|
Mentzer Index
The Mentzer index, described in 1973 by William C. Mentzer, is the MCV divided by the RBC count. It is said to be helpful in differentiating iron deficiency anemia from beta thalassemia. The index is calculated from the results of a complete blood count. If the quotient of the mean corpuscular volume (MCV, in fL) divided by the red blood cell Red blood cells (RBCs), also referred to as red cells, red blood corpuscles (in humans or other animals not having nucleus in red blood cells), haematids, erythroid cells or erythrocytes (from Greek ''erythros'' for "red" and ''kytos'' for "holl ... count (RBC, in Millions per microLiter) is less than 13, thalassemia is said to be more likely. If the result is greater than 13, then iron-deficiency anemia is said to be more likely. The principle involved is as follows: In iron deficiency, the marrow cannot produce as many RBCs and they are small (microcytic), so the RBC count and the MCV will both be low, and as a result, the index will b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iron Deficiency Anemia
Iron-deficiency anemia is anemia caused by a lack of iron. Anemia is defined as a decrease in the number of red blood cells or the amount of hemoglobin in the blood. When onset is slow, symptoms are often vague such as feeling tired, weak, short of breath, or having decreased ability to exercise. Anemia that comes on quickly often has more severe symptoms, including confusion, feeling like one is going to pass out or increased thirst. Anemia is typically significant before a person becomes noticeably pale. Children with iron deficiency anemia may have problems with growth and development. There may be additional symptoms depending on the underlying cause. Iron-deficiency anemia is caused by blood loss, insufficient dietary intake, or poor absorption of iron from food. Sources of blood loss can include heavy periods, childbirth, uterine fibroids, stomach ulcers, colon cancer, and urinary tract bleeding. Poor absorption of iron from food may occur as a result of an intestina ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beta Thalassemia
Beta thalassemias (β thalassemias) are a group of inherited blood disorders. They are forms of thalassemia caused by reduced or absent synthesis of the beta chains of hemoglobin that result in variable outcomes ranging from severe anemia to clinically asymptomatic individuals. Global annual incidence is estimated at one in 100,000. Beta thalassemias occur due to malfunctions in the hemoglobin subunit beta or HBB. The severity of the disease depends on the nature of the mutation. HBB blockage over time leads to decreased beta-chain synthesis. The body's inability to construct new beta-chains leads to the underproduction of HbA (adult hemoglobin). Reductions in HbA available overall to fill the red blood cells in turn leads to microcytic anemia. Microcytic anemia ultimately develops in respect to inadequate HBB protein for sufficient red blood cell functioning. Due to this factor, the patient may require blood transfusions to make up for the blockage in the beta-chains. Repeated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
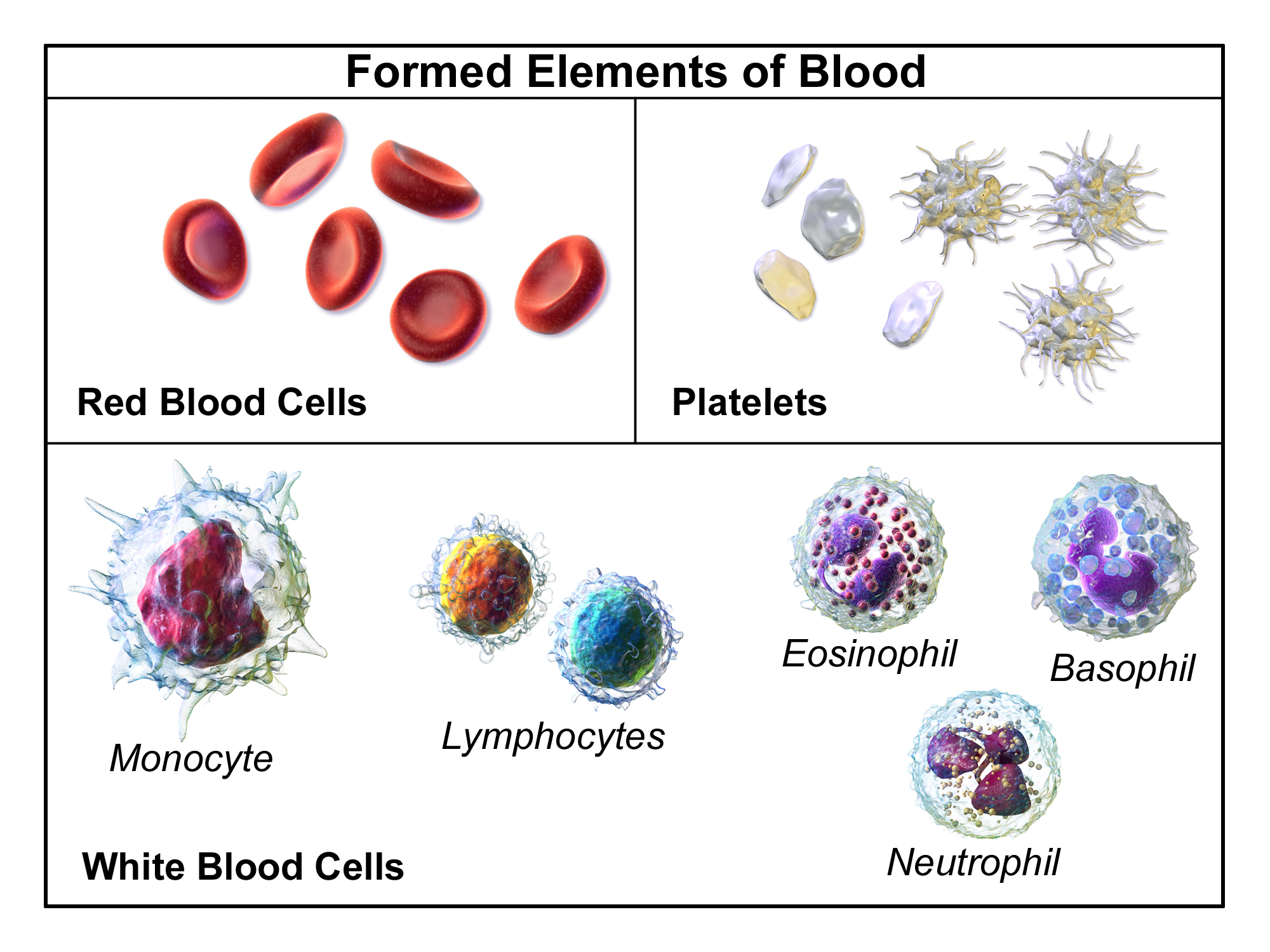
Complete Blood Count
A complete blood count (CBC), also known as a full blood count (FBC), is a set of medical laboratory tests that provide cytometry, information about the cells in a person's blood. The CBC indicates the counts of white blood cells, red blood cells and platelets, the concentration of hemoglobin, and the hematocrit (the volume percentage of red blood cells). The red blood cell indices, which indicate the average size and hemoglobin content of red blood cells, are also reported, and a white blood cell differential, which counts the different types of white blood cells, may be included. The CBC is often carried out as part of a medical assessment and can be used to monitor health or diagnose diseases. The results are interpreted by comparing them to Reference ranges for blood tests, reference ranges, which vary with sex and age. Conditions like anemia and thrombocytopenia are defined by abnormal complete blood count results. The red blood cell indices can provide information about the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quotient
In arithmetic, a quotient (from lat, quotiens 'how many times', pronounced ) is a quantity produced by the division of two numbers. The quotient has widespread use throughout mathematics, and is commonly referred to as the integer part of a division (in the case of Euclidean division), or as a fraction or a ratio (in the case of proper division). For example, when dividing 20 (the ''dividend'') by 3 (the ''divisor''), the ''quotient'' is "6 with a remainder of 2" in the Euclidean division sense, and 6\tfrac in the proper division sense. In the second sense, a quotient is simply the ratio of a dividend to its divisor. Notation The quotient is most frequently encountered as two numbers, or two variables, divided by a horizontal line. The words "dividend" and "divisor" refer to each individual part, while the word "quotient" refers to the whole. \dfrac \quad \begin & \leftarrow \text \\ & \leftarrow \text \end \Biggr \} \leftarrow \text Integer part definition The quo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mean Corpuscular Volume
The mean corpuscular volume, or mean cell volume (MCV), is a measure of the average volume of a red blood corpuscle (or red blood cell). The measure is obtained by multiplying a volume of blood by the proportion of blood that is cellular (the hematocrit), and dividing that product by the number of erythrocytes (red blood cells) in that volume. The mean corpuscular volume is a part of a standard complete blood count. In patients with anemia, it is the MCV measurement that allows classification as either a microcytic anemia (MCV below normal range), normocytic anemia (MCV within normal range) or macrocytic anemia (MCV above normal range). Normocytic anemia is usually deemed so because the bone marrow has not yet responded with a change in cell volume. It occurs occasionally in acute conditions, namely blood loss and hemolysis. If the MCV was determined by automated equipment, the result can be compared to RBC morphology on a peripheral blood smear, where a normal RBC is about the si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Red Blood Cell
Red blood cells (RBCs), also referred to as red cells, red blood corpuscles (in humans or other animals not having nucleus in red blood cells), haematids, erythroid cells or erythrocytes (from Greek ''erythros'' for "red" and ''kytos'' for "hollow vessel", with ''-cyte'' translated as "cell" in modern usage), are the most common type of blood cell and the vertebrate's principal means of delivering oxygen (O2) to the body tissues—via blood flow through the circulatory system. RBCs take up oxygen in the lungs, or in fish the gills, and release it into tissues while squeezing through the body's capillaries. The cytoplasm of a red blood cell is rich in hemoglobin, an iron-containing biomolecule that can bind oxygen and is responsible for the red color of the cells and the blood. Each human red blood cell contains approximately 270 million hemoglobin molecules. The cell membrane is composed of proteins and lipids, and this structure provides properties essential for physiolo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |