|
Meryey
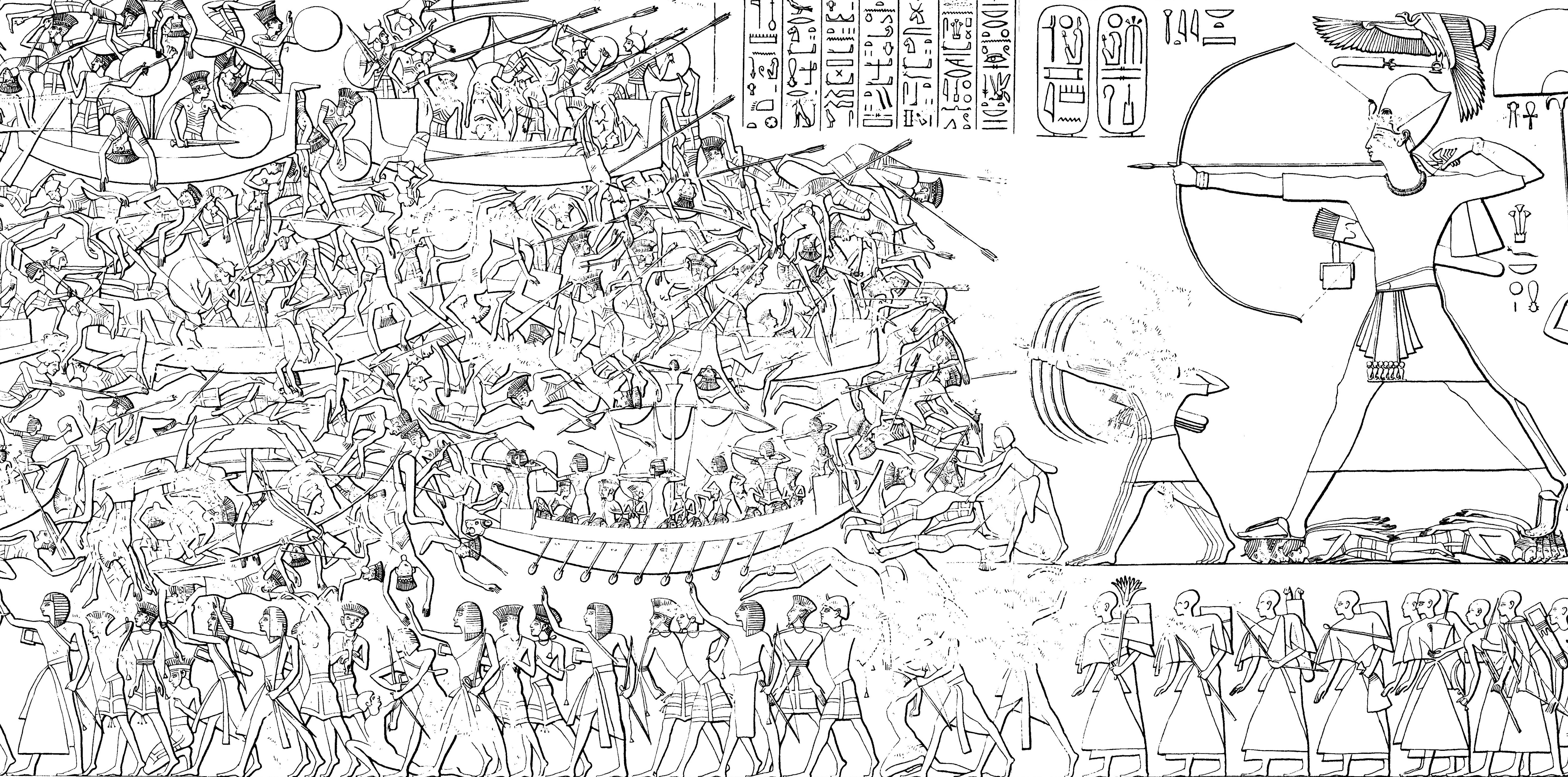
Meryey was a king of ancient Libya (or the ''Libu''), during the late 13th century BC. He was the son of Ded. His reign was contemporary with pharaoh Merneptah of Egypt (1213-1203 BC). He is mentioned as the architect of a major military alliance amongst his nation, the Meshwesh, Lukka, and the Sea Peoples known as the Ekwesh, Teresh, Shekelesh, and the Sherden. This confederacy went to war against Merneptah in the western delta during the 5th and 6th years of his reign. The "Great chief Meryey" had 6 sons, all of whom were slain at Perire. He led a confederacy or an army of 40,000 men to war against Merneptah and, though successful at the beginning, was eventually defeated at Prosopis. Literary sources The Great Karnak Inscription describes the scene when Merneptah receives news of the attack: "... the third season, saying: 'The wretched, fallen chief of Libya, Meryey, son of Ded, has fallen upon the country of Tehenu with his bowmen — Sherden, Shekelesh, Ekwesh, Lukka, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sea Peoples
The Sea Peoples are a hypothesized seafaring confederation that attacked ancient Egypt and other regions in the East Mediterranean prior to and during the Late Bronze Age collapse (1200–900 BCE).. Quote: "First coined in 1881 by the French Egyptologist G. Maspero (1896), the somewhat misleading term 'Sea Peoples' encompasses the ethnonyms Lukka, Sherden, Shekelesh, Teresh, Eqwesh, Denyen, Sikil / Tjekker, Weshesh, and Peleset (Philistines). [Footnote: The modern term 'Sea Peoples' refers to peoples that appear in several New Kingdom Egyptian texts as originating from 'islands' (tables 1–2; Adams and Cohen, this volume; see, e.g., Drews 1993, 57 for a summary). The use of quotation marks in association with the term 'Sea Peoples' in our title is intended to draw attention to the problematic nature of this commonly used term. It is noteworthy that the designation 'of the sea' appears only in relation to the Sherden, Shekelesh and Eqwesh. Subsequently, this term was applied ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shekelesh
The Shekelesh (Egyptian language: ''šꜣkrwšꜣꜣ'' or ''šꜣꜣkrwšꜣꜣ'') were one of the several ethnic groups the Sea Peoples were said to be composed of, appearing in fragmentary historical and iconographic records in ancient Egyptian from the Eastern Mediterranean in the late 2nd millennium BC. Earliest records The Shekelesh first appears in Egyptian records during accounts of the pharaoh Merneptah's military campaigns in modern Libya in the closing years of the 13th century BC, as recounted on the Great Karnak Inscription. In the text, the Shekelesh, alongside other clans of the Sea Peoples, are described as auxiliary troops of the Libyan ruler Meryey, and Merneptah recounts he killed between 200 and 222 of them. Nearly thirty years later, the Shekelesh are mentioned within the exploits of Ramesses III, where they, along with the Peleset, Tjeker, Denyen, and Weshesh, are described as forming a foothold in the Amurru kingdom during the 8th year of his reign. Ramesses, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Libu
The Libu ( egy, rbw; also transcribed Rebu, Lebu, Lbou, Libou) were an Ancient Libyan tribe of Berber origin, from which the name ''Libya'' derives. Early history Their occupation of Ancient Libya is first attested in Egyptian language texts from the New Kingdom, especially from the Ramesside Period. The earliest occurrence is in a Ramesses II inscription. There were no vowels in the Egyptian script. The name Libu is written as '' rbw'' in Egyptian hieroglyphs. In the Great Karnak Inscription Merneptah describes how hostilities between Egypt and Libya broke out in his regnal year 5 (1208 BCE) and how a coalition of Libu and Sea Peoples led by the chief of the Libu Meryey was defeated. ''Libu'' appears as an ethnic name on ''the Merneptah Stele'', also known as the ''Israel Stele''. Ramesses III defeated the Libyans in the 5th year of his reign, but six years later the Libyans joined the Meshwesh and invaded the western Delta and were defeated again. This name ''Libu'' was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Libya
The Latin name ''Libya'' (from Greek Λιβύη: ''Libyē'', which came from Berber: ''Libu'') referred to North Africa during the Iron Age and Classical Antiquity. Berbers occupied the area for thousands of years before the recording of history in ancient Egypt. Climate changes affected the locations of the settlements. More narrowly, ''Libya'' could also refer to the country immediately west of Egypt, viz Marmarica (''Libya Inferior'') and Cyrenaica (''Libya Superior''). The Libyan Sea or ''Mare Libycum'' was the part of the Mediterranean Sea south of Crete, between Cyrene and Alexandria. In the Hellenistic period, the Berbers were known collectively as ''Libyans'', a Greek term for the inhabitants of the Berber world. Their lands were called "Libya" and referred to the known African continent at that time, excluding Sub-Saharan Africa which was known as Aethiopia. Egypt contains the Siwa Oasis, which was part of ancient Libya. The Siwi language, a Berber language, is stil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Peoples
Ancient history is a time period from the beginning of writing and recorded human history to as far as late antiquity. The span of recorded history is roughly 5,000 years, beginning with the Sumerian cuneiform script. Ancient history covers all continents inhabited by humans in the period 3000 BCAD 500. The three-age system periodizes ancient history into the Stone Age, the Bronze Age, and the Iron Age, with recorded history generally considered to begin with the Bronze Age. The start and end of the three ages varies between world regions. In many regions the Bronze Age is generally considered to begin a few centuries prior to 3000 BC, while the end of the Iron Age varies from the early first millennium BC in some regions to the late first millennium AD in others. During the time period of ancient history, the world population was already exponentially increasing due to the Neolithic Revolution, which was in full progress. While in 10,000 BC, the world population stood ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Libyan Rulers
Ancient history is a time period from the beginning of writing and recorded human history to as far as late antiquity. The span of recorded history is roughly 5,000 years, beginning with the Sumerian cuneiform script. Ancient history covers all continents inhabited by humans in the period 3000 BCAD 500. The three-age system periodizes ancient history into the Stone Age, the Bronze Age, and the Iron Age, with recorded history generally considered to begin with the Bronze Age. The start and end of the three ages varies between world regions. In many regions the Bronze Age is generally considered to begin a few centuries prior to 3000 BC, while the end of the Iron Age varies from the early first millennium BC in some regions to the late first millennium AD in others. During the time period of ancient history, the world population was already exponentially increasing due to the Neolithic Revolution, which was in full progress. While in 10,000 BC, the world population stood at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amun
Amun (; also ''Amon'', ''Ammon'', ''Amen''; egy, jmn, reconstructed as (Old Egyptian and early Middle Egyptian) → (later Middle Egyptian) → (Late Egyptian), cop, Ⲁⲙⲟⲩⲛ, Amoun) romanized: ʾmn) was a major ancient Egyptian deity who appears as a member of the Hermopolitan Ogdoad. Amun was attested from the Old Kingdom together with his wife Amunet. With the 11th Dynasty ( 21st century BC), Amun rose to the position of patron deity of Thebes by replacing Montu. After the rebellion of Thebes against the Hyksos and with the rule of Ahmose I (16th century BC), Amun acquired national importance, expressed in his fusion with the Sun god, Ra, as Amun-Ra (alternatively spelled Amon-Ra or Amun-Re). Amun-Ra retained chief importance in the Egyptian pantheon throughout the New Kingdom (with the exception of the " Atenist heresy" under Akhenaten). Amun-Ra in this period (16th to 11th centuries BC) held the position of transcendental, self-created creator dei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ptah
Ptah ( egy, ptḥ, reconstructed ; grc, Φθά; cop, ⲡⲧⲁϩ; Phoenician: 𐤐𐤕𐤇, romanized: ptḥ) is an ancient Egyptian deity, a creator god and patron deity of craftsmen and architects. In the triad of Memphis, he is the husband of Sekhmet and the father of Nefertem. He was also regarded as the father of the sage Imhotep. Origin and symbolism Ptah is an Egyptian creator god who conceived the world and brought it into being through the creative power of speech. A hymn to Ptah dating to the Twenty-second Dynasty of Egypt says Ptah "crafted the world in the design of his heart," and the Shabaka Stone, from the Twenty-Fifth Dynasty, says Ptah "gave life to all the gods and their '' ka''s as well, through this heart and this tongue." He bears many epithets that describe his role in ancient Egyptian religion and its importance in society at the time: * ''Ptah the begetter of the first beginning'' * ''Ptah lord of truth'' * ''Ptah lord of eternity'' * ''Ptah ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tehenou
The Latin name ''Libya'' (from Greek Λιβύη: ''Libyē'', which came from Berber: ''Libu'') referred to North Africa during the Iron Age and Classical Antiquity. Berbers occupied the area for thousands of years before the recording of history in ancient Egypt. Climate changes affected the locations of the settlements. More narrowly, ''Libya'' could also refer to the country immediately west of Egypt, viz Marmarica (''Libya Inferior'') and Cyrenaica (''Libya Superior''). The Libyan Sea or ''Mare Libycum'' was the part of the Mediterranean Sea south of Crete, between Cyrene and Alexandria. In the Hellenistic period, the Berbers were known collectively as ''Libyans'', a Greek term for the inhabitants of the Berber world. Their lands were called "Libya" and referred to the known African continent at that time, excluding Sub-Saharan Africa which was known as Aethiopia. Egypt contains the Siwa Oasis, which was part of ancient Libya. The Siwi language, a Berber language, is still ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Karnak Inscription
The Great Karnak Inscription is an ancient Egyptian hieroglyphic inscription belonging to the 19th Dynasty Pharaoh Merneptah. A long epigraph, it was discovered at Karnak in 1828–1829. According to Wilhelm Max Müller, it is "one of the famous standard texts of Egyptology... nd has been... one of the greatest desiderata of scholars for many years."Muller, p.25 The Great Karnak Inscription is located on the west (inside) of the east wall of the Cachette Court, in the Precinct of Amun-Re of the Karnak temple complex, in modern Luxor. It runs from the fourth pylon of the great sanctuary to the eighth pylon. It was first identified by Champollion, and later partly published by Karl Richard Lepsius. It includes a record of the campaigns of this king against the Sea Peoples The Sea Peoples are a hypothesized seafaring confederation that attacked ancient Egypt and other regions in the East Mediterranean prior to and during the Late Bronze Age collapse (1200–900 BCE).. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tyrrhenians
Tyrrhenians (Attic Greek: ''Turrhēnoi'') or Tyrsenians (Ionic Greek, Ionic: ''Tursēnoi''; Doric Greek, Doric: ''Tursānoi'') was the name used by the Ancient Greece, ancient Greeks authors to refer, in a generic sense, to pre-Greek, non-Greek people. While ancient sources have been interpreted in a variety of ways, one theory identifies the Tyrsenians with the Etruscan civilization, Etruscans, and therefore with the Raeti, Rhaetian and Lemnian cultures, whose languages have been grouped together as the Tyrsenian languages, based on strong similarities in their written languages. Earliest references The names are believed to be exonyms, only known to have been used by authors of Ancient Greek, though their origin is uncertain and apparently not Greek. They have been connected to wikt:τύρσις#Ancient_Greek, τύρσις (''túrsis''), also a "Mediterranean" loan into Greek, meaning "tower". Direct connections with ''wikt:tuscus#Latin, Tuscī'', the Latin exonym for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sherden
The Sherden (Egyptian: ''šrdn'', ''šꜣrdꜣnꜣ'' or ''šꜣrdynꜣ'', Ugaritic: ''šrdnn(m)'' and ''trtn(m)'', possibly Akkadian: ''še-er-ta-an-nu''; also glossed “Shardana” or “Sherdanu”) are one of the several ethnic groups the Sea Peoples were said to be composed of, appearing in fragmentary historical and iconographic records ( ancient Egyptian and Ugaritic) from the Eastern Mediterranean in the late 2nd millennium BC. On reliefs, they are shown carrying round shields and spears, dirks or swords, perhaps of Naue II type. In some cases, they are shown wearing corslets and kilts, but their key distinguishing feature is a horned helmet, which, in all cases but three, features a circular accouterment at the crest. At Medinet Habu the corslet appears similar to that worn by the Philistines. The Sherden sword, it has been suggested by archaeologists since James Henry Breasted, may have developed from an enlargement of European daggers and been associated with the expl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



_(2865505031).jpg)


