|
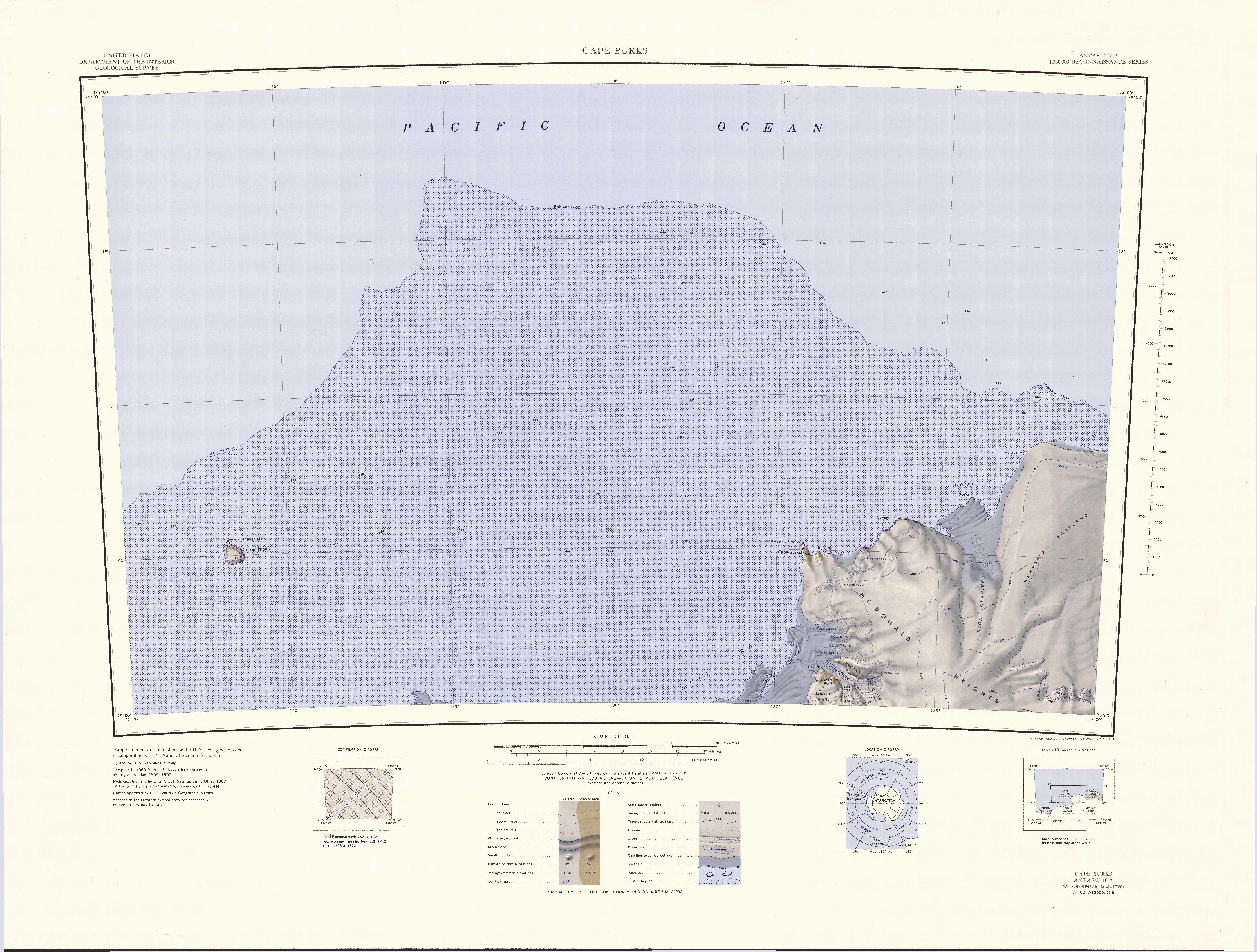
Melville Point
Melville Point () is a point marking the east side of the entrance to Siniff Bay on the coast of Marie Byrd Land, Antarctica. It was mapped by United States Geological Survey from surveys and U.S. Navy air photos, 1959–65, and was named by the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names The Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names (ACAN or US-ACAN) is an advisory committee of the United States Board on Geographic Names responsible for recommending commemorative names for features in Antarctica. History The committee was established ... for Captain Frederick C. Melville, master of the barquentine '' City of New York'' in voyages to the Bay of Whales during the Byrd Antarctic Expedition, 1928–30. References Headlands of Marie Byrd Land {{MarieByrdLand-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siniff Bay
Siniff Bay () is a bay wide between Verleger Point and Melville Point, along the coast of Marie Byrd Land, Antarctica. Discovery and name Siniff Bay was mapped by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) from surveys and United States Navy air photos, 1959–65. It was named by United States Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names (US-ACAN) for Donald B. Siniff, leader of a United States Antarctic Research Program (USARP) party that studied population dynamics and behavior of Weddell seals in the McMurdo Sound area, 1971–72. He also worked in the McMurdo Station area the three preceding austral summers and participated in the International Weddell Sea Oceanographic Expedition The International Weddell Sea Oceanographic Expeditions or IWSOE are a series of scientific research expeditions to the Weddell Sea began in 1967, involving cooperation among Norway, Canada, Chile and the United States. The Weddell Sea, part of t ..., 1967–68. Location Siniff Bay is on the Paci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marie Byrd Land
Marie Byrd Land (MBL) is an unclaimed region of Antarctica. With an area of , it is the largest unclaimed territory on Earth. It was named after the wife of American naval officer Richard E. Byrd, who explored the region in the early 20th century. The territory lies in West Antarctica, east of the Ross Ice Shelf and the Ross Sea and south of the Pacific Ocean portion of the Southern Ocean, extending eastward approximately to a line between the head of the Ross Ice Shelf and Eights Coast. It stretches between 158°W and 103°24'W. The inclusion of the area between the Rockefeller Plateau and Eights Coast is based upon Byrd's exploration. Overview Because of its remoteness, even by Antarctic standards, most of Marie Byrd Land (the portion east of 150°W) has not been claimed by any sovereign state. It is by far the largest single unclaimed territory on Earth, with an area of (including Eights Coast, immediately east of Marie Byrd Land). In 1939, United States President Frankl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Geological Survey
The United States Geological Survey (USGS), formerly simply known as the Geological Survey, is a scientific agency of the United States government. The scientists of the USGS study the landscape of the United States, its natural resources, and the natural hazards that threaten it. The organization's work spans the disciplines of biology, geography, geology, and hydrology. The USGS is a fact-finding research organization with no regulatory responsibility. The agency was founded on March 3, 1879. The USGS is a bureau of the United States Department of the Interior; it is that department's sole scientific agency. The USGS employs approximately 8,670 people and is headquartered in Reston, Virginia. The USGS also has major offices near Lakewood, Colorado, at the Denver Federal Center, and Menlo Park, California. The current motto of the USGS, in use since August 1997, is "science for a changing world". The agency's previous slogan, adopted on the occasion of its hundredt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Advisory Committee On Antarctic Names
The Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names (ACAN or US-ACAN) is an advisory committee of the United States Board on Geographic Names responsible for recommending commemorative names for features in Antarctica. History The committee was established in 1943 as the Special Committee on Antarctic Names (SCAN). It became the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names in 1947. Fred G. Alberts was Secretary of the Committee from 1949 to 1980. By 1959, a structured nomenclature was reached, allowing for further exploration, structured mapping of the region and a unique naming system. A 1990 ACAN gazeeter of Antarctica listed 16,000 names. Description The United States does not recognise territorial boundaries within Antarctica, so ACAN assigns names to features anywhere within the continent, in consultation with other national nomenclature bodies where appropriate, as defined by the Antarctic Treaty System. The research and staff support for the ACAN is provided by the United States Geologi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frederick C
Frederick may refer to: People * Frederick (given name), the name Nobility Anhalt-Harzgerode *Frederick, Prince of Anhalt-Harzgerode (1613–1670) Austria * Frederick I, Duke of Austria (Babenberg), Duke of Austria from 1195 to 1198 * Frederick II, Duke of Austria (1219–1246), last Duke of Austria from the Babenberg dynasty * Frederick the Fair (Frederick I of Austria (Habsburg), 1286–1330), Duke of Austria and King of the Romans Baden * Frederick I, Grand Duke of Baden (1826–1907), Grand Duke of Baden * Frederick II, Grand Duke of Baden (1857–1928), Grand Duke of Baden Bohemia * Frederick, Duke of Bohemia (died 1189), Duke of Olomouc and Bohemia Britain * Frederick, Prince of Wales (1707–1751), eldest son of King George II of Great Britain Brandenburg/Prussia * Frederick I, Elector of Brandenburg (1371–1440), also known as Frederick VI, Burgrave of Nuremberg * Frederick II, Elector of Brandenburg (1413–1470), Margrave of Brandenburg * Frederick William, Elector ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
City Of New York (1885 Ship)
The ''City of New York'' was a steam barquentine best known for being Richard E. Byrd's flagship on his 1928–30 exploration of Antarctica, mistakenly for the rescue of Shackleton in 1915, and most infamously for possibly being the ship that failed to come to the aid of the ''Titanic'' in 1912. Her name was changed several times; originally named ''Samson'' (1885–1914), she was renamed the ''Jacobsen'' (1915–1919), and then the ''Belsund'' (1919–1926), and back to ''Samson'' (1926–1928), before being finally dubbed the ''City of New York'' in 1928. Description As built, the ship was long, with a beam of and a depth of . She was rigged as a barque and had an auxiliary two-cylinder compound steam engine of 70nhp, 350 ihp. The steam engine could propel her at . Early career She was built by Tjøstolv Bastian Larsen in Løgebergskåret, Arendal, Norway in 1885. Byrd tells us in error she and her boiler were built in 1882. The keel was laid in March 1884, the launching ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bay Of Whales
The Bay of Whales was a natural ice harbour, or iceport, indenting the front of the Ross Ice Shelf just north of Roosevelt Island, Antarctica. It is the southernmost point of open ocean not only of the Ross Sea, but worldwide. The Ross Sea extends much further south – as far as the Gould Coast, some from the South Pole – but most of that area is covered by the Ross Ice Shelf rather than open sea. Discovery and naming Ernest Shackleton named the feature on January 24, 1908, during the Nimrod Expedition, because of the large number of whales seen near this location. History During his quest for the South Pole, Norwegian explorer Roald Amundsen established a temporary base, which he named Framheim, at the Bay of Whales. The base was used between January 1911February 1912, and was named after Amundsen's ship ''Fram''. The Bay of Whales has also served as a logistical support base for several other important Antarctic expeditions, including: * 1928–1930: Richard Evelyn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Byrd Antarctic Expedition
Richard Evelyn Byrd Jr. (October 25, 1888 – March 11, 1957) was an American naval officer and explorer. He was a recipient of the Medal of Honor, the highest honor for valor given by the United States, and was a pioneering American aviator, polar explorer, and organizer of polar logistics. Aircraft flights in which he served as a navigator and expedition leader crossed the Atlantic Ocean, a segment of the Arctic Ocean, and a segment of the Antarctic Plateau. Byrd said that his expeditions had been the first to reach both the North Pole and the South Pole by air. His belief to have reached the North Pole is disputed. He is also known for discovering Mount Sidley, the largest dormant volcano in Antarctica. Family Ancestry Byrd was born in Winchester, Virginia, the son of Esther Bolling (Flood) and Richard Evelyn Byrd Sr. He was a descendant of one of the First Families of Virginia. His ancestors include planter John Rolfe and his wife Pocahontas, William Byrd II of Westover Pl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

_a_steam_powered_whale_catcher.jpg)
