|
Mermithida
Mermithida is an order of nematode worms. The order includes two families, and most members are endoparasites on arthropods. One of the morphological characteristic of the order is the presence of a stichosome.Chitwood, B. G. & Chitwood, M. B. (1950). Introduction to Nematology (Vol. 1). Baltimore: Monumental Printing Co.Z. X. Chen, D. W. Dickson (eds.) (2004) Nematology: Nematode Management and Utilization. CABI Publishing. p. 847 References Enoplea Parasitic nematodes of animals Nematode orders {{Enoplea-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mermithidae
Mermithidae is a family of nematode worms that are endoparasites in arthropods. As early as 1877, Mermithidae was listed as one of nine subdivisions of the Nematoidea. Mermithidae are confused with the horsehair worms of the phylum Nematomorpha that have a similar life history and appearance. Mermithids are parasites, mainly of arthropods. Most are known from insects, but some are recorded from spiders, scorpions and crustaceans. A few are known to parasitize earthworms, leeches and molluscs, and a specimen is known from a spider preserved in Baltic amber. At least 25 species are known to parasitize mosquito larvae, making them of considerable interest in biological control. A species, probably '' Pheromermis vesparum'', was recorded from the invasive Asian hornet (''Vespa velutina'') in France. The parasite was considered to be a member of the local fauna which had adapted to a new host. However, the authors concluded that the mermithid could not hamper the hornet invasion nor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enoplea
Enoplea (enopleans) is a class, which with the classes SecernenteaTree of Life Web Project (ToL) (2002)Nematoda Version of January 1, 2002. Retrieved November 2, 2008. and Chromadorea make up the phylum Nematoda in current taxonomy. The Enoplea are considered to be a more ancestral group than the Chromadorea, and researchers have referred to its members as the "ancestrally diverged nematodes", compared to the "more recently diverged nematodes" of Chromadorea. Description The Enoplea are distinguished from the Chromadorea by a number of characteristics. The enoplean esophagus is cylindrical or "bottle-shaped", compared to the bulbous chromadorean esophagus. Enopleans have pocket-like amphids, while chromadoreans have amphids shaped like slits, pores, coils, or spirals. An enoplean is smooth or marked with fine lines, while a chromadorean may have rings, projections, or setae. The enoplean excretory system is simple, sometimes made up of a single cell, while chromadoreans have more ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
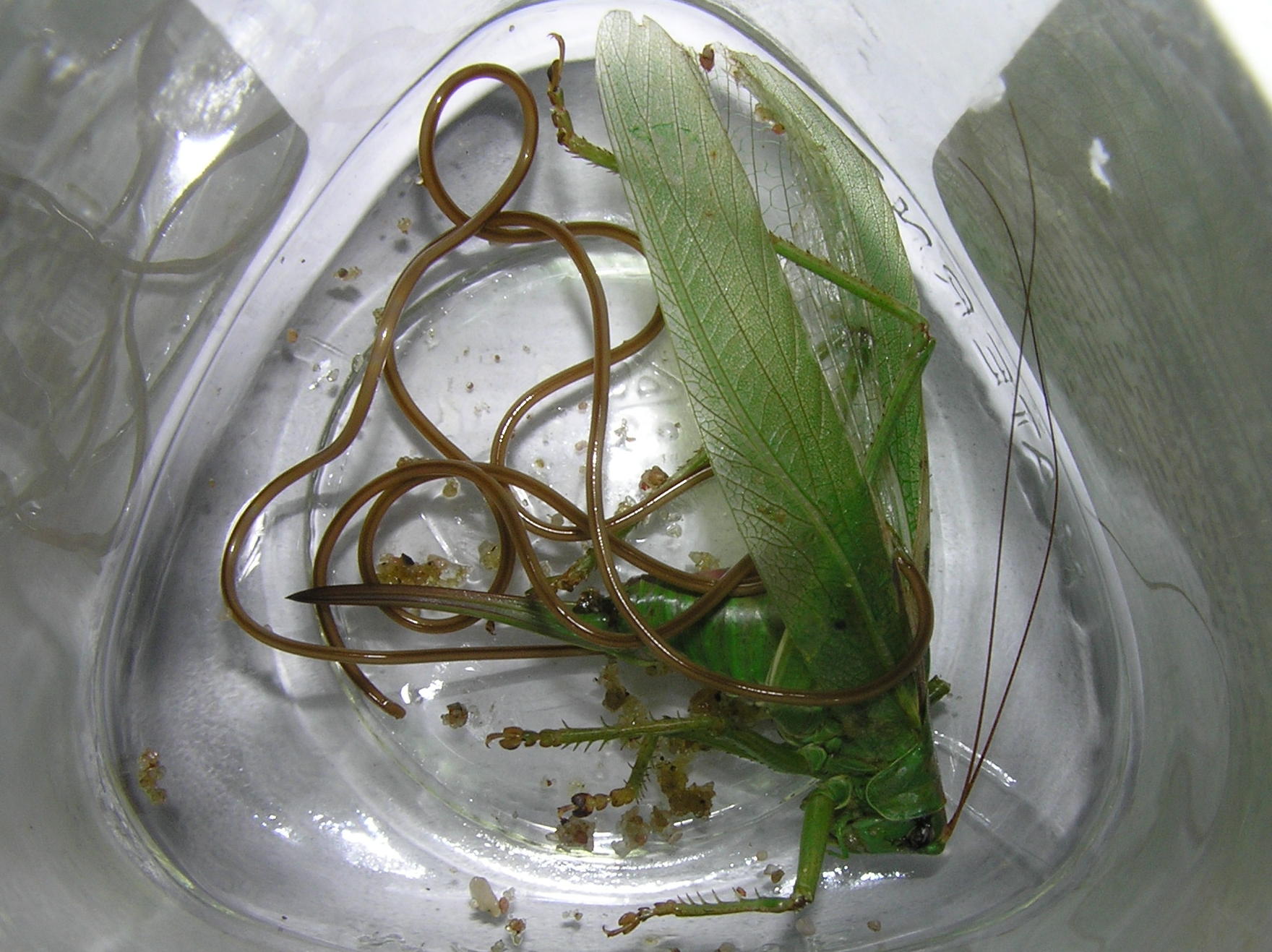
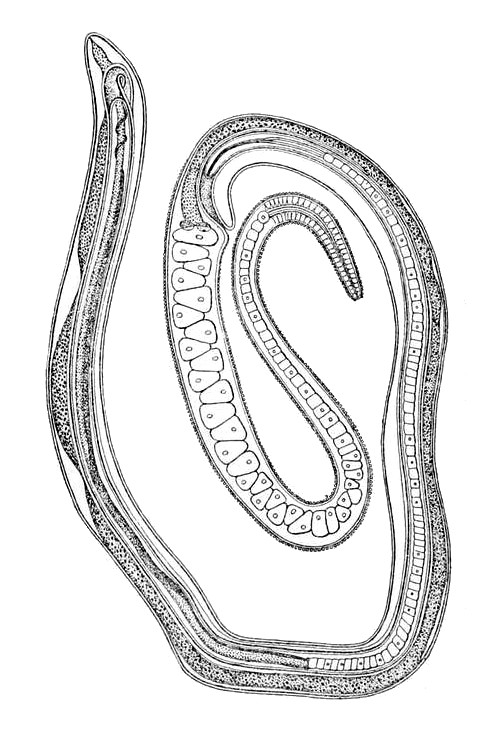
Mermis Nigrescens
''Mermis nigrescens'' is a species of nematode known commonly as the grasshopper nematode.Capinera, JGrasshopper nematode, ''Mermis nigrescens''.EENY-500. University of Florida, IFAS. 2011.Cranshaw, WColorado State University Extension. 2008. Revised 2013. It is distributed in the Americas, Europe, and Asia. It occurs in Tasmania, but it has not been observed on mainland Australia. It has been rarely observed in Africa. It is a parasite of insects, especially grasshoppers. Description This is a very large nematode, the male about 4 to 6 centimetres long and the female known to exceed 20 centimetres.''Mermis nigrescens''. Nematology. University of Nebraska, Lincoln. The size is unusual for entomopathogenic nematodes, which are generally almost microscopic. The body is pale brown, and the |
Tetradonematidae
Tetradonematidae is a family of nematodes, most being endoparasites of arthropods. A species discovered in 2008 was found to alter the morphology of its ant host, apparently so as to make the ant resemble fruits leading to their predation by birds. The ants forage on bird droppings and are infected by the nematodes. Some species infect the invasive ant ''Solenopsis invicta'' making them of interest in applied biological control Biological control or biocontrol is a method of controlling pests, such as insects, mites, weeds, and plant diseases, using other organisms. It relies on predation, parasitism, herbivory, or other natural mechanisms, but typically also invo .... References Enoplea Nematode families Parasites of arthropods {{Chromadorea-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nematode
The nematodes ( or grc-gre, Νηματώδη; la, Nematoda) or roundworms constitute the phylum Nematoda (also called Nemathelminthes), with plant-Parasitism, parasitic nematodes also known as eelworms. They are a diverse animal phylum inhabiting a broad range of environments. Less formally, they are categorized as Helminths, but are taxonomically classified along with Arthropod, arthropods, Tardigrade, tardigrades and other moulting animalia, animals in the clade Ecdysozoa, and unlike platyhelminthe, flatworms, have tubular digestion, digestive systems with openings at both ends. Like tardigrades, they have a reduced number of Hox genes, but their sister phylum Nematomorpha has kept the ancestral protostome Hox genotype, which shows that the reduction has occurred within the nematode phylum. Nematode species can be difficult to distinguish from one another. Consequently, estimates of the number of nematode species described to date vary by author and may change rapidly over ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tettigonia Viridissima
''Tettigonia viridissima'', the great green bush-cricket, is a large species of bush-cricket belonging to the subfamily Tettigoniinae. Distribution and habitat This species can be encountered in most of Europe, in the eastern Palearctic realm, in the Near East, and in North Africa, especially in meadows, grasslands, prairies and occasionally in gardens at an elevation up to above sea level. Description The adult males grow up to long, while females reach . This insect is most often completely green (but there are specimens completely yellowish or with yellow legs), excluding a rust-colored band on top of the body. The organ of the stridulation of the males is generally brown. ''Tettigonia viridissima'' is distinguished by its very long and thin antennae, which can sometimes reach up to three times the length of the body, thus differentiating them from grasshoppers, which always carry short antennae. It could be confused with '' Tettigonia cantans'', whose wings are a centi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Order (biology)
Order ( la, wikt:ordo#Latin, ordo) is one of the eight major hierarchical taxonomic ranks in Linnaean taxonomy. It is classified between Family_(biology), family and Class_(biology), class. In biological classification, the order is a taxonomic rank used in the classification of organisms and recognized by the nomenclature codes. An immediately higher rank, superorder, is sometimes added directly above order, with suborder directly beneath order. An order can also be defined as a group of related families. What does and does not belong to each order is determined by a taxonomist, as is whether a particular order should be recognized at all. Often there is no exact agreement, with different taxonomists each taking a different position. There are no hard rules that a taxonomist needs to follow in describing or recognizing an order. Some taxa are accepted almost universally, while others are recognized only rarely. The name of an order is usually written with a capital letter. Fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stichosome
Stichosome (from Greek ''stichos (στίχος)'' = row; ''soma (σῶµα)'' = body) is a multicellular organ that is very prominent in some stages of nematodes and consists of a longitudinal series of glandular unicellular cells ( stichocytes) arranged in a row along the oesophagus The esophagus (American English) or oesophagus (British English; both ), non-technically known also as the food pipe or gullet, is an organ in vertebrates through which food passes, aided by peristaltic contractions, from the pharynx to the ... that form the posterior esophageal glands. It opens into the esophageal lumen and apparently functions as a secretory gland and storage organ.Despommier DD, Müller M. The stichosome and its secretion granules in the mature muscle larva of ''Trichinella spiralis''. Journal of Parasitology, 1976 Oct;62(5):775-85. HG Sheffield. Electron microscopy of the bacillary band and stichosome of ''Trichuris muris'' and ''T. vulpis''. Journal of Parasitology, 1963 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parasitic Nematodes Of Animals
Parasitism is a close relationship between species, where one organism, the parasite, lives on or inside another organism, the host, causing it some harm, and is adapted structurally to this way of life. The entomologist E. O. Wilson has characterised parasites as "predators that eat prey in units of less than one". Parasites include single-celled protozoans such as the agents of malaria, sleeping sickness, and amoebic dysentery; animals such as hookworms, lice, mosquitoes, and vampire bats; fungi such as honey fungus and the agents of ringworm; and plants such as mistletoe, dodder, and the broomrapes. There are six major parasitic strategies of exploitation of animal hosts, namely parasitic castration, directly transmitted parasitism (by contact), trophicallytransmitted parasitism (by being eaten), vector-transmitted parasitism, parasitoidism, and micropredation. One major axis of classification concerns invasiveness: an endoparasite lives inside the host's body; an ect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |