|
Melithaeidae
''Melithaeidae'' is a family of corals in the suborder Scleraxonia. Members of the family are commonly known as sea fans and are found on reefs in the tropical regions of the Indo-Pacific.Family Melithaeidae Marine Species Identification Portal. Retrieved 2012-02-22. Description Members of the family Melithaeidae are arborescent corals forming fans, bushes or trees. The axis or main skeletal "trunk" is jointed, there being nodes, flexible horny joints, separated by internodes composed of hard, calcareous material. The branches divide dichotomously at the nodes and these are often swollen. The minute calcareous spicul ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Melithaeidae
''Melithaeidae'' is a family of corals in the suborder Scleraxonia. Members of the family are commonly known as sea fans and are found on reefs in the tropical regions of the Indo-Pacific.Family Melithaeidae Marine Species Identification Portal. Retrieved 2012-02-22. Description Members of the family Melithaeidae are arborescent corals forming fans, bushes or trees. The axis or main skeletal "trunk" is jointed, there being nodes, flexible horny joints, separated by internodes composed of hard, calcareous material. The branches divide dichotomously at the nodes and these are often swollen. The minute calcareous spicul ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Melithaea Ochracea
''Melithaea ochracea'' is a species of colonial soft coral in the family Melithaeidae, commonly known as knotted fan coral. It grows in tree-like fans on coral reefs in the South China Sea. It is used in the jewellery industry under the name red spongy coral. Description Colonies of ''Melithaea ochracea'' are arborescent and usually grow to about long although much larger specimens can be found. They grow in one plane and have a branching, fan-shaped structure. The main skeletal stalk and branches are jointed, with swellings at the larger joints. The internodes are composed of hard, calcareous material while the joints are flexible and made of a horny material. The skeleton is covered by a flexible membrane, the mesoglea, which contains minute calcareous spicules or sclerites. The identity of these is important for distinguishing between different closely related species. In ''Melithaea ochracea'', they include capstans, double discs, disc-spindles and unilaterally spinose spin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scleraxonia
Scleraxonia is a suborder of corals, a member of the phylum Cnidaria. Characteristics Members of Scleraxonia have a skeletal axis made of calcified spicules, organic fibres or both, which may be separate, linked or fused together. Families and genera There are nine recognised families in this suborder and over thirty genera, with four families (Anthothelidae, Briareidae, Coralliidae and Subergorgiidae) containing some deep-water species and two families (Paragorgiidae and Parisididae) being exclusively deep water. Families and genera in this suborder include: * Anthothelidae Broch, 1916 ** '' Alertigorgia'' Kükenthal, 1908 ** '' Anthothela'' Verrill, 1879 ** '' Briareopsis'' Bayer, 1993 ** '' Erythropodium'' Kölliker, 1865 ** '' Iciligorgia'' Duchassaing, 1870 ** '' Lateothela'' Moore, Alderslade & Miller, 2017 ** '' Solenocaulon'' Gray, 1862 ** '' Stereogorgia'' ** '' Tubigorgia'' Pasternak, 1985 ** '' Williamsium'' Moore, Alderslade & Miller, 2017 * Briareidae Gray, 1859 ** ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Melithaea
''Melithaea'' is a genus of octocorals in the family Melithaeidae. Members of the genus are commonly known as fan corals and are found in the tropical Indo-Pacific region. The type species is ''Melithaea ochracea''.''Melithaea'' Marine Species Identification Portal. Retrieved 2012-02-22. Description Members of the genus ''Melithaea'' are arborescent corals forming fan, bush or tree shapes. The axis or main skeletal "trunk" is jointed, there being nodes, flexible horny joints, separated by internodes composed of hard, calcareous material. The branches divide off at the nodes which are often swollen. The minute calcareous spicules in the f ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bali
Bali () is a province of Indonesia and the westernmost of the Lesser Sunda Islands. East of Java and west of Lombok, the province includes the island of Bali and a few smaller neighbouring islands, notably Nusa Penida, Nusa Lembongan, and Nusa Ceningan to the southeast. The provincial capital, Denpasar, is the most populous city in the Lesser Sunda Islands and the second-largest, after Makassar, in Eastern Indonesia. The upland town of Ubud in Greater Denpasar is considered Bali's cultural centre. The province is Indonesia's main tourist destination, with a significant rise in tourism since the 1980s. Tourism-related business makes up 80% of its economy. Bali is the only Hindu-majority province in Indonesia, with 86.9% of the population adhering to Balinese Hinduism. It is renowned for its highly developed arts, including traditional and modern dance, sculpture, painting, leather, metalworking, and music. The Indonesian International Film Festival is held every year in Bal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Edward Gray
John Edward Gray, FRS (12 February 1800 – 7 March 1875) was a British zoologist. He was the elder brother of zoologist George Robert Gray and son of the pharmacologist and botanist Samuel Frederick Gray (1766–1828). The same is used for a zoological name. Gray was keeper of zoology at the British Museum in London from 1840 until Christmas 1874, before the natural history holdings were split off to the Natural History Museum. He published several catalogues of the museum collections that included comprehensive discussions of animal groups and descriptions of new species. He improved the zoological collections to make them amongst the best in the world. Biography Gray was born in Walsall, but his family soon moved to London, where Gray studied medicine. He assisted his father in writing ''The Natural Arrangement of British Plants'' (1821). After being blackballed by the Linnean Society of London, Gray shifted his interest from botany to zoology. He began his zoologica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Family (biology)
Family ( la, familia, plural ') is one of the eight major hierarchical taxonomic ranks in Linnaean taxonomy. It is classified between order and genus. A family may be divided into subfamilies, which are intermediate ranks between the ranks of family and genus. The official family names are Latin in origin; however, popular names are often used: for example, walnut trees and hickory trees belong to the family Juglandaceae, but that family is commonly referred to as the "walnut family". What belongs to a family—or if a described family should be recognized at all—are proposed and determined by practicing taxonomists. There are no hard rules for describing or recognizing a family, but in plants, they can be characterized on the basis of both vegetative and reproductive features of plant species. Taxonomists often take different positions about descriptions, and there may be no broad consensus across the scientific community for some time. The publishing of new data and opini ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colony (biology)
In biology, a colony is composed of two or more conspecific individuals living in close association with, or connected to, one another. This association is usually for mutual benefit such as stronger defense or the ability to attack bigger prey. Colonies can form in various shapes and ways depending on the organism involved. For instance, the bacterial colony is a cluster of identical cells (clones). These colonies often form and grow on the surface of (or within) a solid medium, usually derived from a single parent cell. Colonies, in the context of development, may be composed of two or more unitary (or solitary) organisms or be modular organisms. Unitary organisms have determinate development (set life stages) from zygote to adult form and individuals or groups of individuals (colonies) are visually distinct. Modular organisms have indeterminate growth forms (life stages not set) through repeated iteration of genetically identical modules (or individuals), and it can be diffic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesoglea
Mesoglea refers to the extracellular matrix found in cnidarians like coral or jellyfish that functions as a hydrostatic skeleton. It is related to but distinct from mesohyl, which generally refers to extracellular material found in sponges. Description The mesoglea is mostly water. Other than water, the mesoglea is composed of several substances including fibrous proteins, like collagen and heparan sulphate proteoglycans. The mesoglea is mostly acellular, but in both cnidaria and ctenophora the mesoglea contains muscle bundles and nerve fibres. Other nerve and muscle cells lie just under the epithelial layers. The mesoglea also contains wandering amoebocytes that play a role in phagocytosing debris and bacteria. These cells also fight infections by producing antibacterial chemicals. The mesoglea may be thinner than either of the cell layers in smaller coelenterates like a hydra or may make up the bulk of the body in larger jellyfish. The mesoglea serves as an internal skeleton, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sclerite
A sclerite (Greek , ', meaning "hard") is a hardened body part. In various branches of biology the term is applied to various structures, but not as a rule to vertebrate anatomical features such as bones and teeth. Instead it refers most commonly to the hardened parts of arthropod exoskeletons and the internal spicules of invertebrates such as certain sponges and soft corals. In paleontology, a scleritome is the complete set of sclerites of an organism, often all that is known from fossil invertebrates. Sclerites in combination Sclerites may occur practically isolated in an organism, such as the sting of a cone shell. Also, they can be more or less scattered, such as tufts of defensive sharp, mineralised bristles as in many marine Polychaetes. Or, they can occur as structured, but unconnected or loosely connected arrays, such as the mineral "teeth" in the radula of many Mollusca, the valves of Chitons, the beak of Cephalopod, or the articulated exoskeletons of Arthropoda. When ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Symbiosis
Symbiosis (from Greek , , "living together", from , , "together", and , bíōsis, "living") is any type of a close and long-term biological interaction between two different biological organisms, be it mutualistic, commensalistic, or parasitic. The organisms, each termed a symbiont, must be of different species. In 1879, Heinrich Anton de Bary defined it as "the living together of unlike organisms". The term was subject to a century-long debate about whether it should specifically denote mutualism, as in lichens. Biologists have now abandoned that restriction. Symbiosis can be obligatory, which means that one or more of the symbionts depend on each other for survival, or facultative (optional), when they can generally live independently. Symbiosis is also classified by physical attachment. When symbionts form a single body it is called conjunctive symbiosis, while all other arrangements are called disjunctive symbiosis."symbiosis." Dorland's Illustrated Medical Dictionary. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
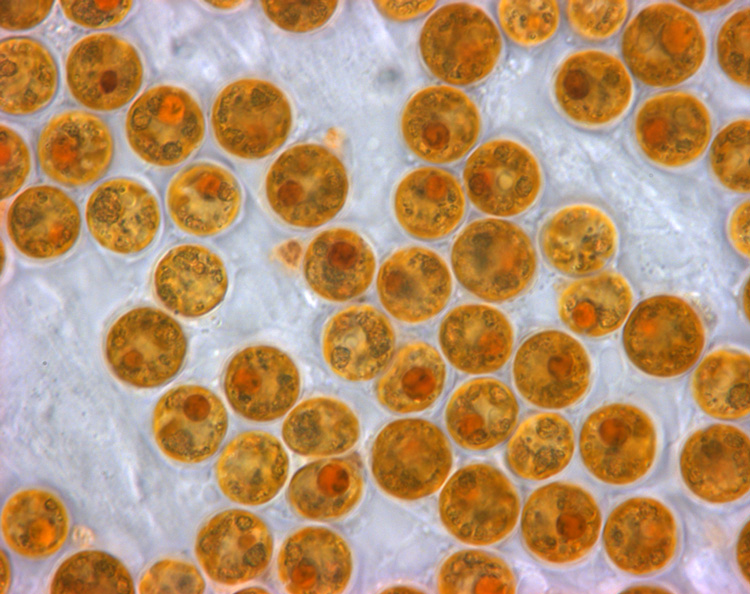
Zooxanthellae
Zooxanthellae is a colloquial term for single-celled dinoflagellates that are able to live in symbiosis with diverse marine invertebrates including demosponges, corals, jellyfish, and nudibranchs. Most known zooxanthellae are in the genus ''Symbiodinium'', but some are known from the genus '' Amphidinium'', and other taxa, as yet unidentified, may have similar endosymbiont affinities. The true ''Zooxanthella'' K.brandt is a mutualist of the radiolarian ''Collozoum inerme'' (Joh.Müll., 1856) and systematically placed in Peridiniales. Another group of unicellular eukaryotes that partake in similar endosymbiotic relationships in both marine and freshwater habitats are green algae zoochlorellae. Zooxanthellae are photosynthetic organisms, which contain chlorophyll a and chlorophyll c, as well as the dinoflagellate pigments peridinin and diadinoxanthin. These provide the yellowish and brownish colours typical of many of the host species. During the day, they provide their host ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |