|
Metrosideros Vitiensis
''Metrosideros vitiensis'' is a species of flowering plant in the family Myrtaceae. It is a shrub or tree native to Vanuatu, Fiji, and the Samoan Islands. Taxonomy ''Metrosideros vitiensis'' was formerly included within ''Metrosideros collina, M. collina''. A phylogenetic study, published in 2015 by Pillon ''et al.'', found that ''M. collina'' comprised two genetically distinct groups. The populations in Vanuatu, Fiji, and the Samoan Islands were recognized as a distinct species, ''M. vitiensis'', while the populations in the Cook Islands, French Polynesia, and Pitcairn Islands remained in ''M. collina''.Pillon, Y., Lucas, E., Johansen, J. B., Sakishima, T., Hall, B., Geib, S. M., & Stacy, E. A. (2015). An Expanded Metrosideros (Myrtaceae) to Include Carpolepis and Tepualia Based on Nuclear Genes. ''Systematic Botany'', 40(3), 782–790. http://www.jstor.org/stable/24546499 Habitat On the larger Fijian islands, ''Metrosideros vitiensis'' is a characteristic tree in Fiji tropical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plants Of The World Online
Plants of the World Online (POWO) is an online database published by the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew. It was launched in March 2017 with the ultimate aim being "to enable users to access information on all the world's known seed-bearing plants by 2020". The initial focus was on tropical African Floras, particularly Flora Zambesiaca, Flora of West Tropical Africa and Flora of Tropical East Africa. The database uses the same taxonomical source as Kew's World Checklist of Selected Plant Families, which is the International Plant Names Index, and the World Checklist of Vascular Plants (WCVP). POWO contains 1,234,000 global plant names and 367,600 images. See also *Australian Plant Name Index *Convention on Biological Diversity *World Flora Online *Tropicos Tropicos is an online botanical database containing taxonomic information on plants, mainly from the Neotropical realm (Central, and South America). It is maintained by the Missouri Botanical Garden and was established over 25 y ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
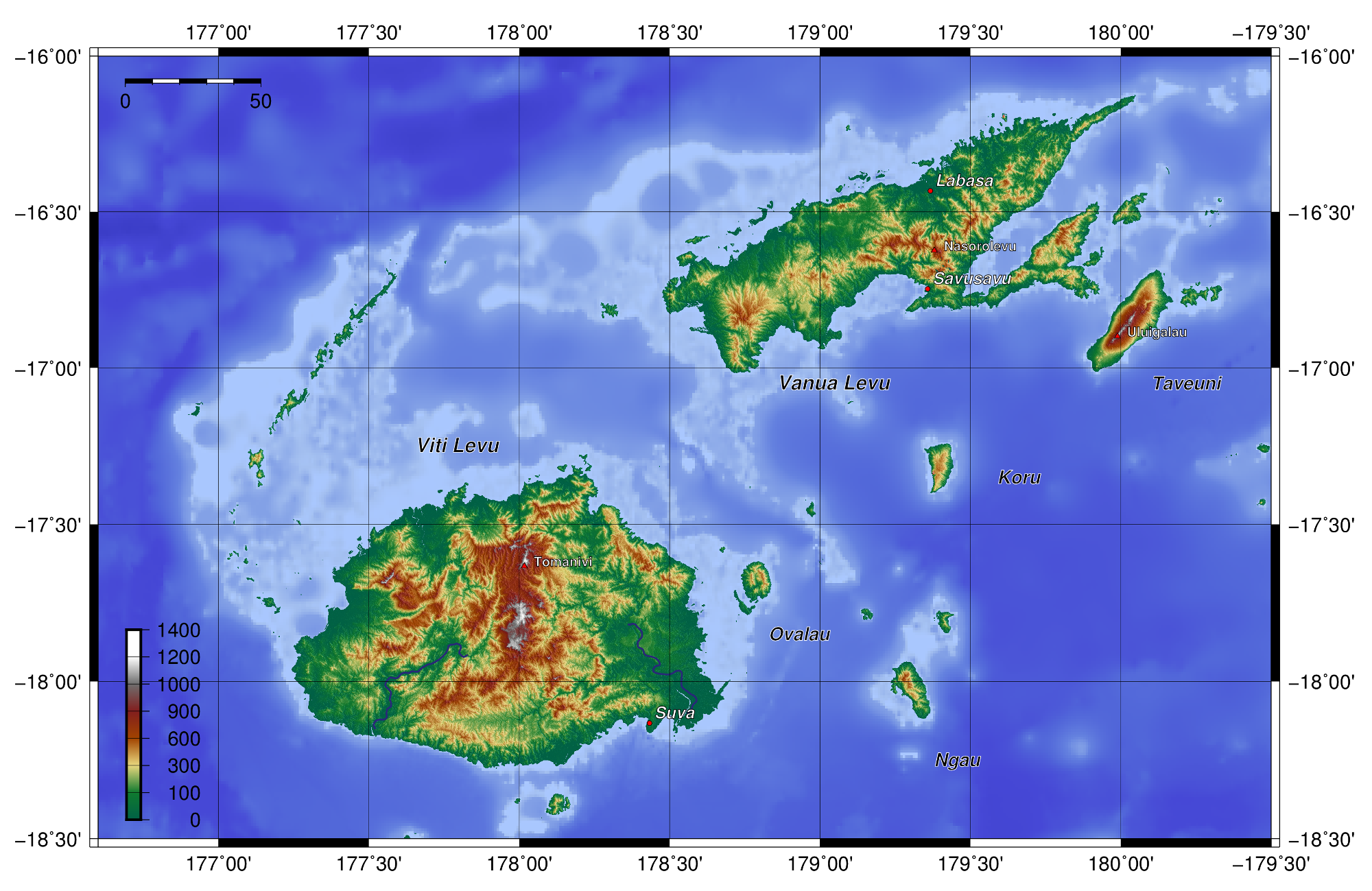
Fiji Tropical Moist Forests
The Fiji tropical moist forests is a tropical moist forest ecoregion in Fiji and Wallis and Futuna. It covers the windward sides of Viti Levu and Vanua Levu, Fiji's largest islands, as well as the smaller Fijian islands and the three islands that make up Wallis and Futuna, an overseas territory of France. Geography Fiji has more than 300 islands. Viti Levu and Vanua Levu are the largest, and together comprise 78% of Fiji's land area. The highest peak in Fiji is Mount Tomanivi (1,324 m) on Viti Levu. The islands are volcanic in origin, formed by the subduction of the Pacific Plate under the Australian Plate. The islands emerged from the sea 5 to 20 million years ago. Wallis and Futuna is made up of three islands, Uvea, Futuna, and Alofi. Futuna and Alofi lie close to one another, approximately 400 km northeast of Vanua Levu. Uvea, or Wallis, is northeast of Futuna and Alofi. The highest peak in the group is Mount Singavi (765 m) on Futuna. Rotuma is a volcanic island 500 km nort ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flora Of Fiji
Fiji is a group of volcanic islands in the South Pacific, lying about southwest of Honolulu and north of New Zealand. Of the 332 islands and 522 smaller islets making up the archipelago, about 106 are permanently inhabited. The total land size is . It has the 26th largest Exclusive Economic Zone of . Viti Levu, the largest island, covers about 57% of the nation's land area, hosts the two official cities (the capital Suva, and Lautoka) and most other major towns, such as Nausori, Vaileka, Ba, Tavua, Kororvou, Nasinu, and Nadi (the site of the international airport), and contains some 69% of the population. Vanua Levu, to the north of Viti Levu, covers just over 30% of the land area though is home to only some 15% of the population. Its main towns are Labasa and Savusavu. In the northeast it features Natewa Bay, carving out the Loa peninsula. Both islands are mountainous, with peaks up to rising abruptly from the shore, and covered with tropical forests. Heavy rains ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metrosideros
''Metrosideros'' is a genus of approximately 60 trees, shrubs, and vines mostly found in the Pacific region in the family Myrtaceae. Most of the tree forms are small, but some are exceptionally large, the New Zealand species in particular. The name derives from the Ancient Greek ''metra'' or "heartwood" and ''sideron'' or "iron". Perhaps the best-known species are the pōhutukawa (''M. excelsa''), northern (''M. robusta'') and southern rātā (''M. umbellata'') of New Zealand, and '' ōhia lehua'' (''M. polymorpha''), from the Hawaiian Islands. Distribution ''Metrosideros'' is one of the most widely spread flowering plant genera in the Pacific. New Caledonia has 21 species of ''Metrosideros'', New Zealand has 12, New Guinea has seven and Hawaii has 5. The genus is present on most other high Pacific Islands, including Solomon Islands, Vanuatu, Fiji, Samoa, Cook islands, French Polynesia, Bonin Islands and Lord Howe Island, but absent from Micronesia . The genus is also represen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dysoxylum
''Dysoxylum'' is a flowering plant genus of trees and shrubs from the mahogany family, Meliaceae. Botanical science has recorded about eighty species in this genus, growing widely across the regions of Malesia, the western Pacific ocean, Australia and south & southeastern Asia; centred on the tropics between the Pacific and Indian Oceans. They grow naturally in New Guinea, eastern and northern Australia, New Caledonia, Fiji, SE Asia, southern China, the Indian subcontinent, the Philippines, Taiwan, and in the western Pacific Ocean their most easterly occurrences, in the Caroline Islands, New Zealand and Niue. The etymology of its name ''Dysoxylum'' derives from the Greek word ‘''Dys''’ meaning "bad" referring to "ill-smelling" and ‘''Xylon''’ meaning "wood". Distribution New Guinea has records of twenty eight species growing naturally, sixteen of them endemic. New Caledonia has recorded nine, eight of them endemic. Fiji has recorded nine, seven of them endemic. In no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myristica Castaneifolia
''Myristica'' is a genus of trees in the family Myristicaceae. There are over 150 species, distributed in Asia and the western Pacific. The type species of the genus, and the most economically important member, is ''Myristica fragrans'' (the nutmeg tree), from which mace is also derived. Etymology The name ' is from the Greek adjective , meaning ‘fragrant, for anointing’, referring to its early use. The adjective is from the noun (‘perfume, ointment, anointing oil’). Description All or nearly all species are dioecious. Knuth (1904) however cites a report of trees being male in their sex expression when young and female later. Perianth of one whorl of three largely united segments. Stamens two to thirty, partly or wholly united. The ovary is superior, consisting of a single uniovulate carpel.Secondary Pollen Presentation. page 7. Peter Yeo 1993 Species in this genus use secondary pollen presentation (pollen presentation in the flower which does not use an anther), t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calophyllum Vitiense
''Calophyllum'' is a genus of tropical flowering plants in the family Calophyllaceae. They are mainly distributed in Asia, with some species in Africa, the Americas, Australasia, and the Pacific Islands. History Members of the genus ''Calophyllum'' native to Malesia and Wallacea are of particular importance to traditional shipbuilding of the larger Austronesian outrigger ships and were carried with them in the Austronesian expansion as they migrated to Oceania and Madagascar. They were comparable in importance to how oaks were in European shipbuilding and timber industries. The most notable species is the mastwood (''Calophyllum inophyllum'') which grows readily in the sandy and rocky beaches of the island environments that the Austronesians colonized. Description ''Calophyllum'' are trees or shrubs. They produce a colorless, white, or yellow latex. The oppositely arranged leaves have leathery blades often borne on petioles. The leaves are distinctive, with narrow parallel vei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Podocarpus
''Podocarpus'' () is a genus of conifers, the most numerous and widely distributed of the podocarp family, the Podocarpaceae. The name comes from Greek πούς (poús, “foot”) + καρπός (karpós, “fruit”). ''Podocarpus'' species are evergreen shrubs or trees, usually from tall, known to reach at times. The cones have two to five fused cone scales, which form a fleshy, berry-like, brightly coloured receptacle at maturity. The fleshy cones attract birds, which then eat the cones and disperse the seeds in their droppings. About 97 to 107 species are placed in the genus depending on the circumscription of the species.Earle, Chris J.''Podocarpus''.The Gymnosperm Database. 2013. Species are cultivated as ornamental plants for parks and large gardens. The cultivar 'County Park Fire' has won the Royal Horticultural Society's Award of Garden Merit. Names and etymology Common names for various species include "yellowwood" and "pine", as in the plum pine (''Podocarpu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agathis Vitiensis
''Agathis macrophylla'' (also '' Agathis silbae'') known as Pacific kauri, is a coniferous tree native to the islands of the southwestern Pacific Ocean in tropical humid lowlands and lower montane regions, notably in Fiji, Vanuatu, the Santa Cruz Islands, and the Solomon Islands. The Pacific kauri is one of the largest and fastest growing species in its genus, and is important in forestry. Description It is a large evergreen tree, reaching 40 m in height and 3 m in diameter. It possesses the mottled, shedding bark that is characteristic of other kauri species. Young trees are narrow and conic in shape, but begin to grow a wider, deeper canopy after attaining a trunk diameter of 30–50 cm. In mature specimens, the trunk is generally straight or slightly tapered and clear for 15–20 m before branching into a spreading canopy up to 35 m in diameter. The root system is deep and strong, and the trees are highly wind resistant. The leaves are green and glossy, elliptical t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pitcairn Islands
The Pitcairn Islands (; Pitkern: '), officially the Pitcairn, Henderson, Ducie and Oeno Islands, is a group of four volcanic islands in the southern Pacific Ocean that form the sole British Overseas Territory in the Pacific Ocean. The four islands—Pitcairn, Henderson, Ducie and Oeno—are scattered across several hundred miles of ocean and have a combined land area of about . Henderson Island accounts for 86% of the land area, but only Pitcairn Island is inhabited. The islands nearest to the Pitcairn Islands are Mangareva (of French Polynesia) at 688 km to the west and Easter Island at 1,929 km to the east. The Pitcairn Islanders are a biracial ethnic group descended mostly from nine ''Bounty'' mutineers and a handful of Tahitian consorts—as is still apparent from the surnames of many of the islanders. The mutiny and its aftermath have been the subject of many books and films. As of January 2020, the territory had only 47 permanent inhabitants. History Polynesi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flowering Plant
Flowering plants are plants that bear flowers and fruits, and form the clade Angiospermae (), commonly called angiosperms. The term "angiosperm" is derived from the Greek words ('container, vessel') and ('seed'), and refers to those plants that produce their seeds enclosed within a fruit. They are by far the most diverse group of land plants with 64 orders, 416 families, approximately 13,000 known genera and 300,000 known species. Angiosperms were formerly called Magnoliophyta (). Like gymnosperms, angiosperms are seed-producing plants. They are distinguished from gymnosperms by characteristics including flowers, endosperm within their seeds, and the production of fruits that contain the seeds. The ancestors of flowering plants diverged from the common ancestor of all living gymnosperms before the end of the Carboniferous, over 300 million years ago. The closest fossil relatives of flowering plants are uncertain and contentious. The earliest angiosperm fossils ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |