|
Mellifont
Mellifont Abbey ( ga, An Mhainistir Mhór, literally 'the Big Monastery'), was a Cistercian abbey located close to Drogheda in County Louth, Ireland. It was the first abbey of the order to be built in Ireland. In 1152, it hosted the Synod of Kells-Mellifont. After its dissolution in 1539, the abbey became a private manor house. This saw the signing of the Treaty of Mellifont in 1603 and served as William of Orange's headquarters in 1690 during the Battle of the Boyne. Today, the ruined abbey is a National monument of Ireland and accessible to the public. The English language name for the monastery, 'Mellifont', comes from the Latin phrase '' Melli-fons'', meaning 'Font of Honey'. Location Mellifont Abbey sits on the banks of the River Mattock, some 10 km (6 miles) north-west of Drogheda. History Origins The abbey was founded in 1142 on the orders of Saint Malachy, Archbishop of Armagh. By 1170, Mellifont had one hundred monks and three hundred lay brothers. The abbey ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mellifont Abbey Ireland Chapter House Doorway 1755
Mellifont Abbey ( ga, An Mhainistir Mhór, literally 'the Big Monastery'), was a Cistercian abbey located close to Drogheda in County Louth, Ireland. It was the first abbey of the order to be built in Ireland. In 1152, it hosted the Synod of Kells-Mellifont. After its dissolution in 1539, the abbey became a private manor house. This saw the signing of the Treaty of Mellifont in 1603 and served as William of Orange's headquarters in 1690 during the Battle of the Boyne. Today, the ruined abbey is a National monument of Ireland and accessible to the public. The English language name for the monastery, 'Mellifont', comes from the Latin phrase '' Melli-fons'', meaning 'Font of Honey'. Location Mellifont Abbey sits on the banks of the River Mattock, some 10 km (6 miles) north-west of Drogheda. History Origins The abbey was founded in 1142 on the orders of Saint Malachy, Archbishop of Armagh. By 1170, Mellifont had one hundred monks and three hundred lay brothers. The abbey ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cistercians
The Cistercians, () officially the Order of Cistercians ( la, (Sacer) Ordo Cisterciensis, abbreviated as OCist or SOCist), are a Catholic religious order of monks and nuns that branched off from the Benedictines and follow the Rule of Saint Benedict, as well as the contributions of the highly-influential Saint Bernard of Clairvaux, known as the Latin Rule. They are also known as Bernardines, after Saint Bernard himself, or as White Monks, in reference to the colour of the "cuculla" or cowl (choir robe) worn by the Cistercians over their habits, as opposed to the black cowl worn by Benedictines. The term ''Cistercian'' derives from ''Cistercium,'' the Latin name for the locale of Cîteaux, near Dijon in eastern France. It was here that a group of Benedictine monks from the monastery of Molesme founded Cîteaux Abbey in 1098, with the goal of following more closely the Rule of Saint Benedict. The best known of them were Robert of Molesme, Alberic of Cîteaux and the English ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synod Of Kells-Mellifont
The Synod of Kells (, ) took place in 1152, under the presidency of Giovanni Cardinal Paparoni, and continued the process begun at the Synod of Ráth Breasail (1111) of reforming the Irish church. The sessions were divided between the abbeys of Kells and Mellifont, and in later times the synod has been called the Synod of Kells-Mellifont and the Synod of Mellifont-Kells. Its main effect was to increase the number of archbishops from two to four, and to redefine the number and size of dioceses. The Primacy of Ireland was granted to the Archdiocese of Armagh. Background Máel Máedóc Ua Morgair (Saint Malachy) was made a priest in 1119, as vicar to Celsus. His first sees were Down and Connor, and he was located at Bangor Abbey. On the death of Celsus in 1129, Malachy was nominated as his successor at Armagh, now the prime see in Ireland. An internal church dispute over the succession and proposals for reform obliged him to concede the position to Gelasius. In 1137, Gelasi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treaty Of Mellifont
The Treaty of Mellifont ( ga, Conradh na Mainistreach Móire), also known as the Articles of Mellifont, was signed in 1603 and ended the Nine Years' War which took place in the Kingdom of Ireland from 1594 to 1603. End of war Following the English victory in the Battle of Kinsale, the leaders fighting in Cork returned to protect their homelands. The Lord Deputy of Ireland, Charles Blount, 8th Baron Mountjoy, had succeeded where his predecessor, Robert Devereux, 2nd Earl of Essex, had failed. However, Mountjoy knew that as long as Hugh O'Neill was still in hiding, O'Neill was still a threat. Although most of the lesser chiefs allied with him had been compelled to submit, Rory O'Donnell, Brian Oge O'Rourke, Cuchonnacht Maguire (brother of Hugh Maguire), and Donal Cam O'Sullivan Beare remained loyal to ''The Great Earl''. During the spring of 1603, Lord Mountjoy concentrated his campaign in the northern counties and the province of Leinster. He ordered all land be scorched. Harv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
County Louth
County Louth ( ; ga, An Lú) is a coastal county in the Eastern and Midland Region of Ireland, within the province of Leinster. Louth is bordered by the counties of Meath to the south, Monaghan to the west, Armagh to the north and Down to the north-east, across Carlingford Lough. It is the smallest county in Ireland by land area and the 17th most populous, with just over 139,100 residents as of 2022. The county is named after the village of Louth. Louth County Council is the local authority for the county. History County Louth is named after the village of Louth, which in turn is named after Lugh, a god of the ancient Irish. Historically, the placename has had various spellings; , , and (see Historic Names List, for full listing). is the modern simplified spelling. The county is steeped in myth, legend and history, and is a setting in the epic. Later it saw the influence of the Vikings, as seen in the name of Carlingford Lough. They also established a longphort a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saint Malachy
Malachy (}; Modern ga, Maelmhaedhoc Ó Morgair; ) ( 1094 – 2 November 1148) is an Irish saint who was Archbishop of Armagh, to whom were attributed several miracles and an alleged vision of 112 popes later attributed to the apocryphal (i.e. of doubtful authenticity) Prophecy of the Popes. Malachy was the first native-born Irish saint to be formally canonised. His brother was Gilla Críst Ua Morgair, who later became Bishop Christian of Clogher from 1126 to 1138. Life Máel Máedóc, whose surname was Ua Morgair, was born in Armagh in 1094. Bernard of Clairvaux describes him as having noble birth. He was baptised Máel Máedóc, meaning 'devotee or servant' of Máedóc (Máedóc of Ferns) which was rendered ''Malachus'' in Latin (and subsequently as ''Malachy'' in English) and was trained under the famous recluse Imhar O'Hagan, subsequently Abbot of Armagh. Imhar was in sympathy with the aims of those who sought to reform the Irish church, and it was probably through ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Collon
Collon () is a village and townland in the south west corner of County Louth, Ireland, on the N2 road (Ireland), N2 national primary road. The village is home to the Cistercian Abbey of New Mellifont, and to Collon House, the ancestral home of the Foster family. History The Church of Ireland parish church at the lower end was built in 1810 to a design by Daniel Augustus Beaufort who was the rector between 1789 and 1821. There is a memorial in the graveyard at the front of the church to men of the parish who died during the 1914–18 Great War, inscribed on the front is the name of Lt. James Emerson Victoria Cross, V.C. who was born in the village. The church has been described as "dramatic and atmospheric" and hosted the 2008 Ardee Baroque Festival. The Foster Family first settled in Dunleer in County Louth in 1660 until they moved into their estate in the heart of Collon in 1744, which can still be seen today. At the time the family estate was our 6,000 acres. The Foster famil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Donnchad Ua Cearbhall
Achaidh Leithdeircc (modern spelling ''Achadh Leith-dheirg'') is an ancient location in Ireland reputed to be the site of a historic battle, or series of battles, around the year 331AD, in which the forces of the Three Collas along with men of Connaught eventually conquered vast tracts of territory from the tribes of the Ulaid. The prehistoric royal site of Navan Fort was burnt and plundered and ultimately this territory would re-emerge as part of the kingdom or federation of Airgíalla. The Battle of Achadh Leith-dheirg was fought in the territory of "Fearnmhagh", according to 19th-century Celtic scholar John O'Donovan. The place of the battle has been disputed between Fearn-mhagh, County Monaghan and Aghaderg, near Loughbrickland, County Down. Sources for the Battle of Achadh Leith-dheirg The 17th-century historian Geoffrey Keating in his "History of Ireland", in a stylized narrative of events, states: The Annals of the Four Masters, in the 19th-century translation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
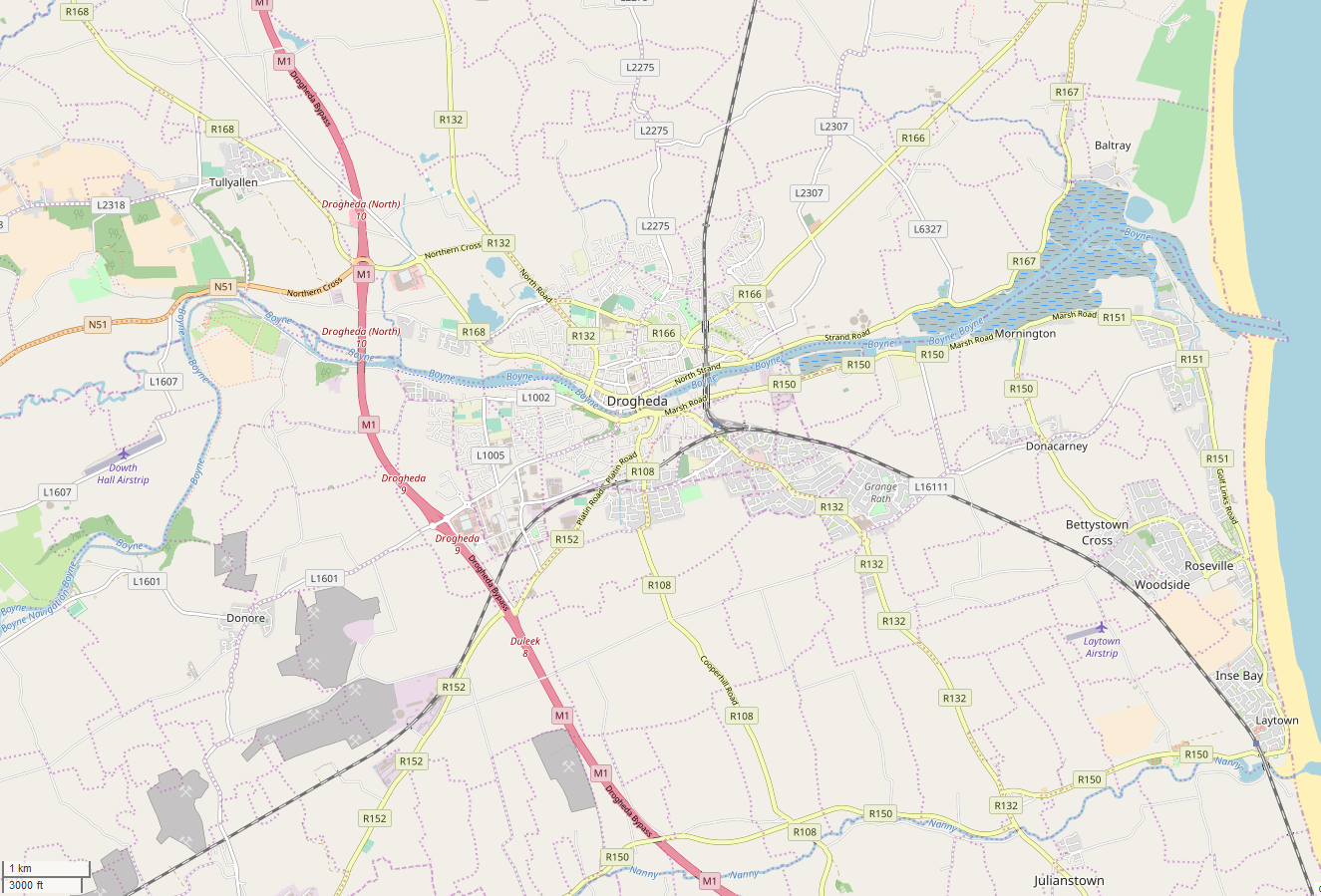
Drogheda
Drogheda ( , ; , meaning "bridge at the ford") is an industrial and port town in County Louth on the east coast of Ireland, north of Dublin. It is located on the Dublin–Belfast corridor on the east coast of Ireland, mostly in County Louth but with the south fringes of the town in County Meath, north of Dublin. Drogheda has a population of approximately 41,000 inhabitants (2016), making it the List of settlements on the island of Ireland by population, eleventh largest settlement by population in all of Ireland, and the largest town in the Republic of Ireland by both population and area. It is the last bridging point on the River Boyne before it enters the Irish Sea. The UNESCO World Heritage Site of Newgrange is located west of the town. Drogheda was founded as two separately administered towns in two different territories: Drogheda-in-Kingdom of Meath, Meath (i.e. the Lordship of Meath, Lordship and Liberty of Meath, from which a charter was granted in 1194) and Drogheda ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cistercian Architecture
Cistercian architecture is a style of architecture associated with the churches, monasteries and abbeys of the Roman Catholic Cistercian Order. It was heavily influenced by Abbot Bernard of Clairvaux (d. 1153), who believed that churches should avoid superfluous ornamentation so as not to distract from prayer. Cistercian architecture was simple and utilitarian. Although a few images of religious subjects were allowed, such as the crucifix, elaborate figures common in medieval churches were prohibited. Bernard noted their capacity for distracting monks in a famous letter. Early Cistercian architecture shows a transition between Romanesque and Gothic architecture. Later abbeys were constructed in Renaissance and Baroque styles, which were more ornate by nature. In terms of construction, buildings were made where possible of smooth, pale, stone. Columns, pillars and windows fell at the same base level, and if plastering was done at all, it was kept extremely simple. The sanctuary k ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synod
A synod () is a council of a Christian denomination, usually convened to decide an issue of doctrine, administration or application. The word ''wikt:synod, synod'' comes from the meaning "assembly" or "meeting" and is analogous with the Latin word meaning "council". Originally, synods were meetings of bishops, and the word is still used in that sense in Roman Catholic Church, Catholicism, Oriental Orthodoxy and Eastern Orthodoxy. In modern usage, the word often refers to the governing body of a particular church, whether its members are meeting or not. It is also sometimes used to refer to a church that is governed by a synod. Sometimes the phrase "general synod" or "general council" refers to an ecumenical council. The word ''synod'' also refers to the standing council of high-ranking bishops governing some of the autocephaly, autocephalous Eastern Orthodox Church, Eastern Orthodox churches. Similarly, the day-to-day governance of patriarchal and major archbishop, major arch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gold
Gold is a chemical element with the symbol Au (from la, aurum) and atomic number 79. This makes it one of the higher atomic number elements that occur naturally. It is a bright, slightly orange-yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile metal in a pure form. Chemically, gold is a transition metal and a group 11 element. It is one of the least reactive chemical elements and is solid under standard conditions. Gold often occurs in free elemental ( native state), as nuggets or grains, in rocks, veins, and alluvial deposits. It occurs in a solid solution series with the native element silver (as electrum), naturally alloyed with other metals like copper and palladium, and mineral inclusions such as within pyrite. Less commonly, it occurs in minerals as gold compounds, often with tellurium (gold tellurides). Gold is resistant to most acids, though it does dissolve in aqua regia (a mixture of nitric acid and hydrochloric acid), forming a soluble tetrachloroaurate anion. Gold is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |