|
Mellophone
The mellophone is a brass instrument typically pitched in the key of F, though models in E, D, C, and G (as a bugle) have also historically existed. It has a conical bore, like that of the euphonium and flugelhorn. The mellophone is used as the middle-voiced brass instrument in marching bands and drum and bugle corps in place of French horns, and can also be used to play French horn parts in concert bands and orchestras. These instruments are used instead of French horns for marching because their bells face forward instead of to the back (or to the side), as dissipation of the sound becomes a concern in the open-air environment of marching. Tuning is done solely by adjusting the tuning slide, unlike the French horn where the pitch is affected by the hand position in the bell. Fingerings for the mellophone are the same as fingerings for the trumpet, alto (tenor) horn, and most valved brass instruments. Owing to its use primarily outside concert music, there is little solo litera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German Horn
The German horn is a brass instrument made of tubing wrapped into a coil with a flared bell, and in bands and orchestras is the most widely used of three types of horn, the other two being the French horn (in the less common, narrower meaning of the term) and the Vienna horn. Its use among professional players has become so universal that it is only in France and Vienna that any other kind of horn is used today. A musician who plays the German horn is called a horn player (or less frequently, a hornist). The word "German" is used only to distinguish this instrument from the now-rare French and Viennese instruments. Although the expression "French horn" is still used colloquially in English for any orchestral horn (German, French, or Viennese), since the 1930s professional musicians and scholars have generally avoided this term in favour of just "horn". Vienna horns today are played only in Vienna, and are made only by Austrian firms. German horns, by contrast, are not all made by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
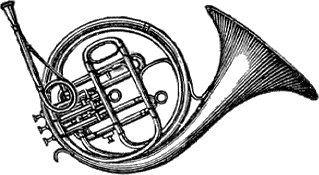
Horn (instrument)
A horn is any of a family of musical instruments made of a tube, usually made of metal and often curved in various ways, with one narrow end into which the musician blows, and a wide end from which sound emerges. In horns, unlike some other brass instruments such as the trumpet, the bore gradually increases in width through most of its length—that is to say, it is conical rather than cylindrical. In jazz and popular-music contexts, the word may be used loosely to refer to any wind instrument, and a section of brass or woodwind instruments, or a mixture of the two, is called a horn section in these contexts. Types Variations include: *Lur (prehistoric) *Shofar *Roman horns: ** Cornu **Buccina * Dung chen *Dord * Sringa * Nyele *Wazza *Alphorn *Cornett *Serpent * Ophicleide *Natural horn **Bugle **Post horn *French horn *Vienna horn *Wagner tuba *Saxhorns, including: **Alto horn (UK: tenor horn), pitched in E ** Baritone horn, pitched in B * Valved bugles, including ** c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Horn
The French horn (since the 1930s known simply as the horn in professional music circles) is a brass instrument made of tubing wrapped into a coil with a flared bell. The double horn in F/B (technically a variety of German horn) is the horn most often used by players in professional orchestras and bands, although the descant and triple horn have become increasingly popular. A musician who plays a horn is known as a list of horn players, horn player or hornist. Pitch is controlled through the combination of the following factors: speed of air through the instrument (controlled by the player's lungs and thoracic diaphragm); diameter and tension of lip aperture (by the player's lip muscles—the embouchure) in the mouthpiece; plus, in a modern horn, the operation of Brass instrument valve, valves by the left hand, which route the air into extra sections of tubing. Most horns have lever-operated rotary valves, but some, especially older horns, use piston valves (similar to a trumpet's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Horn
The French horn (since the 1930s known simply as the horn in professional music circles) is a brass instrument made of tubing wrapped into a coil with a flared bell. The double horn in F/B (technically a variety of German horn) is the horn most often used by players in professional orchestras and bands, although the descant and triple horn have become increasingly popular. A musician who plays a horn is known as a list of horn players, horn player or hornist. Pitch is controlled through the combination of the following factors: speed of air through the instrument (controlled by the player's lungs and thoracic diaphragm); diameter and tension of lip aperture (by the player's lip muscles—the embouchure) in the mouthpiece; plus, in a modern horn, the operation of Brass instrument valve, valves by the left hand, which route the air into extra sections of tubing. Most horns have lever-operated rotary valves, but some, especially older horns, use piston valves (similar to a trumpet's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
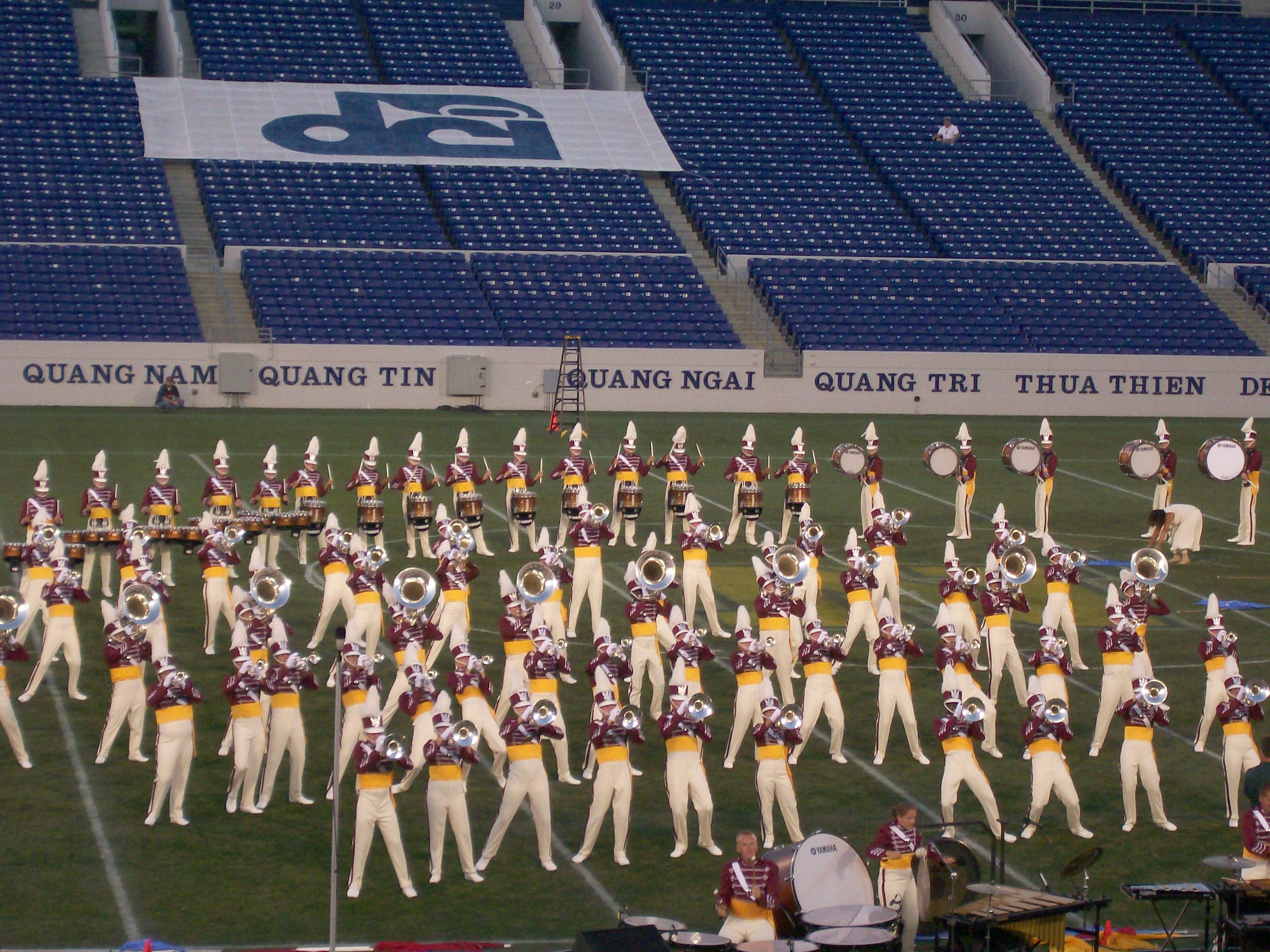
Marching Band
A marching band is a group of instrumental musicians who perform while marching, often for entertainment or competition. Instrumentation typically includes brass, woodwind, and percussion instruments. Most marching bands wear a uniform, often of a military-style, that includes an associated organization's colors, name or symbol. Most high school marching bands, and some college marching bands, are accompanied by a color guard, a group of performers who add a visual interpretation to the music through the use of props, most often flags, rifles, and sabres. Marching bands are generally categorized by function, size, age, instrumentation, marching style, and type of show they perform. In addition to traditional parade performances, many marching bands also perform field shows at sporting events and marching band competitions. Increasingly, marching bands perform indoor concerts that implement many songs, traditions, and flair from outside performances. In some cases, at higher ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
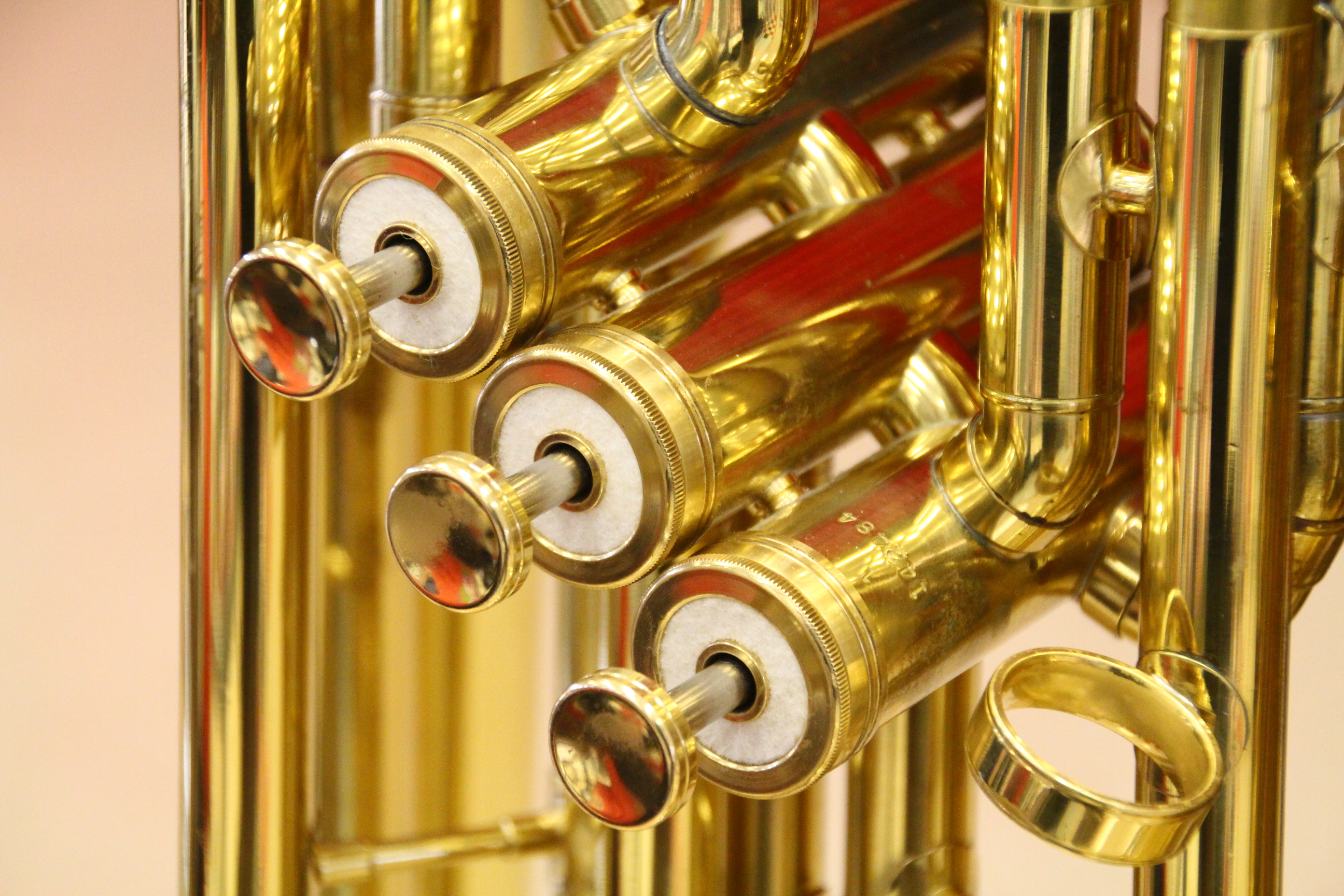
Brass Instrument
A brass instrument is a musical instrument that produces sound by sympathetic vibration of air in a tubular resonator in sympathy with the vibration of the player's lips. Brass instruments are also called labrosones or labrophones, from Latin and Greek elements meaning 'lip' and 'sound'. There are several factors involved in producing different pitches on a brass instrument. Slides, valves, crooks (though they are rarely used today), or keys are used to change vibratory length of tubing, thus changing the available harmonic series, while the player's embouchure, lip tension and air flow serve to select the specific harmonic produced from the available series. The view of most scholars (see organology) is that the term "brass instrument" should be defined by the way the sound is made, as above, and not by whether the instrument is actually made of brass. Thus one finds brass instruments made of wood, like the alphorn, the cornett, the serpent and the didgeridoo, while some ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brass Instrument
A brass instrument is a musical instrument that produces sound by sympathetic vibration of air in a tubular resonator in sympathy with the vibration of the player's lips. Brass instruments are also called labrosones or labrophones, from Latin and Greek elements meaning 'lip' and 'sound'. There are several factors involved in producing different pitches on a brass instrument. Slides, valves, crooks (though they are rarely used today), or keys are used to change vibratory length of tubing, thus changing the available harmonic series, while the player's embouchure, lip tension and air flow serve to select the specific harmonic produced from the available series. The view of most scholars (see organology) is that the term "brass instrument" should be defined by the way the sound is made, as above, and not by whether the instrument is actually made of brass. Thus one finds brass instruments made of wood, like the alphorn, the cornett, the serpent and the didgeridoo, while some ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drum And Bugle Corps (modern)
A modern drum and bugle corps is a musical marching unit consisting of brass instruments, percussion instruments, electronic instruments, and color guard. Typically operating as independent non-profit organizations, corps perform in competitions, parades, festivals, and other civic functions. Participants of all ages are represented within the corps activity, but the majority are between the ages of 13 and 22 and are members of corps within Drum Corps International or Drum Corps Associates. Competitive summer drum corps participate in summer touring circuits, such as Drum Corps International (DCI) and Drum Corps Associates (DCA). Corps prepare a new show each year, approximately 8–12 minutes in length, and refine it throughout the summer tour. Shows are performed on football fields and are judged in various musical and visual categories, or "captions". Musical repertoires vary widely among corps and include symphonic, jazz, big band, contemporary, rock, wind band, vocal, r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Concert Band
A concert band, also called a wind band, wind ensemble, wind symphony, wind orchestra, symphonic band, the symphonic winds, or symphonic wind ensemble, is a performing ensemble consisting of members of the woodwind, brass, and percussion families of instruments, and occasionally including the harp, double bass, or bass guitar. On rare occasions, additional, non-traditional instruments may be added to such ensembles such as piano, synthesizer, or electric guitar. Concert band music generally includes original wind compositions, concert marches, transcriptions of orchestral arrangements, light music, and popular music. Though the concert band does have similar instrumentation to the marching band, a marching band's main purpose is to perform while marching. In contrast, a concert band strictly performs as a stationary ensemble. Origins The origins of concert band can be traced back to the French Revolution, in which large bands would often gather for patriotic festivals and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parabola
In mathematics, a parabola is a plane curve which is mirror-symmetrical and is approximately U-shaped. It fits several superficially different mathematical descriptions, which can all be proved to define exactly the same curves. One description of a parabola involves a point (the focus) and a line (the directrix). The focus does not lie on the directrix. The parabola is the locus of points in that plane that are equidistant from both the directrix and the focus. Another description of a parabola is as a conic section, created from the intersection of a right circular conical surface and a plane parallel to another plane that is tangential to the conical surface. The line perpendicular to the directrix and passing through the focus (that is, the line that splits the parabola through the middle) is called the "axis of symmetry". The point where the parabola intersects its axis of symmetry is called the "vertex" and is the point where the parabola is most sharply curved. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
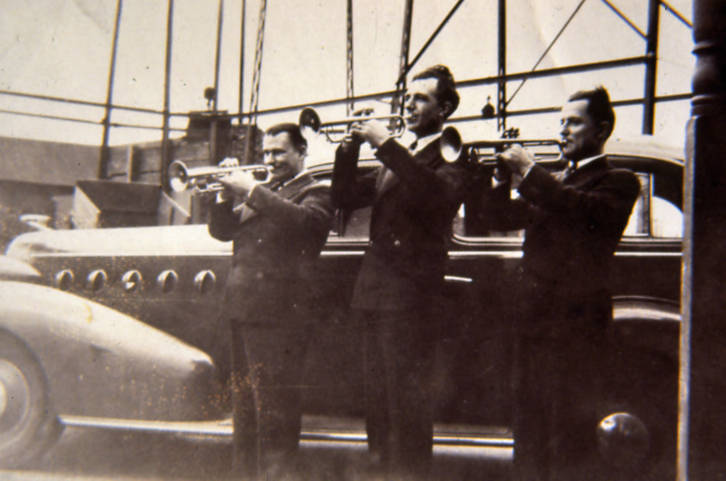
Trumpet
The trumpet is a brass instrument commonly used in classical and jazz ensembles. The trumpet group ranges from the piccolo trumpet—with the highest register in the brass family—to the bass trumpet, pitched one octave below the standard B or C trumpet. Trumpet-like instruments have historically been used as signaling devices in battle or hunting, with examples dating back to at least 1500 BC. They began to be used as musical instruments only in the late 14th or early 15th century. Trumpets are used in art music styles, for instance in orchestras, concert bands, and jazz ensembles, as well as in popular music. They are played by blowing air through nearly-closed lips (called the player's embouchure), producing a "buzzing" sound that starts a standing wave vibration in the air column inside the instrument. Since the late 15th century, trumpets have primarily been constructed of brass tubing, usually bent twice into a rounded rectangular shape. There are many distinc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mouthpiece (brass)
The mouthpiece on brass instruments is the part of the instrument placed on the player's lips. The mouthpiece is a circular opening that is enclosed by a rim and that leads to the instrument via a semi-spherical or conical cavity called the cup. From the cup, a smaller opening (the throat) leads into a tapered cylindrical passage called the backbore. The backbore is housed in a tapered shank, which is inserted into an opening called the receiver on the main body of the instrument. On all brass instruments, sound is produced when the player's vibrating lips (embouchure) cause the air column inside the instrument to vibrate. This is done by pressing the lips together and blowing air through them in order to produce a 'buzz.' The mouthpiece is where this lip vibration takes place. On most instruments, the mouthpiece can be detached from the main instrument in order to facilitate putting the instrument in its case, to use different mouthpieces with the same instrument, or to 'play' th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |