|
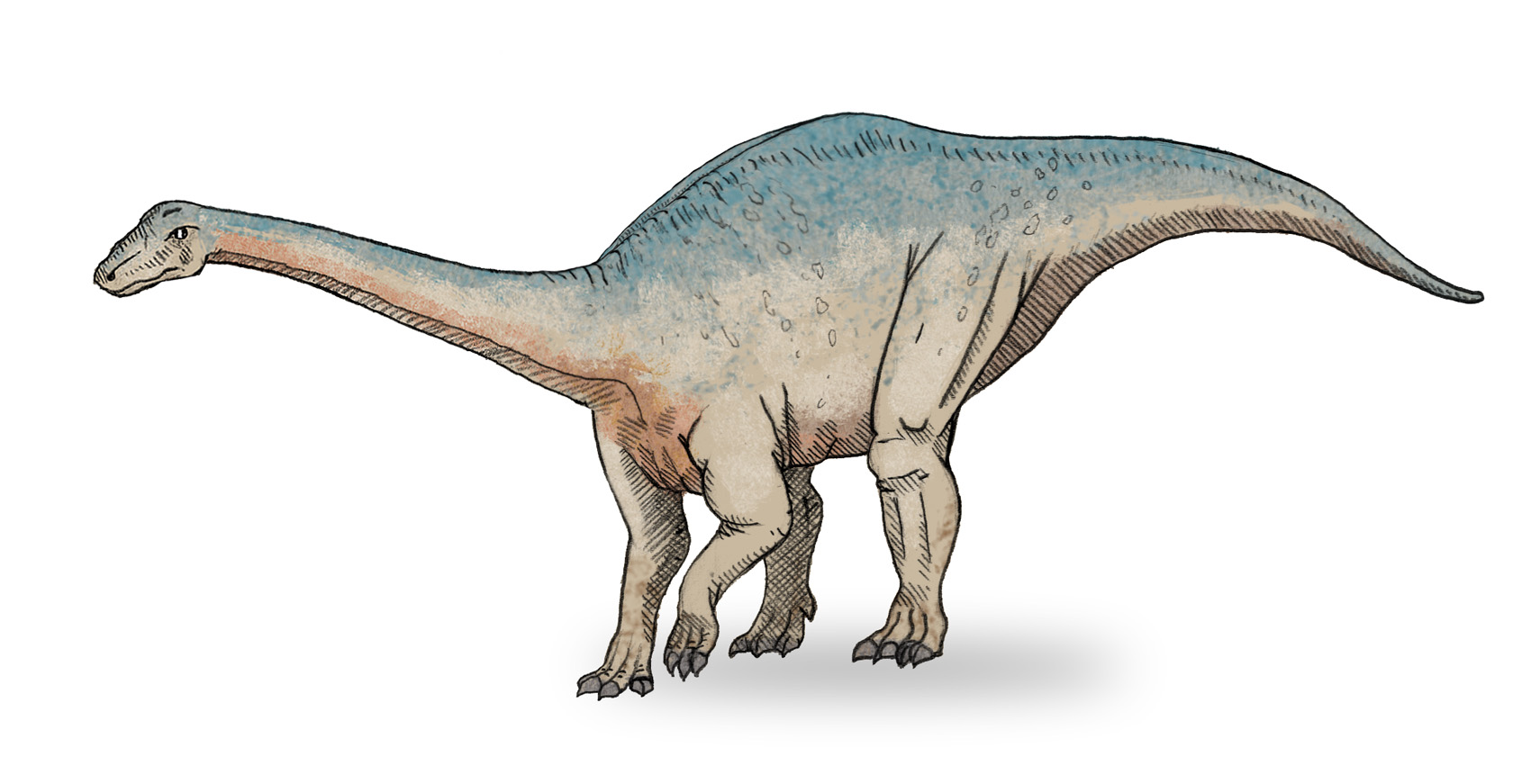
Meroktenos
''Meroktenos'' is a genus of basal sauropodomorph dinosaur that lived during the Late Triassic period of what is now Lesotho. Discovery and naming In 1959, François Ellenberger, Paul Ellenberger, Jean Fabre and Leonard Ginsburg discovered the type specimen, a thighbone or femur and other assorted bones, south of the village of Thabana Morena. In 1962 these were addressed in a thesis by D. Costedoat. The exact location the bones were recovered, is today unknown. In 1993, François-Xavier Gauffre assigned the remains to a second species of ''Melanorosaurus'': ''Melanorosaurus thabanensis''. The description was provisional, and in 1997 the fossil was described in more detail in a publication by Jacques van Heerden and Peter Malcolm Galton. The specific name refers to the site Thabana-Morena in Lesotho. Gauffre assumed that the specimen had been found in the Upper Elliot Formation dating from the Hettangian-Sinemurian and thus was about twenty million year younger than '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meroktenos Caudal Vertebra
''Meroktenos'' is a genus of basal sauropodomorph dinosaur that lived during the Late Triassic period of what is now Lesotho. Discovery and naming In 1959, François Ellenberger, Paul Ellenberger, Jean Fabre and Leonard Ginsburg discovered the type specimen, a thighbone or femur and other assorted bones, south of the village of Thabana Morena. In 1962 these were addressed in a thesis by D. Costedoat. The exact location the bones were recovered, is today unknown. In 1993, François-Xavier Gauffre assigned the remains to a second species of ''Melanorosaurus'': ''Melanorosaurus thabanensis''. The description was provisional, and in 1997 the fossil was described in more detail in a publication by Jacques van Heerden and Peter Malcolm Galton. The specific name refers to the site Thabana-Morena in Lesotho. Gauffre assumed that the specimen had been found in the Upper Elliot Formation dating from the Hettangian-Sinemurian and thus was about twenty million year younger than '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Melanorosaurus
''Melanorosaurus'' (meaning "Black Mountain Lizard", from the Greek ''melas/'', "black", ''oros/'', "mountain" + ''/'', "lizard") is a genus of basal sauropodomorph dinosaur that lived during the Late Triassic period. A herbivore from South Africa, it had a large body and sturdy limbs, suggesting it moved about on all fours. Its limb bones were massive and heavy like the limb bones of true sauropods. Description ''Melanorosaurus'' had a skull which measured approximately 250 mm. The snout was somewhat pointed, and the skull was somewhat triangular when seen from above or below. The premaxilla had four teeth on each side, a characteristic of primitive sauropodomorphs. The maxilla had 19 teeth on each side of the jaw. ''Melanorosaurus'' was around long, with a weight of . Discovery and species The type specimens, syntypes SAM 3449 and SAM 3450, were discovered, described and named in 1924 by Sidney H. Haughton. They were collected from the Triassic Lower ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Upper Elliot Formation
The Elliot Formation is a geological formation and forms part of the Stormberg Group, the uppermost geological group that comprises the greater Karoo Supergroup. Outcrops of the Elliot Formation have been found in the northern Eastern Cape, southern Free State, and in the eastern KwaZulu-Natal provinces of South Africa. Outcrops and exposures are also found in several localities in Lesotho such as Qacha's Neck, Hill Top, Quthing, and near the capital, Maseru. The Elliot Formation is further divided into the lower (LEF) and upper (UEF) Elliot formations to differentiate significant sedimentological differences between these layers. The LEF is dominantly Late Triassic (Norian-Hettangian) in age while the UEF is mainly Early Jurassic (Sinemurian-Pliensbachian) and is tentatively regarded to preserve a continental record of the Triassic-Jurassic boundary in southern Africa. This geological formation is named after the town of Elliot in the Eastern Cape, and its stratotype locality ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lower Elliot Formation
The Elliot Formation is a geological formation and forms part of the Stormberg Group, the uppermost geological group that comprises the greater Karoo Supergroup. Outcrops of the Elliot Formation have been found in the northern Eastern Cape, southern Free State, and in the eastern KwaZulu-Natal provinces of South Africa. Outcrops and exposures are also found in several localities in Lesotho such as Qacha's Neck, Hill Top, Quthing, and near the capital, Maseru. The Elliot Formation is further divided into the lower (LEF) and upper (UEF) Elliot formations to differentiate significant sedimentological differences between these layers. The LEF is dominantly Late Triassic ( Norian- Hettangian) in age while the UEF is mainly Early Jurassic (Sinemurian-Pliensbachian) and is tentatively regarded to preserve a continental record of the Triassic-Jurassic boundary in southern Africa. This geological formation is named after the town of Elliot in the Eastern Cape, and its stratotype loc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aardonyx
''Aardonyx'' (Afrikaans ''aard'', "earth" + Greek , "nail, claw") is a genus of basal sauropodomorph dinosaur. It is known from the type species ''Aardonyx celestae'' found from the Early Jurassic Elliot Formation of South Africa. ''A. celestae'' was named after Celeste Yates, who prepared much of the first known fossil material of the species. It has arm features that are intermediate between prosauropods and sauropods. Based on the structure of the hind limbs and pelvic girdle of ''Aardonyx'', the dinosaur normally moved bipedally but could drop to quadrupedal movement similar to ''Iguanodon''. It shares some attributes with giant quadrupedal sauropods like ''Apatosaurus''.Associated Press (November 11, 2009)Scientists: New dinosaur species found in South AfricaNPR. Australian paleontologist Adam Yates and his team's discovery of the genus was published online before print in ''Proceedings of the Royal Society B'' in November 2009, and was scheduled to appear in the March 20 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sauropodomorpha
Sauropodomorpha ( ; from Greek, meaning "lizard-footed forms") is an extinct clade of long-necked, herbivorous, saurischian dinosaurs that includes the sauropods and their ancestral relatives. Sauropods generally grew to very large sizes, had long necks and tails, were quadrupedal, and became the largest animals to ever walk the Earth. The '' prosauropods,'' which preceded the sauropods, were smaller and were often able to walk on two legs. The sauropodomorphs were the dominant terrestrial herbivores throughout much of the Mesozoic Era, from their origins in the Late Triassic (approximately 230 Ma) until their decline and extinction at the end of the Cretaceous. Description Sauropodomorphs were adapted to browsing higher than any other contemporary herbivore, giving them access to high tree foliage. This feeding strategy is supported by many of their defining characteristics, such as: a light, tiny skull on the end of a long neck (with ten or more elongated cervical vertebrae) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Forelimb Bones Of Meroktenos
A forelimb or front limb is one of the paired articulated appendages (limbs) attached on the cranial (anterior) end of a terrestrial tetrapod vertebrate's torso. With reference to quadrupeds, the term foreleg or front leg is often used instead. In bipedal animals with an upright posture (e.g. humans and some primates), the term upper limb is often used. A forelimb is not to be confused with a forearm, which is a distal portion of the human upper limb between the elbow and the wrist. All vertebrate forelimbs are homologous, meaning that they all evolved from the same structures. For example, the flipper of a turtle or of a dolphin, the arm of a human, the foreleg of a horse, and the wings of both bats and birds are ultimately homologous, despite the large differences between them. Specific uses of the forelimbs may be analogous if they evolved from different sub-structures of the forelimb, such as the flippers of turtles and dolphins, and the wings of birds and bats. Evolut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cladistic
Cladistics (; ) is an approach to biological classification in which organisms are categorized in groups (" clades") based on hypotheses of most recent common ancestry. The evidence for hypothesized relationships is typically shared derived characteristics ( synapomorphies'')'' that are not present in more distant groups and ancestors. However, from an empirical perspective, common ancestors are inferences based on a cladistic hypothesis of relationships of taxa whose character states can be observed. Theoretically, a last common ancestor and all its descendants constitute a (minimal) clade. Importantly, all descendants stay in their overarching ancestral clade. For example, if the terms ''worms'' or ''fishes'' were used within a ''strict'' cladistic framework, these terms would include humans. Many of these terms are normally used paraphyletically, outside of cladistics, e.g. as a 'grade', which are fruitless to precisely delineate, especially when including extinct species. R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neural Arch
The spinal column, a defining synapomorphy shared by nearly all vertebrates,Hagfish are believed to have secondarily lost their spinal column is a moderately flexible series of vertebrae (singular vertebra), each constituting a characteristic irregular bone whose complex structure is composed primarily of bone, and secondarily of hyaline cartilage. They show variation in the proportion contributed by these two tissue types; such variations correlate on one hand with the cerebral/caudal rank (i.e., location within the backbone), and on the other with phylogenetic differences among the vertebrate taxa. The basic configuration of a vertebra varies, but the bone is its ''body'', with the central part of the body constituting the ''centrum''. The upper (closer to) and lower (further from), respectively, the cranium and its central nervous system surfaces of the vertebra body support attachment to the intervertebral discs. The posterior part of a vertebra forms a vertebral arch (in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blikanasaurus
''Blikanasaurus'' is a genus of sauropodomorph dinosaur from the late Triassic of South Africa. The generic name ''Blikanasaurus'' is derived from Greek, meaning "lizard from Blikana". The species name ''cromptoni'' is taken from the surname of A.W. “Fuzz” Crompton, an American paleontologist who led numerous field expeditions in Elliot Formation outcrop localities in South Africa. ''Blikanasaurus'' is only known from partial hindlimb bones that were recovered from the lower Elliot Formation (LEF) in the Eastern Cape. History of discovery ''Blikanasaurus'' was first discovered by a partial hindlimb (epipodium and pes) found in the lower Elliot Formation (LEF) at the foot of Blikana mountain in Herschel, Eastern Cape of South Africa around 1965. In the early 2000s, a second specimen - consisting of only a right metatarsal - was recovered from lower Elliot Formation deposits on the farm, Damplaats, in Ladybrand of the eastern Free State. A possible ilium that has been attr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Type Species
In zoological nomenclature, a type species (''species typica'') is the species name with which the name of a genus or subgenus is considered to be permanently taxonomically associated, i.e., the species that contains the biological type specimen(s). Article 67.1 A similar concept is used for suprageneric groups and called a type genus. In botanical nomenclature, these terms have no formal standing under the code of nomenclature, but are sometimes borrowed from zoological nomenclature. In botany, the type of a genus name is a specimen (or, rarely, an illustration) which is also the type of a species name. The species name that has that type can also be referred to as the type of the genus name. Names of genus and family ranks, the various subdivisions of those ranks, and some higher-rank names based on genus names, have such types. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Combinatio Nova
''Combinatio nova'', abbreviated ''comb. nov.'' (sometimes ''n. comb.''), is Latin for "new combination". It is used in taxonomic biology literature when a new name is introduced based on a pre-existing name. The term should not to be confused with ', used for a previously unnamed species. There are three situations: * the taxon is moved to a different genus * an infraspecific taxon is moved to a different species * the rank of the taxon is changed. Examples When an earlier named species is assigned to a different genus, the new genus name is combined with of said species, e.g. when ''Calymmatobacterium granulomatis'' was renamed ''Klebsiella granulomatis'', it was referred to as ''Klebsiella granulomatis comb. nov.'' to denote it was a new combination. See also * Glossary of scientific naming * Basionym * List of Latin phrases * Nomenclature code Nomenclature codes or codes of nomenclature are the various rulebooks that govern biological taxonomic nomenclature, each in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |






_(2).jpg)