|
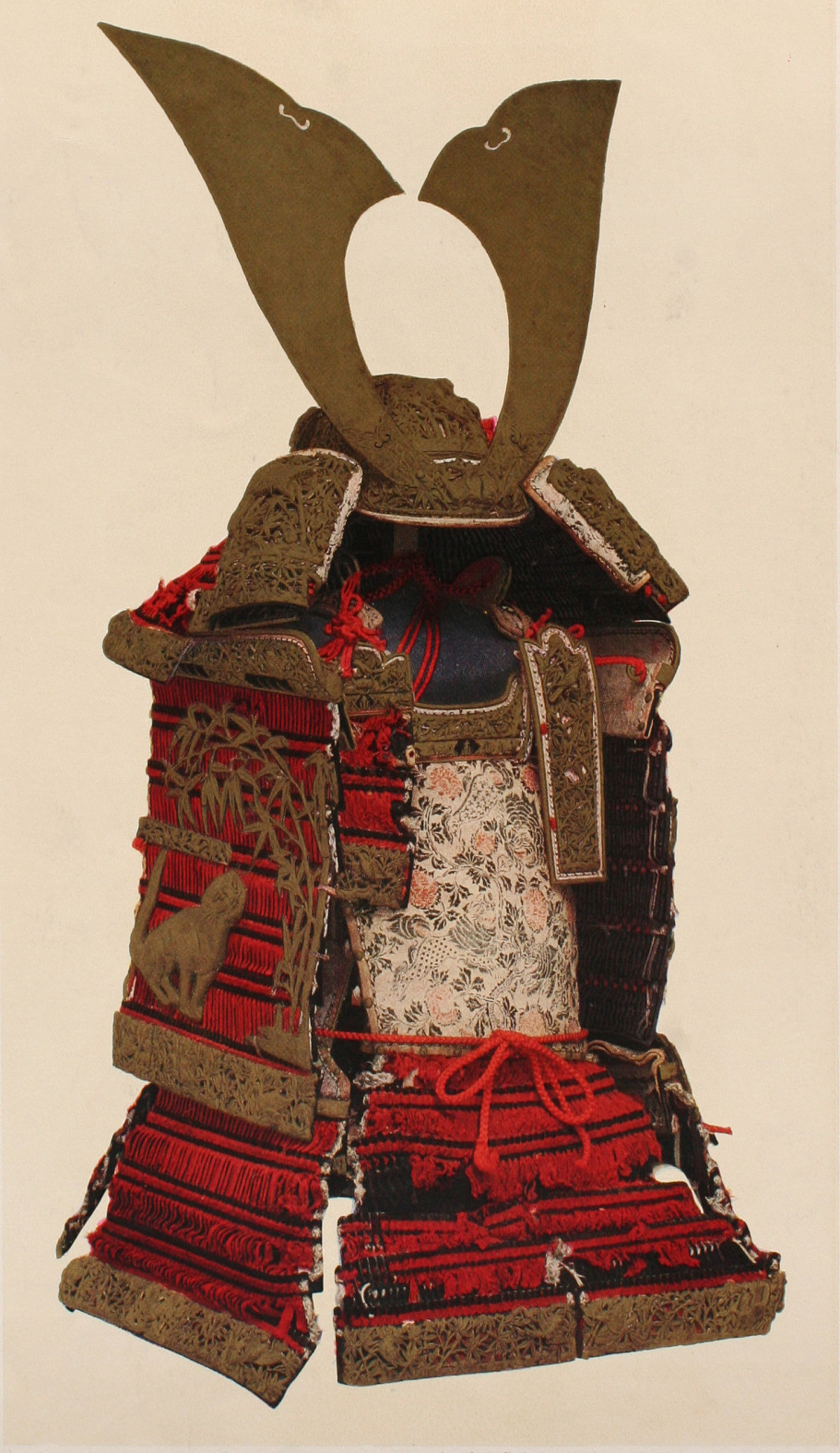
Menpō
, also called or , are various types of facial armour that were worn by the samurai class and their retainers in feudal Japan. These include the ''sōmen'', ''menpō'', ''hanbō'' or ''hanpō'', and ''happuri''. Description The ''men-yoroi'', which covered all or part of the face, provided a way to secure the top-heavy ''kabuto'' (helmet). The ''Shinobi-no-o'' (chin cord) of the kabuto would be tied under the chin. Small hooks called ''ori-kugi'' or posts called ''odome'' located on various places would help secure the chin cord. The ''men-yoroi'' was constructed from iron, leather, or a combination of both. It had a lacquered or rusted type of finish and included a variety of facial details, such as a moustache, fierce teeth and a detachable nose. With the exception of the happuri, a men-yoroi had a small hole underneath the chin for sweat drainage. History Face armour in Japan begins with the ''happuri'', which is depicted in Heian- and Kamakura-era yamato-e paintings, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mengu (samurai Facial Armor)
, also called or , are various types of facial armour that were worn by the samurai class and their retainers in feudal Japan. These include the ''sōmen'', ''menpō'', ''hanbō'' or ''hanpō'', and ''happuri''. Description The ''men-yoroi'', which covered all or part of the face, provided a way to secure the top-heavy ''kabuto'' (helmet). The ''Shinobi-no-o'' (chin cord) of the kabuto would be tied under the chin. Small hooks called ''ori-kugi'' or posts called ''odome'' located on various places would help secure the chin cord. The ''men-yoroi'' was constructed from iron, leather, or a combination of both. It had a lacquered or rusted type of finish and included a variety of facial details, such as a moustache, fierce teeth and a detachable nose. With the exception of the happuri, a men-yoroi had a small hole underneath the chin for sweat drainage. History Face armour in Japan begins with the ''happuri'', which is depicted in Heian- and Kamakura-era yamato-e paintings, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samurai
were the hereditary military nobility and officer caste of medieval and early-modern Japan from the late 12th century until their abolition in 1876. They were the well-paid retainers of the '' daimyo'' (the great feudal landholders). They had high prestige and special privileges such as wearing two swords and ''Kiri-sute gomen'' (right to kill anyone of a lower class in certain situations). They cultivated the '' bushido'' codes of martial virtues, indifference to pain, and unflinching loyalty, engaging in many local battles. Though they had predecessors in earlier military and administrative officers, the samurai truly emerged during the Kamakura shogunate, ruling from 1185 to 1333. They became the ruling political class, with significant power but also significant responsibility. During the 13th century, the samurai proved themselves as adept warriors against the invading Mongols. During the peaceful Edo period (1603 to 1868), they became the stewards and chamberlains of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japanese Armour
Scholars agree that Japanese armour first appeared in the 4th century, with the discovery of the cuirass and basic helmets in graves. During the ''Heian period'' (794-1185), the unique Japanese samurai armour ''ō-yoroi'' and ''dō-maru'' appeared.式正の鎧・大鎧 Costume Museum The Japanese cuirass evolved into the more familiar style of worn by the samurai known as the dou or dō, with the use of leather straps (nerigawa), and lacquer for weatherproofing. Leather and/or iron scales were also used to construct samurai armours, with leather and eventually silk lace used t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samurai Armour
Scholars agree that Japanese armour first appeared in the 4th century, with the discovery of the cuirass and basic helmets in graves. During the ''Heian period'' (794-1185), the unique Japanese samurai armour ''ō-yoroi'' and ''dō-maru'' appeared.式正の鎧・大鎧 Costume Museum The Japanese cuirass evolved into the more familiar style of worn by the samurai known as the dou or dō, with the use of leather straps (nerigawa), and lacquer for weatherproofing. Leather and/or iron scales were also used to construct samurai armours, with leather and eventually silk lace used to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
:Category:Japanese Words And Phrases
{{Commons Words and phrases by language Words Words A word is a basic element of language that carries an objective or practical meaning, can be used on its own, and is uninterruptible. Despite the fact that language speakers often have an intuitive grasp of what a word is, there is no consen ... Words ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Face Guard (Shirohige Ressei-menpo)
The face is the front of an animal's head that features the eyes, nose and mouth, and through which animals express many of their emotions. The face is crucial for human identity, and damage such as scarring or developmental deformities may affect the psyche adversely. Structure The front of the human head is called the face. It includes several distinct areas, of which the main features are: *The forehead, comprising the skin beneath the hairline, bordered laterally by the temples and inferiorly by eyebrows and ears *The eyes, sitting in the orbit and protected by eyelids and eyelashes * The distinctive human nose shape, nostrils, and nasal septum *The cheeks, covering the maxilla and mandibula (or jaw), the extremity of which is the chin *The mouth, with the upper lip divided by the philtrum, sometimes revealing the teeth Facial appearance is vital for human recognition and communication. Facial muscles in humans allow expression of emotions. The face is itself a highl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Facial Armour
Body armor, also known as body armour, personal armor or armour, or a suit or coat of armor, is protective clothing designed to absorb or deflect physical attacks. Historically used to protect military personnel, today it is also used by various types of police (riot police in particular), private security guards or bodyguards, and occasionally ordinary civilians. Today there are two main types: regular non-plated body armor for moderate to substantial protection, and hard-plate reinforced body armor for maximum protection, such as used by combat soldiers. History Many factors have affected the development of personal armor throughout human history. Significant factors in the development of armor include the economic and technological necessities of armor production. For instance full plate armor first appeared in Medieval Europe when water-powered trip hammers made the formation of plates faster and cheaper. At times the development of armor has run parallel to the devel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kabuto
' (兜, 冑) is a type of helmet first used by ancient Japanese warriors which, in later periods, became an important part of the traditional Japanese armour worn by the samurai class and their retainers in feudal Japan. Note that in the Japanese language, the word is an appellative, not a type description, and can refer to any combat helmet. History Japanese helmets dating from the fifth century have been found in excavated tombs. Called (visor-attached helmet), the style of these kabuto came from China and Korea and they had a pronounced central ridge. , which is now known as a samurai helmet, first appeared in the 10th century Heian period with the appearance of ''ō-yoroi''. Until the early Muromachi period, were made by combining dozens of thin iron plates. Generally, only daimyo and samurai at the rank of commander wore ornaments called , which were shaped like a pair of hoes. In the middle of the Muromachi period, as the number of large-scale group battles increas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lacquer
Lacquer is a type of hard and usually shiny coating or finish applied to materials such as wood or metal. It is most often made from resin extracted from trees and waxes and has been in use since antiquity. Asian lacquerware, which may be called "true lacquer", are objects coated with the treated, dyed and dried sap of ''Toxicodendron vernicifluum'' or related trees, applied in several coats to a base that is usually wood. This dries to a very hard and smooth surface layer which is durable, waterproof, and attractive in feel and look. Asian lacquer is sometimes painted with pictures, inlaid with shell and other materials, or carved, as well as dusted with gold and given other further decorative treatments. In modern techniques, lacquer means a range of clear or pigmented coatings that dry by solvent evaporation to produce a hard, durable finish. The finish can be of any sheen level from ultra matte to high gloss, and it can be further polished as required. Lacquer finishes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moustache
A moustache (; en-US, mustache, ) is a strip of facial hair grown above the upper lip. Moustaches have been worn in various styles throughout history. Etymology The word "moustache" is French, and is derived from the Italian ''mustaccio'' (14th century), dialectal ''mostaccio'' (16th century), from Medieval Latin ''mustacchium'' (eighth century), Medieval Greek μουστάκιον (''moustakion''), attested in the ninth century, which ultimately originates as a diminutive of Hellenistic Greek μύσταξ (''mustax'', ''mustak-''), meaning "upper lip" or "facial hair", probably derived from Hellenistic Greek μύλλον (''mullon''), "lip". An individual wearing a moustache is said to be "moustached" or "moustachioed" (the latter often referring to a particularly large or bushy moustache). History Research done on this subject has noticed that the prevalence of moustaches and facial hair in general rise and fall according to the saturation of the marriage market. Thus, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yamato-e
is a style of Japanese painting inspired by Tang dynasty paintings and fully developed by the late Heian period. It is considered the classical Japanese style. From the Muromachi period (15th century), the term Yamato-e has been used to distinguish work from contemporary Chinese-style paintings , which were inspired by Chinese Song and Yuan-era ink wash paintings. Characteristic features of Yamato-e include many small figures and careful depictions of details of buildings and other objects, the selection of only some elements of a scene to be fully depicted, the rest either being ignored or covered by a "floating cloud", an oblique view from above showing interiors of buildings as though through a cutaway roof, and very stylised depiction of landscape. Yamato-e very often depict narrative stories, with or without accompanying text, but also show the beauty of nature, with famous places or the four seasons . The pictures are often on scrolls that can be hung on a wall (), hand ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heiji Monogatari
is a Japanese war epic (''gunki monogatari'') detailing the events of the Heiji Rebellion of 1159–1160, in which samurai clan head Minamoto no Yoshitomo attacked and besieged Kyoto, as part of an Imperial succession dispute, in which he was opposed by Taira no Kiyomori, head of the Taira clan. The Tale, like most ''monogatari'', exists in three main forms: written, oral, and painted. The original text is sometimes attributed to Hamuro Tokinaga, and is written in 36 chapters. As is the case with most other ''monogatari'', the text has been rewritten and revised many times over the years, and developed into an oral tradition as well. Most often, the ''Tale of Heiji'' would be chanted as a continuation of the '' Tale of Hōgen'', which relates the events of the closely related Hōgen Rebellion. The picture scroll version of the tale, called ''Heiji Monogatari Emaki'' or ''Heiji Monogatari Ekotoba'', dates from the 13th century. It tells the tale in color on paper, on five scroll ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)