|
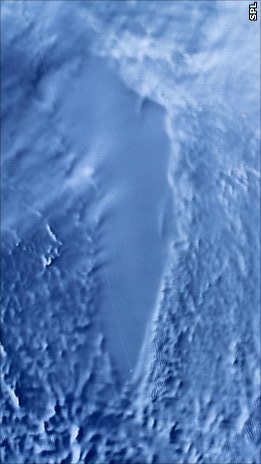
Mercer Lake (Antarctica)
Mercer Subglacial Lake is a subglacial lake in Antarctica covered by a sheet of ice thick; the water below is hydraulically active, with water replacement times on the order of a decade from the Ross Sea. Studies suggest that Mercer Subglacial Lake as well as other subglacial lakes appear to be linked, with drainage events in one reservoir causing filling and follow-on drainage in adjacent lakes. Exploration Helen Amanda Fricker from the Scripps Institution of Oceanography discovered Mercer Subglacial Lake in 2007, while using satellite laser altimetry to search for the grounding line of a glacier. The lake is named after |
Antarctica
Antarctica () is Earth's southernmost and least-populated continent. Situated almost entirely south of the Antarctic Circle and surrounded by the Southern Ocean, it contains the geographic South Pole. Antarctica is the fifth-largest continent, being about 40% larger than Europe, and has an area of . Most of Antarctica is covered by the Antarctic ice sheet, with an average thickness of . Antarctica is, on average, the coldest, driest, and windiest of the continents, and it has the highest average elevation. It is mainly a polar desert, with annual precipitation of over along the coast and far less inland. About 70% of the world's freshwater reserves are frozen in Antarctica, which, if melted, would raise global sea levels by almost . Antarctica holds the record for the lowest measured temperature on Earth, . The coastal regions can reach temperatures over in summer. Native species of animals include mites, nematodes, penguins, seals and tardigrades. Where vegetation o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbon Cycling
The carbon cycle is the biogeochemical cycle by which carbon is exchanged among the biosphere, pedosphere, geosphere, hydrosphere, and atmosphere of the Earth. Carbon is the main component of biological compounds as well as a major component of many minerals such as limestone. Along with the nitrogen cycle and the water cycle, the carbon cycle comprises a sequence of events that are key to make Earth capable of sustaining life. It describes the movement of carbon as it is recycled and reused throughout the biosphere, as well as long-term processes of carbon sequestration to and release from carbon sinks. Carbon sinks in the land and the ocean each currently take up about one-quarter of anthropogenic carbon emissions each year. Humans have disturbed the biological carbon cycle for many centuries by modifying land use, and moreover with the recent industrial-scale mining of fossil carbon (coal, petroleum and gas extraction, and cement manufacture) from the geosphere. Carbon di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Underground Lake
An underground lake or subterranean lake is a lake underneath the surface of the Earth. Most naturally occurring underground lakes are found in areas of Karst topography, where limestone or other soluble rock has been weathered away, leaving a cave where water can flow and accumulate. Natural underground lakes are an uncommon hydrogeological feature. More often, groundwater gathers in formations such as aquifers or springs. The largest subterranean lake in the world is in Dragon's Breath Cave in Namibia, with an area of almost ; the second largest is The Lost Sea, located inside Craighead Caverns in Tennessee, United States, with an area of Characteristics In general terms, an underground lake is any body of water that is similar in size to a surface lake and exists mostly or entirely underground; though, a precise scientific definition of what may be considered a lake is not yet well-established. Underground lakes could be classified as either “lakes” or "ponds", de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supraglacial Lake
A supraglacial lake is any pond of liquid water on the top of a glacier. Although these pools are ephemeral, they may reach kilometers in diameter and be several meters deep. They may last for months or even decades at a time, but can empty in the course of hours. Lifetime Lakes may be created by surface melting during summer months, or over the period of years by rainfall, such as monsoons. They may dissipate by overflowing their banks, or creating a moulin. Effects on ice masses Lakes of a diameter greater than ~300 m are capable of driving a fluid-filled crevasse to the glacier/bed interface, through the process of hydrofracture. A surface-to-bed connection made in this way is referred to as a moulin. When these crevasses form, it can take a mere 2–18 hours to empty a lake, supplying warm water to the base of the glacier - lubricating the bed and causing the glacier to surge. The rate of emptying such a lake is equivalent to the rate of flow of the Niagara Falls. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Antarctic Subglacial Lakes ...
An ongoing inventory of subglacial lakes in Antarctica. Compiled from: * Discoveries from the 1970's to 2012 via: Wright, A., and Siegert, M. (2012)A fourth inventory of Antarctic subglacial lakes Antarctic Science 24, 659-664 References {{portal, Lakes Antarctice subglacial lakes Antarctic subglacial lakes subglacial lakes A subglacial lake is a lake that is found under a glacier, typically beneath an ice cap or ice sheet. Subglacial lakes form at the boundary between ice and the underlying bedrock, where gravitational pressure decreases the pressure melting point o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lake Untersee
Lake Untersee (german: Untersee, "Lower Lake") is the largest surface freshwater lake in the interior of the Gruber Mountains of central Queen Maud Land in East Antarctica. It is situated to the southwest of the Schirmacher Oasis. The lake is approximately long and wide, with a surface area of , and a maximum depth of . The lake is permanently covered with ice and is partly bounded by glacier ice. Lake Untersee is an unusual lake, with pH between 9.8 and 12.1, dissolved oxygen at 150 percent supersaturation, and very low primary production in the water column. Despite the high oxygen supersaturation in most of the lake, there is a small sub-basin at the southern end that is anoxic and its sediments may have a higher methane concentration than those of any other known lake on Earth. Much of the primary production is in microbial communities that grow on the floor of the lake as stromatolites. The water temperature varies between and and the ice cover on the lake is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hodgson Lake
Hodgson Lake is a perennially ice-covered freshwater lake, which is about 2 km (1.2 mi) long by about 1.5 km (0.93 mi) wide. It is located within the southern part of Alexander Island, west of Palmer Land in Antarctica, at approximately 72°S latitude and 68°W longitude. This lake has a 93.4 m (306 ft) deep water column that lies sealed beneath a 3.6 to 4.0 m (12 to 13 ft) thick perennial lake ice. The lake is an ultra-oligotrophic lake with very low nutrient content and very low productivity. There is no detectable life living in Hodgson Lake. The lake extends eastward into George VI Sound and the George VI Ice Shelf making it adjacent to the sound. The northern side of this lake is bounded by the Saturn Glacier, which flows east into George VI Sound. The lake lies next to and southeast of Citadel Bastion, a pre-eminent mountain on Alexander Island.Stewart, J. (2011) ''Antarctic An Encyclopedia'' McFarland & Company Inc, New York. 1776 pp. . ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lake Ellsworth (Antarctica)
Lake Ellsworth is a natural freshwater liquid subglacial lake located in West Antarctica under approximately of ice. It is approximately 10 km long and is estimated to be in depth. The lake is named after the American explorer Lincoln Ellsworth. The surface of the lake itself is located over below sea level. Exploration Lake Ellsworth was discovered in 1996 by British scientist Professor Martin Siegert of the University of Bristol; it is one of 387 known subglacial Antarctic lakes and it is a target site for exploration due to the speculation that new forms of microbial life could have evolved in the unique habitats of Antarctica’s sub-glacial lakes after half a million years of isolation.Siegert, Martin J. and the Lake Ellsworth Consortium, "Exploration of Subglacial Lake Ellsworth", Poster, University of Bristol, September 2004 Life in subglacial lakes would have to adapt to total darkness, low nutrient levels, high water pressure, and isolation from the atmosphere ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lake Vostok
Lake Vostok (russian: озеро Восток, ''ozero Vostok'') is the largest of Antarctica's almost 400 known subglacial lakes. Lake Vostok is located at the southern Pole of Cold, beneath Russia's Vostok Station under the surface of the central East Antarctic Ice Sheet, which is at above mean sea level. The surface of this fresh water lake is approximately under the surface of the ice, which places it at approximately below sea level. Measuring long by wide at its widest point, it covers an area of making it the 16th largest lake by surface area. With an average depth of , it has an estimated volume of , making it the 6th largest lake by volume. The lake is divided into two deep basins by a ridge. The liquid water depth over the ridge is about , compared to roughly deep in the northern basin and deep in the southern. The lake is named after Vostok Station, which in turn is named after the ''Vostok'' (Восток), a sloop-of-war, which means "East" in Russian. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glacial Lake
A glacial lake is a body of water with origins from glacier activity. They are formed when a glacier erodes the land and then melts, filling the depression created by the glacier. Formation Near the end of the last glacial period, roughly 10,000 years ago, glaciers began to retreat. A retreating glacier often left behind large deposits of ice in hollows between drumlins or hills. As the ice age ended, these melted to create lakes. This is apparent in the Lake District in Northwestern England where post-glacial sediments are normally between 4 and 6 metres deep. These lakes are often surrounded by drumlins, along with other evidence of the glacier such as moraines, eskers and erosional features such as striations and chatter marks. These lakes are clearly visible in aerial photos of landforms in regions that were glaciated during the last ice age. The formation and characteristics of glacial lakes vary between location and can be classified into glacial erosion lake, ice-bloc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biodiversity
Biodiversity or biological diversity is the variety and variability of life on Earth. Biodiversity is a measure of variation at the genetic (''genetic variability''), species (''species diversity''), and ecosystem (''ecosystem diversity'') level. Biodiversity is not distributed evenly on Earth; it is usually greater in the tropics as a result of the warm climate and high primary productivity in the region near the equator. Tropical forest ecosystems cover less than 10% of earth's surface and contain about 90% of the world's species. Marine biodiversity is usually higher along coasts in the Western Pacific, where sea surface temperature is highest, and in the mid-latitudinal band in all oceans. There are latitudinal gradients in species diversity. Biodiversity generally tends to cluster in hotspots, and has been increasing through time, but will be likely to slow in the future as a primary result of deforestation. It encompasses the evolutionary, ecological, and cultural ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subglacial Lake
A subglacial lake is a lake that is found under a glacier, typically beneath an ice cap or ice sheet. Subglacial lakes form at the boundary between ice and the underlying bedrock, where gravitational pressure decreases the pressure melting point of ice. Over time, the overlying ice gradually melts at a rate of a few millimeters per year. Meltwater flows from regions of high to low hydraulic pressure under the ice and pools, creating a body of liquid water that can be isolated from the external environment for millions of years. Since the first discoveries of subglacial lakes under the Antarctic Ice Sheet, more than 400 subglacial lakes have been discovered in Antarctica, beneath the Greenland Ice Sheet, and under Iceland's Vatnajökull ice cap. Subglacial lakes contain a substantial proportion of Earth's liquid freshwater, with the volume of Antarctic subglacial lakes alone estimated to be about 10,000 km3, or about 15% of all liquid freshwater on Earth. As ecosystems is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |