|
Meng Huo
Meng Huo was a local leader in the Nanzhong region in the state of Shu Han during the Three Kingdoms period of China. He was popularly depicted as a local leader representing the gentries of the Nanzhong region, but some historians doubt his historical existence. Meng Huo's popular image comes from the 14th-century historical novel ''Romance of the Three Kingdoms'', which romanticises the events before and during the Three Kingdoms period. The novel portrays Meng Huo as a southern barbarian tribal leader. He also marries the fictional Lady Zhurong, who claims descent from the fire deity Zhurong. Historicity The absurdity of Meng Huo being captured and released seven times led many to doubt the story, and even of Meng Huo's existence. The Republican-era historian Zhang Hualan (張華爛) wrote in his article "Discussion on Meng Huo" (孟獲辯) that Meng was a fictional character invented by later historians, noting that the name "Huo" (獲), which means "captured" in Chine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meng (surname)
Meng () is a Chinese surname. Meng is a ''shi'' surname or clan name (氏), as opposed to the xing (姓) category of surname, ancestral name. Meng is of the type of surname which was a member of the list of names denoting seniority within a certain family: in ancient usage, the characters of ''meng'' (孟), '' zhong'' (仲), '' shu'' (叔) and '' ji'' (季) were used to denote the first, second, third and fourth eldest sons in a family. These were sometimes adopted as surnames. Of these, Meng is the best known, being the surname of the philosopher Mencius. It is the 94th name on the ''Hundred Family Surnames'' poem.K. S. Tom. 989(1989). Echoes from Old China: Life, Legends and Lore of the Middle Kingdom. University of Hawaii Press. . Historical people * Mencius (孟子), Mencius; born Mèng Kē (孟軻); or Mengzi (372–289 BC or 385–303 or 302 BC) was a Chinese Confucian philosopher who has often been described as the "second Sage", that is, after only Confucius himself ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wang Ling (Three Kingdoms)
Wang Ling (172—15 June 251), courtesy name Yanyun, was a Chinese military general and politician of the state of Cao Wei during the Three Kingdoms period of China. Early life and career Wang Ling's family fled to the countryside after his uncle, Wang Yun, was executed in 192 for fomenting Lü Bu's assassination of Dong Zhuo. Later he was declared ''xiaolian'', a crucial nomination to be considered for civil service appointments, and became the Administrator of Zhongshan Commandery (). His excellent public service was noticed by chancellor Cao Cao, who moved him into his office. Service in Cao Wei In Cao Cao's army, Wang Ling engaged in several battles with Eastern Wu. As the Inspector of Yan Province, he attacked Sun Quan under Zhang Liao. His victory led to his promotion to General Who Builds Loyalty (). In another battle against Eastern Wu, he rescued the besieged general Cao Xiu. He was promoted to General of Chariots and Cavalry () after a major victory against Quan Con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zhang Ni
Zhang Ni (died 254), courtesy name Boqi, rendered also as Zhang Yi, was a military general of the state of Shu Han during the Three Kingdoms period of China. Famous for his courage and generosity, Zhang Ni made his name known while rescuing a magistrate's wife from bandits and leading her to safety. Zhang Ni often worked with Ma Zhong (Shu Han), Ma Zhong, another general of Shu Han, when pacifying the indigenous tribes residing within and around Shu's borders. He spent at least 18 years dealing with the continuum of domestic uprisings centered around the Yuexi/Yuesui and Ba commanderies. Though he was a talented general, Zhang Ni often looked for humane solutions and sought to make peace or negotiate with the tribes when he could. Thanks to his upright nature, the Records of the Three Kingdoms, ''Sanguozhi'' recorded that the tribes loved him and even weeped and grabbed hold of his carriage when they learned that he would be returning to Chengdu. Feeling he was growing weak a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wang Ping (Three Kingdoms)
Wang Ping (died 248), courtesy name Zijun, was a military general of the state of Shu Han in the Three Kingdoms period of China. Originally a military officer serving under the warlord Cao Cao in the late Eastern Han dynasty, in 218 he defected to Cao Cao's rival Liu Bei, who later became the founding emperor of Shu, during the Hanzhong Campaign. Though he was a talented orator, Wang Ping never learned to read because he joined the army at a young age. Yet he did not let this disadvantage stop him and had his clerk help him with his reports. Known for his self discipline, he steadily rose through the ranks to become a senior general. During his career, he defeated Zhang He, quelled Wei Yan's alleged rebellion and was the leading commander of the Shu forces during the Battle of Xingshi. The highest position he reached was Senior General Who Guards the North (). Early life Wang Ping was from Dangqu County, Baxi Commandery, which was around present-day Qu County, Sichuan. Bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wei Yan
Wei Yan () (died October 234), courtesy name Wenchang, was a Chinese military general and politician of the state of Shu Han during the Three Kingdoms period of China. Originally a subordinate of the warlord Liu Bei in the late Eastern Han dynasty, Wei Yan rose through the ranks and became a general when Liu Bei seized control of Yi Province (covering present-day Sichuan and Chongqing) in 214. His performance in battle helped him to become a prominent figure in the Shu military in a short period of time. He was later appointed as the Administrator of Hanzhong Commandery and as an Area Commander in 219. Between 228 and 234, he participated actively in the Northern Expeditions led by the Shu regent Zhuge Liang against Shu's rival state, Cao Wei. After Zhuge Liang's death in September 234, Wei Yan was killed by another Shu general, Ma Dai, for alleged treason. Early life Wei Yan was from Yiyang Commandery (), which covered parts of present-day Nanyang in southern Henan and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zhao Yun
Zhao Yun ( ) (died 229), courtesy name Zilong (), was a military general who lived during the late Eastern Han dynasty and early Three Kingdoms period of China. Originally a subordinate of the northern warlord Gongsun Zan, Zhao Yun later came to serve another warlord, Liu Bei, and had since accompanied him on most of his military exploits, from the Battle of Changban (208) to the Hanzhong Campaign (217–219). He continued serving in the state of Shu Han – founded by Liu Bei in 221 – in the Three Kingdoms period and participated in the first of the Northern Expeditions until his death in 229. While many facts about Zhao Yun's life remain unclear due to limited information in historical sources, some aspects and activities in his life have been dramatised or exaggerated in folklore and fiction. In the 14th-century historical novel ''Romance of the Three Kingdoms'', he was lauded as a member of the Five Tiger Generals under Liu Bei. Historical sources on Zhao Yun's life Zhao ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yi Province
Yizhou (益州), Yi Province or Yi Prefecture, was a '' zhou'' (province) of ancient China. Its capital city was Chengdu.de Crespigny, p. 256. During the Han dynasty, it included the commanderies Hanzhong, Ba, Guanghan, Shu, Wenshan, Jianwei, Zangke, Yuexi, Yizhou and Yongchang. It was bordered in the north by Liang Province and Yong Province. At its greatest extent, Yi covered present-day central and eastern Sichuan, Chongqing, southern Shaanxi and parts of Yunnan and Guizhou. History During the First Great Qiang Rebellion (107–118) in Liang Province,de Crespigny, p. 10–11. unrest also spread to the Hanzhong and Wudu commanderies. In 188, Liu Yan was appointed governor of Yi Province. Upon his death in 194, Yi passed to his son Liu Zhang. In 213, warlord Cao Cao conquered the city of Hanzhong from the Taoist cult leader Zhang Lu, and threatened the rest of Yi. Liu Zhang requested the help of warlord Liu Bei, a relative of his, but the latter turned against Zhang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
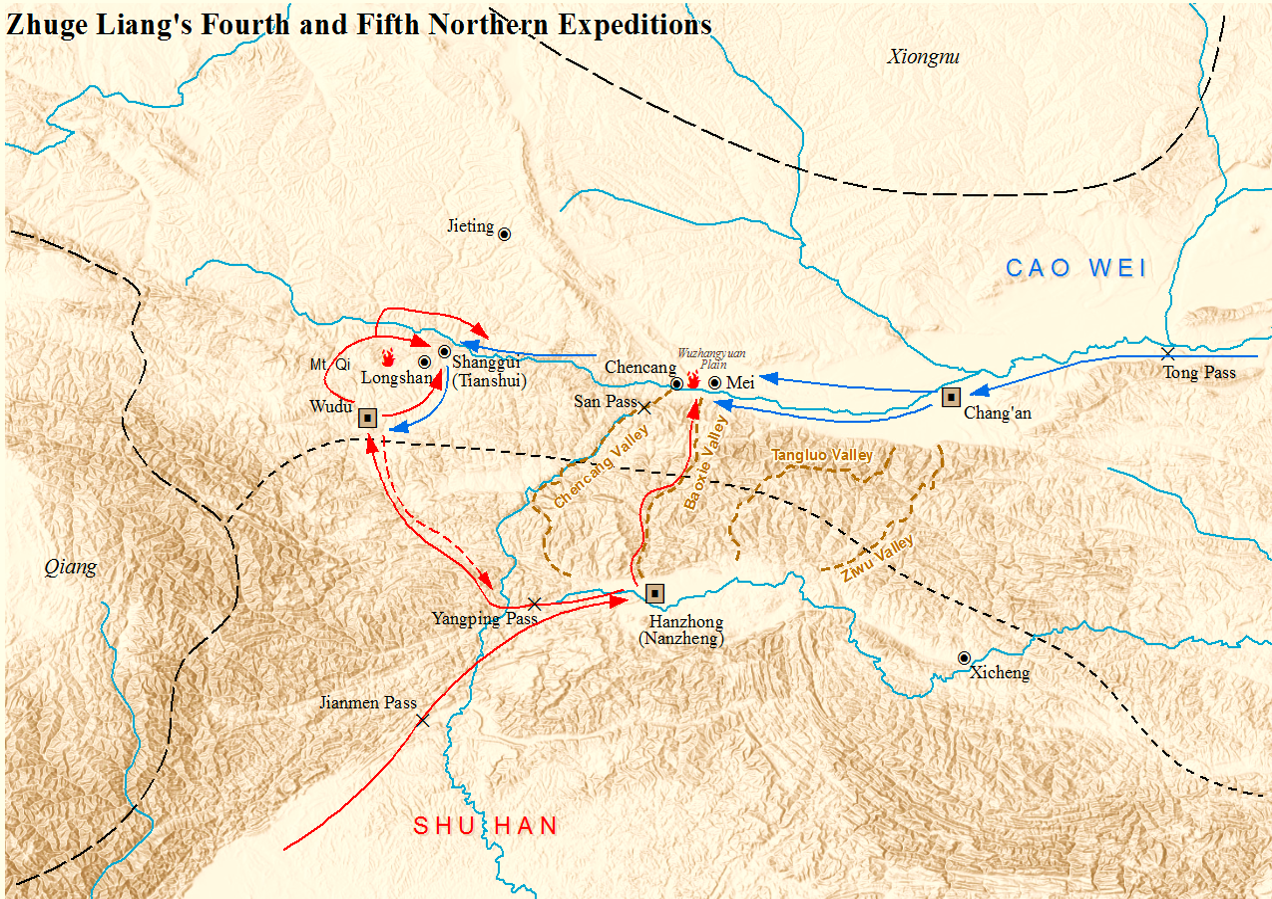
Zhuge Liang
Zhuge Liang ( zh, t=諸葛亮 / 诸葛亮) (181 – September 234), courtesy name Kongming, was a Chinese statesman and military strategist. He was chancellor and later regent of the state of Shu Han during the Three Kingdoms period. He is recognised as the most accomplished strategist of his era, and has been compared to Sun Tzu, the author of ''The Art of War''. His reputation as an intelligent and learned scholar grew even while he was living in relative seclusion, earning him the nickname "Wolong" or "Fulong", meaning "Crouching Dragon" or "Sleeping Dragon". Zhuge Liang is often depicted wearing a Taoist robe and holding a hand fan made of crane feathers. Zhuge Liang was a Confucian-oriented "Legalist". He liked to compare himself to the sage minister Guan Zhong and Yue Yi developing Shu's agriculture and industry to become a regional power, and attached great importance to the works of Shen Buhai and Han Fei, refusing to indulge local elites and adopting strict, but fa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chancellor (China)
The grand chancellor (''zaixiang, tsai-hsiang''), also translated as counselor-in-chief, chancellor, chief councillor, chief minister, imperial chancellor, lieutenant chancellor and prime minister, was the highest-ranking executive official in the imperial Chinese government. The term was known by many different names throughout Chinese history, and the exact extent of the powers associated with the position fluctuated greatly, even during a particular dynasty. During the Six Dynasties period, the term denoted a number of power-holders serving as chief administrators, including ''zhongshun jian'' (Inspector General of the Secretariat), ''zhongshu ling'' (President of the Secretariat), ''shizhong'' (Palace Attendant), ''shangshu ling'' and ''puye'' (president and vice-president of the Department of State Affairs). History In the Spring and Autumn period, Guan Zhong was the first chancellor in China, who became chancellor under the state of Qi in 685 BC. In Qin, during the Warring ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liu Bei
Liu Bei (, ; ; 161 – 10 June 223), courtesy name Xuande (), was a warlord in the late Eastern Han dynasty who founded the state of Shu Han in the Three Kingdoms period and became its first ruler. Although he was a distant relative of the Han imperial family, Liu Bei's father died when he was a child and left his family impoverished. To help his mother, he sold shoes and straw mats. When he reached the age of fifteen, his mother sent him to study under Lu Zhi. In his youth, Liu Bei was known as ambitious and charismatic. He gathered a militia army to fight the Yellow Turbans. Liu Bei fought bravely in many battles and grew famous for his exploits. Later, he participated in the coalition against Dong Zhuo, following this joined his childhood friend Gongsun Zan and fought under him against Yuan Shao. Later he was sent to help Tao Qian against Cao Cao. Thanks to the support of the influential Mi and Chen families along with Tao Qian's last will, Liu Bei inherited the Xu Pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emperor Of China
''Huangdi'' (), translated into English as Emperor, was the superlative title held by monarchs of China who ruled various imperial regimes in Chinese history. In traditional Chinese political theory, the emperor was considered the Son of Heaven and the autocrat of all under Heaven. Under the Han dynasty, Confucianism replaced Legalism as the official political theory and succession in most cases theoretically followed agnatic primogeniture. The lineage of emperors descended from a paternal family line constituted a dynasty. The absolute authority of the emperor came with a variety of governing duties and moral obligations; failure to uphold these was thought to remove the dynasty's Mandate of Heaven and to justify its overthrow. In practice, emperors sometimes avoided the strict rules of succession and dynasties' ostensible "failures" were detailed in official histories written by their successful replacements. The power of the emperor was also limited by the imperial burea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meng Huo's Red Ox , pre-modern Tai polities in southwestern China, mainland Southeast Asia, and parts of ...
Meng may refer to: * Meng (surname) (孟), a Chinese surname * Master of Engineering (MEng or M.Eng.), an academic or professional master's degree in the field of engineering * , "M with hook", letter used in the International Phonetic Alphabet ** Labiodental nasal consonantal sound, the sound transcribed by that letter * Meng (designer), British fashion house * Marketing Executives Network Group, American non-profit professional association * Haku (wrestler), a former wrestler who used "Meng" as his stage name in World Championship Wrestling * Meng (river), in Austria, tributary of the Ill * Meng and Ecker, British underground comic * Mueang Mueang ( th, เมือง ''mɯ̄ang'', ), Muang ( lo, ເມືອງ ''mɯ́ang'', ; Tai Nuea: ᥛᥫᥒᥰ ''muang''), Mong ( shn, ''mə́ŋ'', ), Meng () or Mường (Vietnamese), were pre-modern semi-independent city-states or principal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)


.jpg)


