|
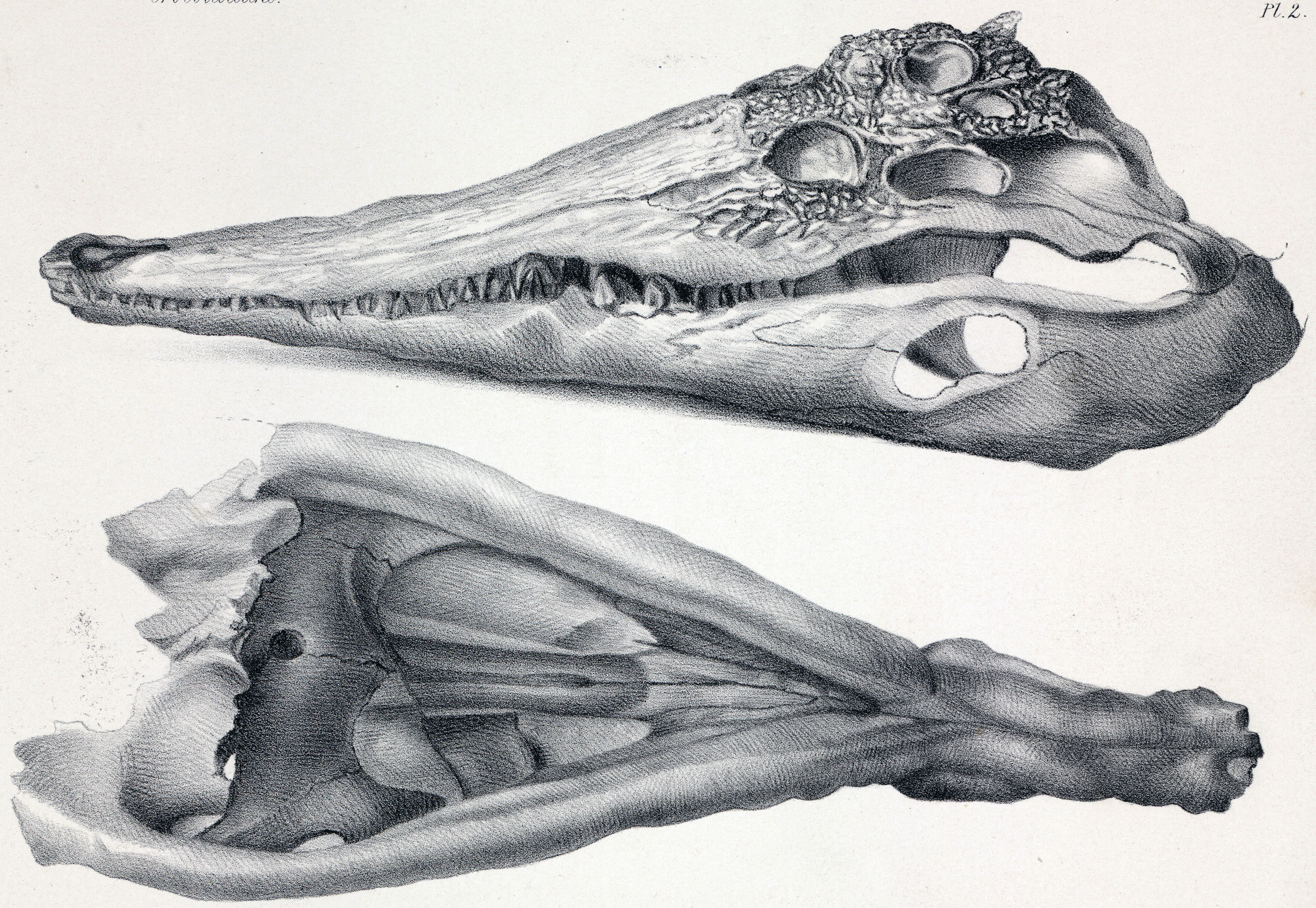
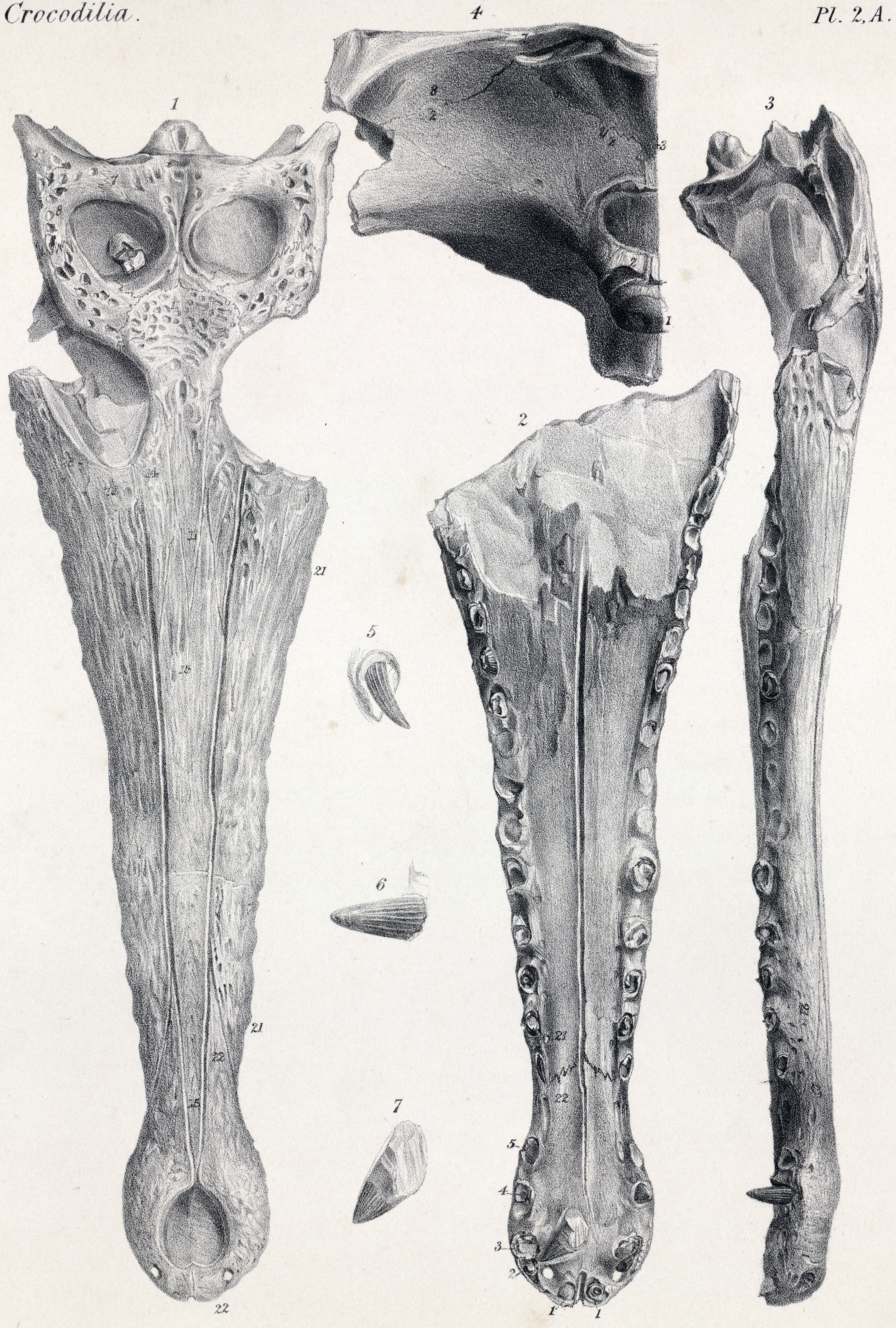
Melitosaurus
''Melitosaurus'' is an extinct genus of gavialid crocodylian discovered in Gozo, Malta in Early Miocene Aquitanian stage marine limestone rock in 1850. It is related to the extant (living) False gharial and a member of the same subfamily Tomistominae, as shown in the cladogram A cladogram (from Greek ''clados'' "branch" and ''gramma'' "character") is a diagram used in cladistics to show relations among organisms. A cladogram is not, however, an evolutionary tree because it does not show how ancestors are related to d ... below: References {{Taxonbar, from=Q41155443, from2=Q41165947 Gavialidae Prehistoric pseudosuchian genera Fossil taxa described in 1850 Taxa named by Richard Owen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gavialidae
Gavialidae is a family (biology), family of large semiaquatic crocodilians with elongated, narrow snouts. Gavialidae consists of two extant taxon, living species, the gharial (''Gavialis gangeticus'') and the false gharial (''Tomistoma schlegelii''), both occurring in Asia. Many extinct members are known from a broader range, including the recently extinct ''Hanyusuchus''. Gavialids are generally regarded as lacking the jaw strength to capture the large mammalian prey favoured by crocodiles and alligators of similar size so their thin snout is best used to catch fish, however the false gharial has been found to have a Generalist and specialist species, generalist diet with mature adults preying upon larger vertebrates, such as Ungulate, ungulates. Taxonomy The family Gavialidae was proposed by Arthur Adams (zoologist), Arthur Adams in 1854 for reptiles with a very long and slender muzzle, webbed feet and nearly equal teeth. It is currently recognized as a crown group, meaning that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gavialid
Gavialidae is a family of large semiaquatic crocodilians with elongated, narrow snouts. Gavialidae consists of two living species, the gharial (''Gavialis gangeticus'') and the false gharial (''Tomistoma schlegelii''), both occurring in Asia. Many extinct members are known from a broader range, including the recently extinct ''Hanyusuchus''. Gavialids are generally regarded as lacking the jaw strength to capture the large mammalian prey favoured by crocodiles and alligators of similar size so their thin snout is best used to catch fish, however the false gharial has been found to have a generalist diet with mature adults preying upon larger vertebrates, such as ungulates. Taxonomy The family Gavialidae was proposed by Arthur Adams in 1854 for reptiles with a very long and slender muzzle, webbed feet and nearly equal teeth. It is currently recognized as a crown group, meaning that it only includes the last common ancestor of all extant (living) gavialids (the gharial and false gha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miocene
The Miocene ( ) is the first geological epoch of the Neogene Period and extends from about (Ma). The Miocene was named by Scottish geologist Charles Lyell; the name comes from the Greek words (', "less") and (', "new") and means "less recent" because it has 18% fewer modern marine invertebrates than the Pliocene has. The Miocene is preceded by the Oligocene and is followed by the Pliocene. As Earth went from the Oligocene through the Miocene and into the Pliocene, the climate slowly cooled towards a series of ice ages. The Miocene boundaries are not marked by a single distinct global event but consist rather of regionally defined boundaries between the warmer Oligocene and the cooler Pliocene Epoch. During the Early Miocene, the Arabian Peninsula collided with Eurasia, severing the connection between the Mediterranean and Indian Ocean, and allowing a faunal interchange to occur between Eurasia and Africa, including the dispersal of proboscideans into Eurasia. During the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crocodyloidea
Crocodyloidea is one of three superfamilies of crocodilians, the other two being Alligatoroidea and Gavialoidea, and it includes the crocodiles. Crocodyloidea may also include the extinct Mekosuchinae, native to Australasia from the Eocene to the Holocene, although this is disputed. Classification Cladistically, it is defined as ''Crocodylus niloticus'' (the Nile crocodile) and all crocodylians more closely related to ''C. niloticus'' than to either ''Alligator mississippiensis'' (the American alligator) or ''Gavialis gangeticus'' (the gharial). This is a stem-based taxon, stem-based definition for crocodiles Crocodiles (family Crocodylidae) or true crocodiles are large semiaquatic reptiles that live throughout the tropics in Africa, Asia, the Americas and Australia. The term crocodile is sometimes used even more loosely to include all extant memb ..., and is more inclusive than the crown group Crocodylidae. As a crown group, Crocodylidae only includes the last common anc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tomistoma Lusitanica
''Tomistoma'' is a genus of gavialid crocodilians. They are noted for their long narrow snouts used to catch fish, similar to the gharial. ''Tomistoma'' contains one extant (living) member, the false gharial (''Tomistoma schlegelii''), as well as potentially several extinct species: ''T. cairense'', ''T. lusitanicum'', ''T. taiwanicus'', ''T. coppensi'', and ''T. dowsoni''. However, these species may need to be reclassified to different genera as studies have shown them to be paraphyletic. Unlike the gharial, the false gharial's snout broadens considerably towards the base and so is more similar to those of true crocodiles than the gharial, whose osteology indicated a distinct lineage from all other living crocodilians.Piras, P., Colangelo, P., Adams, D. C., Buscalioni, A., Cubo, J., Kotsakis, T., & Raia, P. (2010). ''The Gavialis–Tomistoma debate: the contribution of skull ontogenetic allometry and growth trajectories to the study of crocodylian relationships''. Evolution & d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
False Gharial
The false gharial (''Tomistoma schlegelii''), also known by the names Malayan gharial, Sunda gharial and tomistoma is a freshwater crocodilian of the family Gavialidae native to Peninsular Malaysia, Borneo, Sumatra and Java. It is listed as Vulnerable on the IUCN Red List, as the global population is estimated at around 2,500 to 10,000 mature individuals. The specific name ''schlegelii'' honors Hermann Schlegel. Taxonomy The scientific name ''Crocodilus (Gavialis) schlegelii'' was proposed by Salomon Müller in 1838 who described a specimen collected in Borneo. In 1846, he proposed to use the name ''Tomistoma schlegelii'', if it needs to be placed in a distinct genus. The genus ''Tomistoma'' potentially also contains several extinct species like ''T. cairense'', ''T. lusitanicum'', ''T. taiwanicus'', and ''T. coppensi''. However, these species may need to be reclassified to different genera as are paraphyletic. The false gharial's snout broadens considerably towards the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maomingosuchus Petrolica
''Maomingosuchus'' is an extinct genus of gavialoid crocodylian from Late Eocene of Southeast Asia. It was discovered in Priabonian-aged deposits of China and possibly also Thailand. The type species, originally ''Tomistoma petrolica,'' was named in 1958 and was redescribed as ''Maomingosuchus'' in 2017. A second species, ''Maomingosuchus acutirostris'', was described in 2022 from middle-upper Eocence deposits (late Bartonian–Priabonian age, 39–35 Ma) of the Na Duong Basin in northern Vietnam. It is proposed to be a basal member of Gavialoidea, or alternatively within the family Tomistominae Tomistominae is a subfamily of crocodylians that includes one living species, the false gharial. Many more extinct species are known, extending the range of the subfamily back to the Eocene epoch. In contrast to the false gharial, which is a fre .... References Crocodilians Eocene crocodylomorphs Fossil taxa described in 2017 Eocene reptiles of Asia Prehistoric pseu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tomistoma Coppensi
''Tomistoma'' is a genus of gavialid crocodilians. They are noted for their long narrow snouts used to catch fish, similar to the gharial. ''Tomistoma'' contains one extant (living) member, the false gharial (''Tomistoma schlegelii''), as well as potentially several extinct species: ''T. cairense'', ''T. lusitanicum'', ''T. taiwanicus'', ''T. coppensi'', and ''T. dowsoni''. However, these species may need to be reclassified to different genera as studies have shown them to be paraphyletic. Unlike the gharial, the false gharial's snout broadens considerably towards the base and so is more similar to those of true crocodiles than the gharial, whose osteology indicated a distinct lineage from all other living crocodilians.Piras, P., Colangelo, P., Adams, D. C., Buscalioni, A., Cubo, J., Kotsakis, T., & Raia, P. (2010). ''The Gavialis–Tomistoma debate: the contribution of skull ontogenetic allometry and growth trajectories to the study of crocodylian relationships''. Evolution & d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tomistoma Cairense
''Tomistoma cairense'' is an extinct species of gavialoid crocodilian from the Lutetian stage of the Eocene era. It lived in North East Africa, especially Egypt. Remains of ''T. cairense'' have been found in the Mokattam Formation, in Mokattam, Egypt. ''Tomistoma cairense'' did not have a Maxilla process within their lacrimal gland, whereas all extant (living) crocodilians do. Below is a cladogram based morphological studies comparing skeletal features that shows ''Tomistoma cairense'' as a member of Tomistominae, related to the false gharial: Based on morphological studies of extinct taxa, the tomistomines (including the living false gharial) were long thought to be classified as crocodiles and not closely related to gavialoids. However, recent molecular studies using DNA sequencing have consistently indicated that the false gharial (''Tomistoma'') (and by inference other related extinct forms in Tomistominae) actually belong to Gavialoidea (and Gavialidae). Below is a clad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kentisuchus Spenceri
''Kentisuchus'' is an extinct genus of gavialoid crocodylian, traditionally regarded as a member of the subfamily Tomistominae. Fossils have been found from England and France that date back to the early Eocene. The genus has also been recorded from Ukraine, but it unclear whether specimens from Ukraine are referable to ''Kentisuchus''. Species The genus ''Kentisuchus'' was erected by Charles Mook in 1955 for the species ''"Crocodylus" toliapicus'', described by Richard Owen, in 1849. William Buckland named ''"Crocodylus" spenceri'' on the basis of a partial skull found from the Isle of Sheppey in Kent, England. In 1888 Richard Lydekker considered ''"C." toliapicus'' synonymous with ''"C." champsoides'' and ''"C." arduini'', named by De Zigno, and reapplied the name ''"C." spenceri'' to all of these species. The genus name ''Kentisuchus'' was constructed only after it was realized that these specimens were clearly distinct from the genus ''Crocodylus'' and that some specimens o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kentisuchus Astrei
''Kentisuchus'' is an extinct genus of gavialoid crocodylian, traditionally regarded as a member of the subfamily Tomistominae. Fossils have been found from England and France that date back to the early Eocene. The genus has also been recorded from Ukraine, but it unclear whether specimens from Ukraine are referable to ''Kentisuchus''. Species The genus ''Kentisuchus'' was erected by Charles Mook in 1955 for the species ''"Crocodylus" toliapicus'', described by Richard Owen, in 1849. William Buckland named ''"Crocodylus" spenceri'' on the basis of a partial skull found from the Isle of Sheppey in Kent, England. In 1888 Richard Lydekker considered ''"C." toliapicus'' synonymous with ''"C." champsoides'' and ''"C." arduini'', named by De Zigno, and reapplied the name ''"C." spenceri'' to all of these species. The genus name ''Kentisuchus'' was constructed only after it was realized that these specimens were clearly distinct from the genus ''Crocodylus'' and that some specimens o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |