|
Mesopelagic Zone
The mesopelagic zone (Greek μέσον, middle), also known as the middle pelagic or twilight zone, is the part of the pelagic zone that lies between the photic epipelagic and the aphotic bathypelagic zones. It is defined by light, and begins at the depth where only 1% of incident light reaches and ends where there is no light; the depths of this zone are between approximately 200 to 1,000 meters (~656 to 3,280 feet) below the ocean surface. The mesopelagic zone occupies about 60% of the planet's surface and about 20% of the ocean's volume, amounting to a large part of the total biosphere. It hosts a diverse biological community that includes bristlemouths, blobfish, bioluminescent jellyfish, giant squid, and a myriad of other unique organisms adapted to live in a low-light environment. It has long captivated the imagination of scientists, artists and writers; deep sea creatures are prominent in popular culture. Physical conditions The mesopelagic zone includes the reg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greek Language
Greek ( el, label=Modern Greek, Ελληνικά, Elliniká, ; grc, Ἑλληνική, Hellēnikḗ) is an independent branch of the Indo-European family of languages, native to Greece, Cyprus, southern Italy (Calabria and Salento), southern Albania, and other regions of the Balkans, the Black Sea coast, Asia Minor, and the Eastern Mediterranean. It has the longest documented history of any Indo-European language, spanning at least 3,400 years of written records. Its writing system is the Greek alphabet, which has been used for approximately 2,800 years; previously, Greek was recorded in writing systems such as Linear B and the Cypriot syllabary. The alphabet arose from the Phoenician script and was in turn the basis of the Latin, Cyrillic, Armenian, Coptic, Gothic, and many other writing systems. The Greek language holds a very important place in the history of the Western world. Beginning with the epics of Homer, ancient Greek literature includes many works of lasting impo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sound Fixing And Ranging Channel
The SOFAR channel (short for sound fixing and ranging channel), or deep sound channel (DSC), is a horizontal layer of water in the ocean at which depth the speed of sound is at its minimum. The SOFAR channel acts as a waveguide for sound, and low frequency underwater acoustics, sound waves within the channel may travel thousands of miles before dissipating. An example was reception of coded signals generated by the Navy chartered ocean surveillance vessel MV Cory Chouest, ''Cory Chouest'' off Heard Island, located in the southern Indian Ocean (between Africa, Australia and Antarctica), by hydrophones in portions of all five major ocean basins and as distant as the North Atlantic and North Pacific.Figure 1 of the referenc"The Heard Island Feasibility Test"(Munk) shows ray paths to receiving locations. Table 1 lists the sites with one being a Canadian research vessel with a towed array off Cape Cod. This phenomenon is an important factor in ocean surveillance. The deep sound channel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anammox
Anammox, an abbreviation for anaerobic ammonium oxidation, is a globally important microbial process of the nitrogen cycle that takes place in many natural environments. The bacteria mediating this process were identified in 1999, and were a great surprise for the scientific community. In the anammox reaction, nitrite and ammonium ions are converted directly into diatomic nitrogen and water. The bacteria that perform the anammox process are genera that belong to the bacterial phylum Planctomycetota. The anammox bacteria all possess one anammoxosome, a lipid bilayer membrane-bound compartment inside the cytoplasm in which the anammox process takes place. The anammoxosome membranes are rich in ladderane lipids; the presence of these lipids is so far unique in biology. "Anammox" is also the trademarked name for an anammox-based ammonium removal technology developedJetten Michael Silvester Maria, Van Loosdrecht Marinus Corneli; Technische Universiteit Delftpatent WO9807664/ref> by th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Denitrification
Denitrification is a microbially facilitated process where nitrate (NO3−) is reduced and ultimately produces molecular nitrogen (N2) through a series of intermediate gaseous nitrogen oxide products. Facultative anaerobic bacteria perform denitrification as a type of respiration that reduces oxidized forms of nitrogen in response to the oxidation of an electron donor such as organic matter. The preferred nitrogen electron acceptors in order of most to least thermodynamically favorable include nitrate (NO3−), nitrite (NO2−), nitric oxide (NO), nitrous oxide (N2O) finally resulting in the production of dinitrogen (N2) completing the nitrogen cycle. Denitrifying microbes require a very low oxygen concentration of less than 10%, as well as organic C for energy. Since denitrification can remove NO3−, reducing its leaching to groundwater, it can be strategically used to treat sewage or animal residues of high nitrogen content. Denitrification can leak N2O, which is an ozone ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxygen Minimum Zone
The oxygen minimum zone (OMZ), sometimes referred to as the shadow zone, is the zone in which oxygen saturation in seawater in the ocean is at its lowest. This zone occurs at depths of about , depending on local circumstances. OMZs are found worldwide, typically along the western coast of continents, in areas where an interplay of physical and biological processes concurrently lower the oxygen concentration (biological processes) and restrict the water from mixing with surrounding waters (physical processes), creating a "pool" of water where oxygen concentrations fall from the normal range of 4–6 mg/L to below 2 mg/L. Physical and biological processes Surface ocean waters generally have oxygen concentrations close to equilibrium with the Earth's atmosphere. In general, colder waters hold more oxygen than warmer waters. As water moves out of the mixed layer into the thermocline, it is exposed to a rain of organic matter from above. Aerobic bacteria feed on this organi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sediment Trap Sample 63micron Size Fraction
Sediment is a naturally occurring material that is broken down by processes of weathering and erosion, and is subsequently transported by the action of wind, water, or ice or by the force of gravity acting on the particles. For example, sand and silt can be carried in suspension in river water and on reaching the sea bed deposited by sedimentation; if buried, they may eventually become sandstone and siltstone (sedimentary rocks) through lithification. Sediments are most often transported by water (fluvial processes), but also wind (aeolian processes) and glaciers. Beach sands and river channel deposits are examples of fluvial transport and deposition, though sediment also often settles out of slow-moving or standing water in lakes and oceans. Desert sand dunes and loess are examples of aeolian transport and deposition. Glacial moraine deposits and till are ice-transported sediments. Classification Sediment can be classified based on its grain size, grain shape, and compo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diel Vertical Migration
Diel vertical migration (DVM), also known as diurnal vertical migration, is a pattern of movement used by some organisms, such as copepods, living in the ocean and in lakes. The word ''diel'' comes from the Latin ''dies'' day, and means a 24-hour period. The migration occurs when organisms move up to the uppermost layer of the sea at night and return to the bottom of the daylight zone of the oceans or to the dense, bottom layer of lakes during the day. It is important to the functioning of deep-sea food webs and the biologically driven sequestration of carbon. In terms of biomass, it is the largest synchronous migration in the world. It is not restricted to any one taxon as examples are known from crustaceans (copepods), molluscs (squid), and ray-finned fishes (trout). The phenomenon may be advantageous for a number of reasons, most typically to access food and avoid predators. It is triggered by various stimuli, the most prominent being response to changes in light i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photic Zone
The photic zone, euphotic zone, epipelagic zone, or sunlight zone is the uppermost layer of a body of water that receives sunlight, allowing phytoplankton to perform photosynthesis. It undergoes a series of physical, chemical, and biological processes that supply nutrients into the upper water column. The photic zone is home to the majority of aquatic life due to the activity (primary production) of the phytoplankton. Photosynthesis in photic zone In the photic zone, the photosynthesis rate exceeds the respiration rate. This is due to the abundant solar energy which is used as an energy source for photosynthesis by primary producers such as phytoplankton. These phytoplankton grow extremely quickly because of sunlight's heavy influence, enabling it to be produced at a fast rate. In fact, ninety five percent of photosynthesis in the ocean occurs in the photic zone. Therefore, if we go deeper, beyond the photic zone, such as into the compensation point, there is little to no phyto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Remineralisation
In biogeochemistry, remineralisation (or remineralization) refers to the breakdown or transformation of organic matter (those molecules derived from a biological source) into its simplest inorganic forms. These transformations form a crucial link within ecosystems as they are responsible for liberating the energy stored in organic molecules and recycling matter within the system to be reused as nutrients by other organisms. Remineralisation is normally viewed as it relates to the cycling of the major biologically important elements such as carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus. While crucial to all ecosystems, the process receives special consideration in aquatic settings, where it forms a significant link in the biogeochemical dynamics and cycling of aquatic ecosystems. Role in biogeochemistry The term "remineralization" is used in several contexts across different disciplines. The term is most commonly used in the medicinal and physiological fields, where it describes the develo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Euphotic Zone
The photic zone, euphotic zone, epipelagic zone, or sunlight zone is the uppermost layer of a body of water that receives sunlight, allowing phytoplankton to perform photosynthesis. It undergoes a series of physical, chemical, and biological processes that supply nutrients into the upper water column. The photic zone is home to the majority of aquatic life due to the activity (primary production) of the phytoplankton. Photosynthesis in photic zone In the photic zone, the photosynthesis rate exceeds the respiration rate. This is due to the abundant solar energy which is used as an energy source for photosynthesis by primary producers such as phytoplankton. These phytoplankton grow extremely quickly because of sunlight's heavy influence, enabling it to be produced at a fast rate. In fact, ninety five percent of photosynthesis in the ocean occurs in the photic zone. Therefore, if we go deeper, beyond the photic zone, such as into the compensation point, there is little to no phyto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
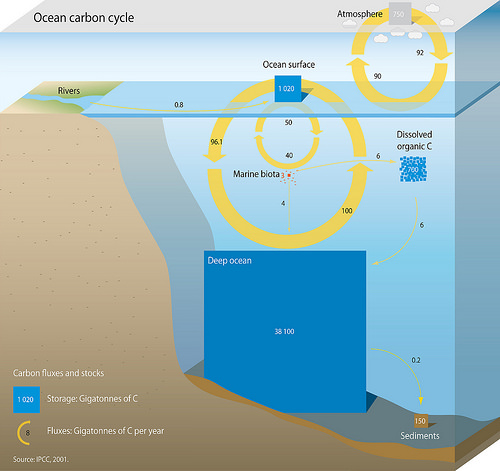
Oceanic Carbon Cycle
The oceanic carbon cycle (or marine carbon cycle) is composed of processes that exchange carbon between various pools within the ocean as well as between the atmosphere, Earth interior, and the seafloor. The carbon cycle is a result of many interacting forces across multiple time and space scales that circulates carbon around the planet, ensuring that carbon is available globally. The Oceanic carbon cycle is a central process to the global carbon cycle and contains both inorganic carbon (carbon not associated with a living thing, such as carbon dioxide) and organic carbon (carbon that is, or has been, incorporated into a living thing). Part of the marine carbon cycle transforms carbon between non-living and living matter. Three main processes (or pumps) that make up the marine carbon cycle bring atmospheric carbon dioxide (CO2) into the ocean interior and distribute it through the oceans. These three pumps are: (1) the solubility pump, (2) the carbonate pump, and (3) the biologi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
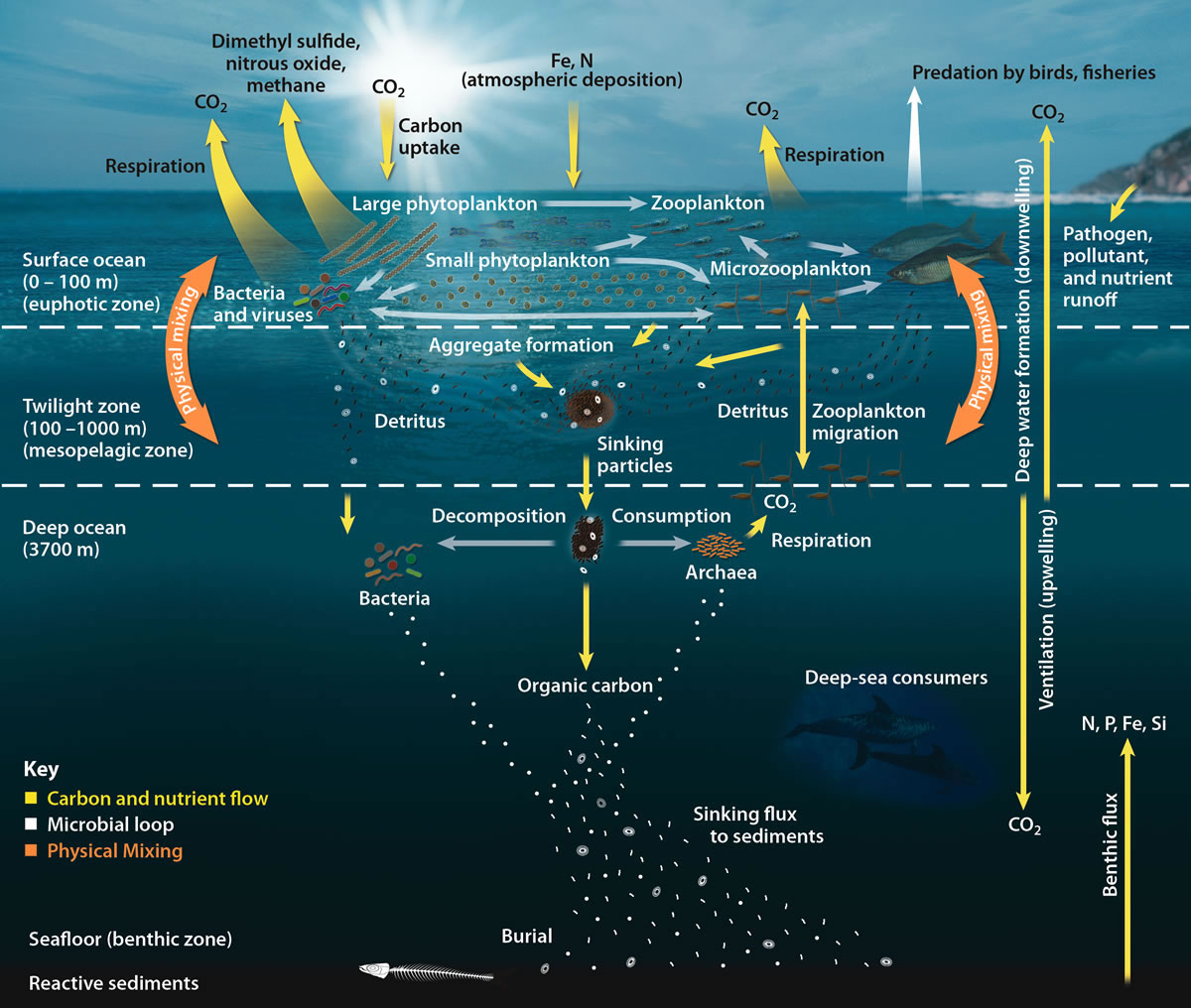
Biological Pump
The biological pump (or ocean carbon biological pump or marine biological carbon pump) is the ocean's biologically driven sequestration of carbon from the atmosphere and land runoff to the ocean interior and seafloor sediments.Sigman DM & GH Haug. 2006. The biological pump in the past. In: Treatise on Geochemistry; vol. 6, (ed.). Pergamon Press, pp. 491-528 In other words, it is a biologically mediated processes which result in the sequestering of carbon in the deep ocean away from the atmosphere and the land. The biological pump is the biological component of the "marine carbon pump" which contains both a physical and biological component. It is the part of the broader oceanic carbon cycle responsible for the cycling of organic matter formed mainly by phytoplankton during photosynthesis (soft-tissue pump), as well as the cycling of calcium carbonate (CaCO3) formed into shells by certain organisms such as plankton and mollusks (carbonate pump). Budget calculations of the biol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |