|
Menedemus
Menedemus of Eretria ( grc-gre, Μενέδημος ὁ Ἐρετριεύς; 345/44 – 261/60 BC) was a Greek philosopher and founder of the Eretrian school. He learned philosophy first in Athens, and then, with his friend Asclepiades, he subsequently studied under Stilpo and Phaedo of Elis. Nothing survives of his philosophical views apart from a few scattered remarks recorded by later writers. Life Menedemus was born at Eretria. Though of noble birth, he worked as builder and tent maker until he was sent with a military expedition to Megara, from where he travelled to the Platonic Academy in Athens and resolved to devote himself to philosophy. At Megara he formed a lifelong friendship with Asclepiades of Phlius, with whom he toiled in the night that he might study philosophy by day. He was subsequently a pupil first of Stilpo and then of Phaedo of Elis, whose school he transferred to Eretria, by which name it was afterwards known. In addition to his philosophical work, he took a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eretrian School
The Eretrian school of philosophy was originally the School of Elis, where it had been founded by Phaedo of Elis; it was later transferred to Eretria by his pupil Menedemus. It can be referred to as the Elian-Eretrian School, on the assumption that the views of the two schools were similar. It died out after the time of Menedemus (3rd century BC), and, consequently, very little is known about its tenets. Phaedo had been a pupil of Socrates, and Plato named a dialogue, ''Phaedo'', in his honor, but it is not possible to infer his doctrines from the dialogue. Menedemus was a pupil of Stilpo at Megara before becoming a pupil of Phaedo; in later times, the views of his school were often linked with those of the Megarian school. Menedemus' friend and colleague in the Eretrian school was Asclepiades of Phlius. Like the Megarians they seem to have believed in the individuality of "the Good," the denial of the plurality of virtue, and of any real difference existing between the Good and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antigonus II Gonatas
Antigonus II Gonatas ( grc-gre, Ἀντίγονος Γονατᾶς, ; – 239 BC) was a Macedonian ruler who solidified the position of the Antigonid dynasty in Macedon after a long period defined by anarchy and chaos and acquired fame for his victory over the Gauls who had invaded the Balkans. Birth and family Antigonus Gonatas was born around 320 BC. The origin of the Hellenistic nickname Gonatas is unknown. He was descended from the Diadochi (the successors of Alexander the Great) on both his father's and mother's side. His father was Demetrius Poliorcetes, himself the son of Antigonus I Monophthalmus, who then controlled much of Asia. His mother was Phila, the daughter of Antipater, who had controlled Macedonia and the rest of Greece since 334 BC and was recognized as regent of the empire, which in theory remained united. In the year of Antigonus Gonatas' birth, however, Antipater died, leading to further struggles for territory and dominance. The careers of Antigo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stilpo
Stilpo (or Stilpon; el, Στίλπων, gen.: Στίλπωνος; c. 360 – c. 280 BC) was a Greek philosopher of the Megarian school. He was a contemporary of Theophrastus, Diodorus Cronus, and Crates of Thebes. None of his writings survive, but he is described in the writings of others as being interested in logic and dialectic, and he argued that the universal is fundamentally separated from the individual and concrete. His ethical teachings approached that of the Cynics and Stoics. His most important followers were Pyrrho, the founder of Pyrrhonism, and Zeno of Citium, the founder of Stoicism. Life He was a native of Megara. He probably lived after the time of Euclid of Megara, which makes it unlikely that he was a pupil of Euclid, as stated by some; and others state that he was the pupil of Thrasymachus of Corinth, or of Pasicles, the brother of Crates of Thebes. According to one account, he engaged in dialectic encounters with Diodorus Cronus at the court of Ptolemy Sot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phaedo Of Elis
Phaedo of Elis (; also ''Phaedon''; grc-gre, Φαίδων ὁ Ἠλεῖος, ''gen''.: Φαίδωνος; fl. 4th century BCE) was a Greek philosopher. A native of Elis, he was captured in war as a boy and sold into slavery. He subsequently came into contact with Socrates at Athens, who warmly received him and had him freed. He was present at the death of Socrates, and Plato named one of his dialogues ''Phaedo''. He returned to Elis, and founded the Elean School of philosophy. Almost nothing is known of his doctrines, but his school survived him and was subsequently transferred to Eretria by his pupil Menedemus, where it became the Eretrian school. Life Born in the last years of the 5th century BCE, Phaedo was a native of Elis and of high birth. He was taken prisoner in his youth, and passed into the hands of an Athenian slave dealer; being of considerable personal beauty,Plato, ''Phaedo'', 89a–b he was forced into prostitution.; ; The occasion on which he wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
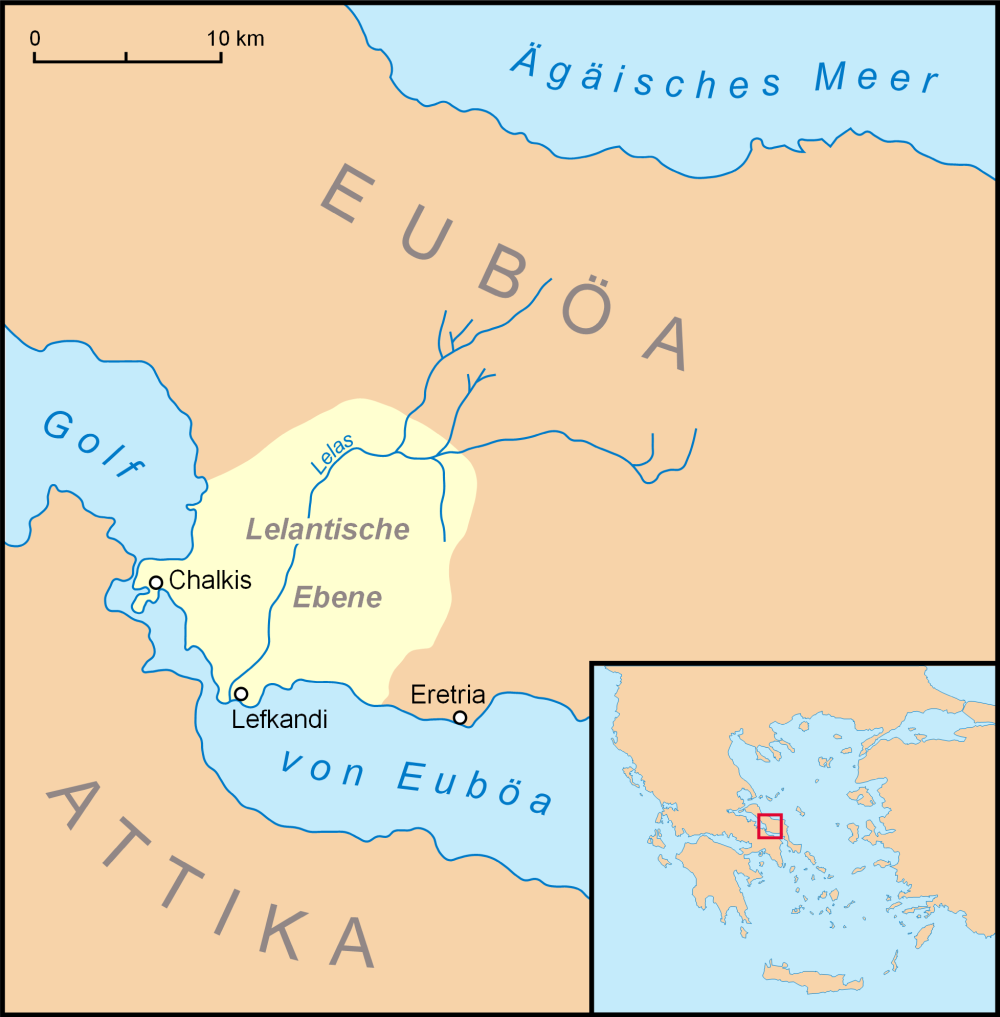
Eretria
Eretria (; el, Ερέτρια, , grc, Ἐρέτρια, , literally 'city of the rowers') is a town in Euboea, Greece, facing the coast of Attica across the narrow South Euboean Gulf. It was an important Greek polis in the 6th and 5th century BC, mentioned by many famous writers and actively involved in significant historical events. Excavations of the ancient city began in the 1890s and have been conducted since 1964 by the Greek Archaeological Service (11th Ephorate of Antiquities) and the Swiss School of Archaeology in Greece. History of Eretria Prehistory The first evidence for human activity in the area of Eretria are pottery shards and stone artifacts from the late Neolithic period (3500–3000 BC) found on the Acropolis as well as in the plain. No permanent structures have yet been found. It is therefore unclear whether a permanent settlement existed at that time. The first known settlement from the Early Helladic period (3000–2000 BC) was located on the plain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epicrates Of Ambracia
Epicrates of Ambracia ( el, Ἐπικράτης Ἀμβρακιώτης), was an Ambraciote who lived in Athens, a comic poet of the Middle Comedy, according to the testimony of Athenaeus (x. p. 422, f.). This is confirmed by extant fragments of his plays, in which he ridicules Plato and his disciples, Speusippus and Menedemus, and in which he refers to the courtesan Lais of Corinth, as being now far advanced in years. (Athen. ii. p. 59, d., xiii. p. 570, b.) From these indications, Augustus Meineke infers that he flourished between the 101st and 108th Olympiads (376–348 BC). Surviving titles and fragments Two plays of Epicrates, ''Emporos'' (Merchant) and ''Antilais'' (Against Lais), are mentioned by Suidas (s. «.), and are quoted by Athenaeus (xiv. p. 655, f., xiii. pp. 570, b., 605, e.), who also quotes his ''Amazones'' (x. p. 422, f.) and ''Dyspratos'' (Hard to Sell) (vi. p. 262, d.), and informs us that in the latter play Epicrates copi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plato
Plato ( ; grc-gre, Πλάτων ; 428/427 or 424/423 – 348/347 BC) was a Greek philosopher born in Athens during the Classical period in Ancient Greece. He founded the Platonist school of thought and the Academy, the first institution of higher learning on the European continent. Along with his teacher, Socrates, and his student, Aristotle, Plato is a central figure in the history of Ancient Greek philosophy and the Western and Middle Eastern philosophies descended from it. He has also shaped religion and spirituality. The so-called neoplatonism of his interpreter Plotinus greatly influenced both Christianity (through Church Fathers such as Augustine) and Islamic philosophy (through e.g. Al-Farabi). In modern times, Friedrich Nietzsche diagnosed Western culture as growing in the shadow of Plato (famously calling Christianity "Platonism for the masses"), while Alfred North Whitehead famously said: "the safest general characterization of the European philosophical tra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Megarian School
The Megarian school of philosophy, which flourished in the 4th century BC, was founded by Euclides of Megara, one of the pupils of Socrates. Its ethical teachings were derived from Socrates, recognizing a single good, which was apparently combined with the Eleatic doctrine of Unity. Some of Euclides' successors developed logic to such an extent that they became a separate school, known as the Dialectical school. Their work on modal logic, logical conditionals, and propositional logic played an important role in the development of logic in antiquity. History The Megarian school of philosophy was founded by Euclides of Megara, who had been one of the pupils of Socrates in the late 5th century BC. His successors, as head of the school in Megara, were said to have been Ichthyas (mid 4th century BC), and Stilpo (late 4th century BC).Diogenes Laërtius, ii. 113 It is unlikely, however, that the Megarian school was a genuine institution, but more of a casual description of its geographic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Classical Greek Philosophers
Classical may refer to: European antiquity *Classical antiquity, a period of history from roughly the 7th or 8th century B.C.E. to the 5th century C.E. centered on the Mediterranean Sea *Classical architecture, architecture derived from Greek and Roman architecture of classical antiquity *Classical mythology, the body of myths from the ancient Greeks and Romans *Classical tradition, the reception of classical Greco-Roman antiquity by later cultures *Classics, study of the language and culture of classical antiquity, particularly its literature *Classicism, a high regard for classical antiquity in the arts Music and arts *Classical ballet, the most formal of the ballet styles *Classical music, a variety of Western musical styles from the 9th century to the present *Classical guitar, a common type of acoustic guitar *Classical Hollywood cinema, a visual and sound style in the American film industry between 1927 and 1963 * Classical Indian dance, various codified art forms whose theo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Eretrians
Ancient history is a time period from the beginning of writing and recorded human history to as far as late antiquity. The span of recorded history is roughly 5,000 years, beginning with the Sumerian cuneiform script. Ancient history covers all continents inhabited by humans in the period 3000 BCAD 500. The three-age system periodizes ancient history into the Stone Age, the Bronze Age, and the Iron Age, with recorded history generally considered to begin with the Bronze Age. The start and end of the three ages varies between world regions. In many regions the Bronze Age is generally considered to begin a few centuries prior to 3000 BC, while the end of the Iron Age varies from the early first millennium BC in some regions to the late first millennium AD in others. During the time period of ancient history, the world population was already exponentially increasing due to the Neolithic Revolution, which was in full progress. While in 10,000 BC, the world population stood at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
3rd-century BC Philosophers
The 3rd century was the period from 201 ( CCI) to 300 ( CCC) Anno Domini (AD) or Common Era (CE) in the Julian calendar.. In this century, the Roman Empire saw a crisis, starting with the assassination of the Roman Emperor Severus Alexander in 235, plunging the empire into a period of economic troubles, barbarian incursions, political upheavals, civil wars, and the split of the Roman Empire through the Gallic Empire in the west and the Palmyrene Empire in the east, which all together threatened to destroy the Roman Empire in its entirety, but the reconquests of the seceded territories by Emperor Aurelian and the stabilization period under Emperor Diocletian due to the administrative strengthening of the empire caused an end to the crisis by 284. This crisis would also mark the beginning of Late Antiquity. In Persia, the Parthian Empire was succeeded by the Sassanid Empire in 224 after Ardashir I defeated and killed Artabanus V during the Battle of Hormozdgan. The Sassanids th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
3rd-century BC Greek People
The 3rd century was the period from 201 ( CCI) to 300 (CCC) Anno Domini (AD) or Common Era (CE) in the Julian calendar.. In this century, the Roman Empire saw a crisis, starting with the assassination of the Roman Emperor Severus Alexander in 235, plunging the empire into a period of economic troubles, barbarian incursions, political upheavals, civil wars, and the split of the Roman Empire through the Gallic Empire in the west and the Palmyrene Empire in the east, which all together threatened to destroy the Roman Empire in its entirety, but the reconquests of the seceded territories by Emperor Aurelian and the stabilization period under Emperor Diocletian due to the administrative strengthening of the empire caused an end to the crisis by 284. This crisis would also mark the beginning of Late Antiquity. In Persia, the Parthian Empire was succeeded by the Sassanid Empire in 224 after Ardashir I defeated and killed Artabanus V during the Battle of Hormozdgan. The Sassanids t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |