|
Mesures Usuelles
Mesures usuelles (, ''customary measurements'') were a French system of measurement introduced by Napoleon I in 1812 to act as compromise between the metric system and traditional measurements. The system was restricted to use in the retail industry and continued in use until 1840, when the laws of measurement from the 1795 and 1799 were reinstituted. Rationale behind the new system In the five years immediately before the French First Republic introduced the metric system, every effort was made to make the citizens aware of the upcoming changes and to prepare them for it. The administration distributed tens of thousands of educational pamphlets, private enterprise produced educational games, guides, almanacs and conversion aids, and metre standards were built into the walls of prominent buildings around Paris. The introduction was phased by district over the next few years, with Paris being the first district to change. The government also realised that the people would need metr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Units Of Measurement In France
200px, Table of the measuring units used in the 17th century at Pernes-les-Fontaines in the covered market at Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur Regions of France">region of southeastern France France has a unique history of Unit of measurement, units of measurement due to its radical decision to invent and adopt the metric system after the French Revolution. In the Ancien régime and until 1795, France used a system of measures that had many of the characteristics of the modern Imperial System of units but with no unified system. There was widespread abuse of the king's standards, to the extent that the ''lieue'' could vary from 3.268 km in Beauce to 5.849 km in Provence. During the revolutionary era and motivated in part by the inhomegeneity of the old system, France switched to the first version of the metric system. This system was not well received by the public, and between 1812 and 1837, the country used the ''mesures usuelles'' – traditional names were restored, bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
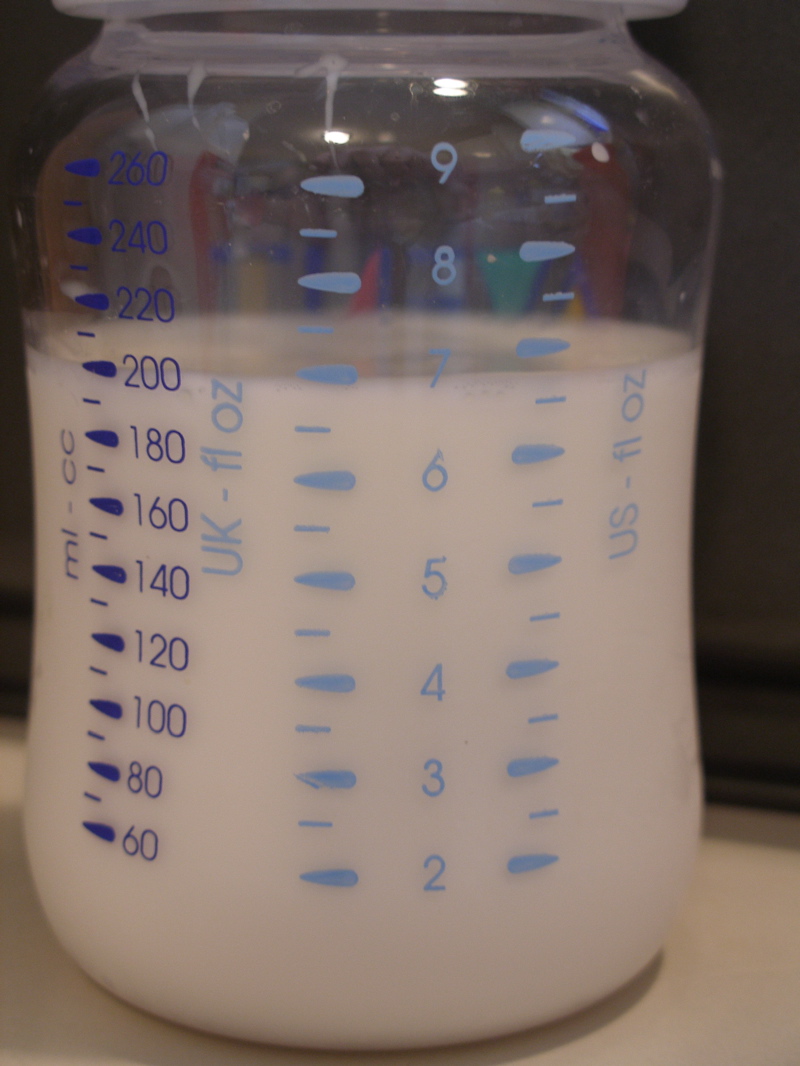
Pint
The pint (, ; symbol pt, sometimes abbreviated as ''p'') is a unit of volume or capacity in both the imperial unit, imperial and United States customary units, United States customary measurement systems. In both of those systems it is traditionally one eighth of a gallon. The British imperial pint is about 20% larger than the American pint because Comparison of the imperial and US customary measurement systems, the two systems are defined differently. Almost all other countries have standardized on the metric system, so although some of them still also have traditional units called pints (such as for beverages), the volume varies by regional custom. The imperial pint (≈) is used in the United Kingdom and Ireland and to a limited extent in Commonwealth of Nations, Commonwealth nations. In the United States, two kinds of pint are used: a liquid pint (≈) and a less-common dry pint (≈). Other Dominion , former British colonies, such as Canada, Australia, South Africa and New Z ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Systems Of Units
A system of measurement is a collection of units of measurement and rules relating them to each other. Systems of measurement have historically been important, regulated and defined for the purposes of science and commerce. Systems of measurement in use include the International System of Units or (the modern form of the metric system), the British imperial system, and the United States customary system. History The French Revolution gave rise to the metric system, and this has spread around the world, replacing most customary units of measure. In most systems, length (distance), mass, and time are ''base quantities''. Later science developments showed that an electromagnetic quantity such as electric charge or electric current could be added to extend the set of base quantities. Gaussian units have only length, mass, and time as base quantities, with no separate electromagnetic dimension. Other quantities, such as power and speed, are derived from the base set: for example, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Units Of Measurement
A unit of measurement is a definite magnitude (mathematics), magnitude of a quantity, defined and adopted by convention or by law, that is used as a standard for measurement of the same kind of quantity. Any other quantity of that kind can be expressed as a multiple of the unit of measurement. For example, a length is a physical quantity. The metre (symbol m) is a unit of length that represents a definite predetermined length. For instance, when referencing "10 metres" (or 10 m), what is actually meant is 10 times the definite predetermined length called "metre". The definition, agreement, and practical use of units of measurement have played a crucial role in human endeavour from early ages up to the present. A multitude of System of measurement, systems of units used to be very common. Now there is a global standard, the International System of Units (SI), the modern form of the metric system. In trade, weights and measures is often a subject of governmental r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Systems Of Measurement
A system of measurement is a collection of units of measurement and rules relating them to each other. Systems of measurement have historically been important, regulated and defined for the purposes of science and commerce. Systems of measurement in use include the International System of Units or (the modern form of the metric system), the British imperial system, and the United States customary system. History The French Revolution gave rise to the metric system, and this has spread around the world, replacing most customary units of measure. In most systems, length (distance), mass, and time are ''base quantities''. Later science developments showed that an electromagnetic quantity such as electric charge or electric current could be added to extend the set of base quantities. Gaussian units have only length, mass, and time as base quantities, with no separate electromagnetic dimension. Other quantities, such as power and speed, are derived from the base set: for example, spe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metric System
The metric system is a system of measurement that succeeded the Decimal, decimalised system based on the metre that had been introduced in French Revolution, France in the 1790s. The historical development of these systems culminated in the definition of the International System of Units (SI) in the mid-20th century, under the oversight of an international standards body. Adopting the metric system is known as ''metrication''. The historical evolution of metric systems has resulted in the recognition of several principles. Each of the fundamental dimensions of nature is expressed by a single base unit (measurement), base unit of measure. The definition of base units has increasingly been realisation (metrology), realised from natural principles, rather than by copies of physical artefacts. For quantities derived from the fundamental base units of the system, units SI derived unit, derived from the base units are used—e.g., the square metre is the derived unit for area, a qu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Unusual Units Of Measurement
An unusual unit of measurement is a unit of measurement that does not form part of a coherent system of measurement, especially because its exact quantity may not be well known or because it may be an inconvenient multiple or fraction of a base unit. This definition is not exact since it includes units such as the ''week'' or the '' light-year'', which are quite "usual" in the sense that they are often used, but can be "unusual" if taken out of their common context, as demonstrated by the furlong-firkin-fortnight (FFF) system of units. Many of the unusual units of measurements listed here are colloquial measurements, units devised to compare a measurement to common and familiar objects. Length Hammer unit Valve's Source game engine uses the ''Hammer unit'' as its base unit of length. This unit refers to Source's official map creation software, Hammer. The exact definition varies from game to game, but a Hammer unit is usually defined as a sixteenth of a foot (16 Ham ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International System Of Units
The International System of Units, known by the international abbreviation SI in all languages and sometimes pleonastically as the SI system, is the modern form of the metric system and the world's most widely used system of measurement. Established and maintained by the General Conference on Weights and Measures (CGPM), it is the only system of measurement with an official status in nearly every country in the world, employed in science, technology, industry, and everyday commerce. The SI comprises a coherent system of units of measurement starting with seven base units, which are the second (symbol s, the unit of time), metre (m, length), kilogram (kg, mass), ampere (A, electric current), kelvin (K, thermodynamic temperature), mole (mol, amount of substance), and candela (cd, luminous intensity). The system can accommodate coherent units for an unlimited number of additional quantities. These are called coherent derived units, which can always be represented as p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of The Metric System
The history of the metric system began during the Age of Enlightenment with measures of length and weight derived from nature, along with their decimal multiples and fractions. The system became the standard of France and Europe within half a century. Other measures with unity ratiosratios of 1 between magnitudes of unit quantities were added, and the system went on to be adopted across the world. The first practical realisation of the metric system came in 1799, during the French Revolution, after the existing system of measures had become impractical for trade, and was replaced by a decimal system based on the kilogram and the metre. The basic units were taken from the natural world. The unit of length, the metre, was based on the dimensions of the Earth, and the unit of mass, the kilogram, was based on the mass of a volume of water of one litre (a cubic decimetre). Reference copies for both units were manufactured in platinum and remained the standards of measure for the nex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Measurement
The earliest recorded systems of weights and measures originate in the 3rd or 4th millennium BC. Even the very earliest civilizations needed measurement for purposes of agriculture, construction and trade. Early standard units might only have applied to a single community or small region, with every area developing its own standards for lengths, areas, volumes and masses. Often such systems were closely tied to one field of use, so that volume measures used, for example, for dry grains were unrelated to those for liquids, with neither bearing any particular relationship to units of length used for measuring cloth or land. With development of manufacturing technologies, and the growing importance of trade between communities and ultimately across the Earth, standardized weights and measures became critical. Starting in the 18th century, modernized, simplified and uniform systems of weights and measures were developed, with the fundamental units defined by ever more precise methods ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Units Of Measurement
200px, Table of the measuring units used in the 17th century at Pernes-les-Fontaines in the covered market at Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur Regions of France">region of southeastern France France has a unique history of Unit of measurement, units of measurement due to its radical decision to invent and adopt the metric system after the French Revolution. In the Ancien régime and until 1795, France used a system of measures that had many of the characteristics of the modern Imperial System of units but with no unified system. There was widespread abuse of the king's standards, to the extent that the ''lieue'' could vary from 3.268 km in Beauce to 5.849 km in Provence. During the revolutionary era and motivated in part by the inhomegeneity of the old system, France switched to the first version of the metric system. This system was not well received by the public, and between 1812 and 1837, the country used the ''mesures usuelles'' – traditional names were restored, bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
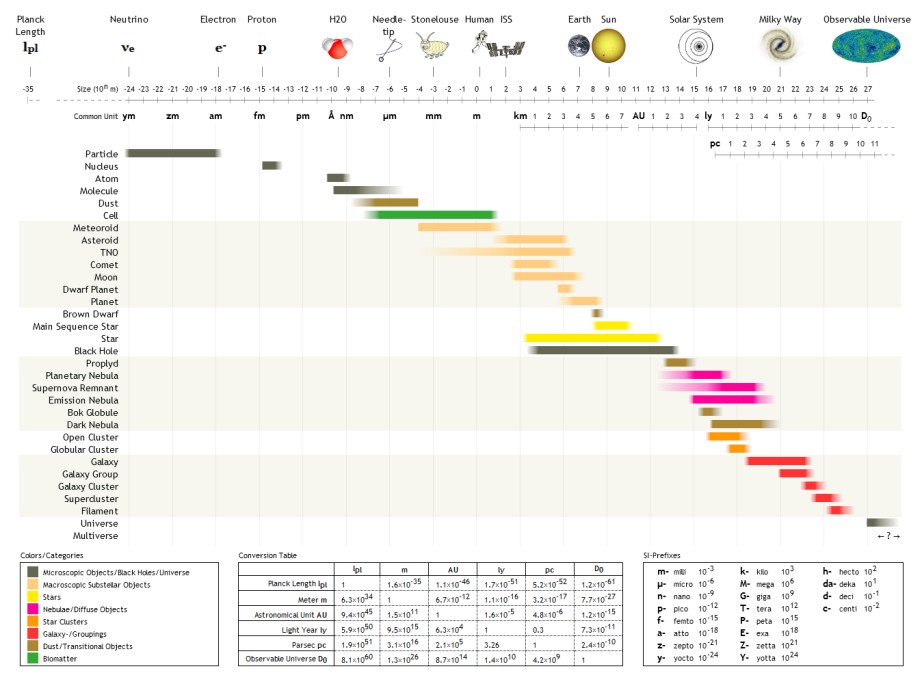
Myriamètre
The following are examples of order of magnitude, orders of magnitude for different lengths. __TOC__ Overview Detailed list To help compare different orders of magnitude, the following list describes various lengths between 1.6 \times 10^ metres and 10^metres. Subatomic scale Atomic to cellular scale Cellular to human scale Human to astronomical scale Astronomical scale Less than 1 zeptometre The ' (SI symbol: ') is a Units of measurement, unit of length in the metric system equal to . To help compare different orders of magnitude, this section lists lengths shorter than 10−21 metre, m (1 zm). *1.6 × 10−5 quectometres (1.6 × 10−35 metres) – the Planck length (Measures of distance shorter than this do not make physical sense, according to current theories of physics.) *1 qm – 1 quectometre, the smallest named subdivision of the metre in the SI base unit of length, one nonillionth of a metre *1 rm – 1 rontometre, a subdivision of the metre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


_cans_in_the_UK.jpg)