''. Widespread in nature, it can be isolated from soil, decaying organic matter, and plants. The major industrial use of this fungus is the production of blue cheeses, flavouring agents, antifungals, polysaccharides, proteases, and other enzymes. The fungus has been a constituent of Roquefort, Stilton, Danish blue, Cabrales, Gorgonzola, and other blue cheeses. Other blue cheeses are made with ''Penicillium glaucum''. Classification First described by American mycologist Charles Thom in 1906, ''P. roqueforti'' was initially a heterogeneous species of blue-green, sporulating fungi. They were grouped into different species based on phenotypic differences, but later combined into one species by Kenneth B. Raper and Thom (1949). The ''P. roqueforti'' group got a reclassification in 1996 due to molecular analysis of ribosomal DNA sequences. Formerly divided into two varieties―cheese-maki ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |