|
Melica Racemosa
''Melica racemosa'' is a species of grass that is native to South Africa and Lesotho. Description It is perennial and caespitose with culms that are long. The leaf sheaths are tubular and have closed at one end. The leaf blades are erect, flat and long by wide with smooth surfaces. The membraneis eciliate. It has an open, linear, and secund panicle which is long. The main panicle branches are indistinct and almost racemose. The spikelets are cuneate, solitary, and have fertile spikelets that are pediceled. It has an acute apex with a chartaceous fertile lemma with hairs that are long. The spikelets carry 2–3 sterile florets which are cuneate, clumped, and long. Both the upper and lower glumes are elliptic, keelless, membranous, and have an acute apex. The lower glume is long while the upper one is long. Just like the lower glume, the fertile lemma is elliptic, keelless, and is 4–8 mm long. The sterile one though is glabrous. The flowers are fleshy, oblong, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thunb
Carl Peter Thunberg, also known as Karl Peter von Thunberg, Carl Pehr Thunberg, or Carl Per Thunberg (11 November 1743 – 8 August 1828), was a Swedish naturalist and an "apostle" of Carl Linnaeus. After studying under Linnaeus at Uppsala University, he spent seven years travelling in southern Africa and Asia, collecting and describing many plants and animals new to European science, and observing local cultures. He has been called "the father of South African botany", "pioneer of Occidental Medicine in Japan", and the "Japanese Linnaeus". Early life Thunberg was born and grew up in Jönköping, Sweden. At the age of 18, he entered Uppsala University where he was taught by Carl Linnaeus, regarded as the "father of modern taxonomy". Thunberg graduated in 1767 after 6 years of studying. To deepen his knowledge in botany, medicine and natural history, he was encouraged by Linnaeus in 1770 to travel to Paris and Amsterdam. In Amsterdam and Leiden Thunberg met the Dutch botanis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lodicule
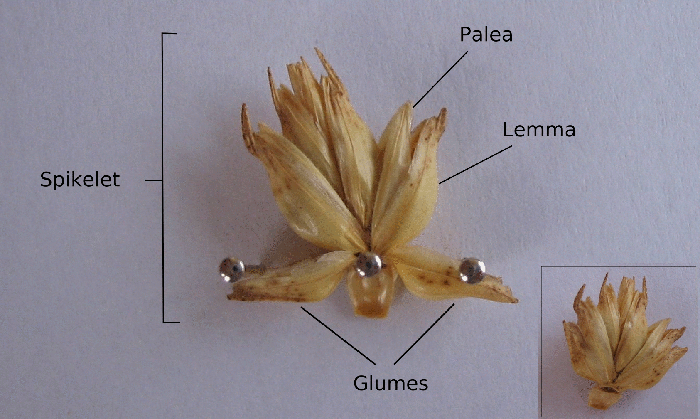
A spikelet, in botany, describes the typical arrangement of the flowers of grasses, sedges and some other Monocots. Each spikelet has one or more florets. The spikelets are further grouped into panicles or spikes. The part of the spikelet that bears the florets is called the rachilla. In grasses In Poaceae, the grass family, a spikelet consists of two (or sometimes fewer) bracts at the base, called glumes, followed by one or more florets. A floret consists of the flower surrounded by two bracts, one external—the lemma—and one internal—the palea. The perianth is reduced to two scales, called lodicules, that expand and contract to spread the lemma and palea; these are generally interpreted to be modified sepals. The flowers are usually hermaphroditic—maize being an important exception—and mainly anemophilous or wind-pollinated, although insects occasionally play a role. Lemma Lemma is a phytomorphological term referring to a part of the spikelet. It is the lowermost ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flora Of Lesotho
{{Lesotho-stub ...
The wildlife of Lesotho is composed of its flora and fauna. Lesotho has 60 species of mammals and 339 species of birds. Fauna Mammals *African leopard *South African cheetah Birds Reptiles Flora Grass is the natural vegetation in Lesotho. The high plateau is covered with montane or subalpine grassland. Red oat grass forms a dry carpet in much of the Drakensberg foothill region. References Sources *Kovtunovich, V. & Ustjuzhanin, P. 2011. On the fauna of the plume moths (Lepidoptera: Pterophoridae) of Lesotho. ''African Invertebrates'' 52 (1): 167-17* * * * * External links Biota of Lesotho Lesotho Lesotho ( ), officially the Kingdom of Lesotho, is a country landlocked country, landlocked as an Enclave and exclave, enclave in South Africa. It is situated in the Maloti Mountains and contains the Thabana Ntlenyana, highest mountains in Sou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flora Of South Africa
The wildlife of South Africa consists of the flora and fauna of this country in southern Africa. The country has a range of different habitat types and an ecologically rich and diverse wildlife, vascular plants being particularly abundant, many of them endemic to the country. There are few forested areas, much savanna grassland, semi-arid Karoo vegetation and the fynbos of the Cape Floristic Region. Famed for its national parks and big game, 297 species of mammal have been recorded in South Africa, as well as 849 species of bird and over 20,000 species of vascular plants. Geography South Africa is located in subtropical southern Africa, lying between 22°S and 35°S. It is bordered by Namibia, Botswana and Zimbabwe to the north, by Mozambique and Eswatini (Swaziland) to the northeast, by the Indian Ocean to the east and south, and the Atlantic Ocean to the west, the coastline extending for more than . The interior of the country consists of a large, nearly flat, plateau with a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Melica
''Melica'' is a genus of perennial Poaceae, grasses known generally as melic or melic grass. They are found in most temperate regions of the world. Melic grasses are clumping to short-rhizome, rhizomatous Poaceae, grasses. They have culm (botany), flowering culms up to tall bearing spikelets of papery flowers. The spikelets have between one and seven fertile flowers with a rudimentary structure at the distal end composed of one to four sterile florets. Some species of melic have corms, lending them the name oniongrass. The genus is most diverse in South America and temperate Asia. Eight species are endemic to China. In North America, most species occur west of the Mississippi River, with exceptions being ''Melica mutica'' and Melica nitens, ''M. nitens'' which occur throughout much of the southeast and lower Midwest respectively. Species Species and hybrids include: * ''Melica altissima'' L. – Siberian melic grass * ''Melica amethystina'' Pourr. * ''Melica animarum'' Muj. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Botanical Research Institute
The National Botanical Research Institute (NBRI) is a research institute of the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR) located in Lucknow, Uttar Pradesh, India. It is engaged in the field of taxonomy and modern biology. History Originally conceptualised and set up as the National Botanic Gardens (NBG) by Professor Kailas Nath Kaul on behalf of the State Government of Uttar Pradesh, it was taken over by the CSIR in 1953. Dr Triloki Nath Khoshoo joined in 1964 as the Assistant Director, shortly afterwards becoming the Director. Initially engaged in research work in the classical botanical disciplines, the NBG went on laying an increasing emphasis in keeping with the national needs and priorities in the field of plant sciences, on its applied and developmental research activities. Due to the untiring efforts of Dr Khoshoo, the institute rose to the stature of being the National Botanical Research Institute in 1978, reflecting the correct nature and extent of its aims a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kirstenbosch National Botanical Garden
Kirstenbosch is an important botanical garden nestled at the eastern foot of Table Mountain in Cape Town. The garden is one of 10 National Botanical Gardens covering five of South Africa's six different biomes and administered by the South African National Biodiversity Institute (SANBI). Prior to 1 September 2004, the institute was known as the National Botanical Institute. Kirstenbosch places a strong emphasis on the cultivation of indigenous plants. When Kirstenbosch was founded in 1913 to preserve the flora native to the South Africa’s territory, it was the first botanical garden in the world with this ethos, at a time when invasive species were not considered an ecological and environmental problem. The garden includes a large conservatory (The Botanical Society Conservatory) exhibiting plants from a number of different regions, including savanna, fynbos, karoo and others. Outdoors, the focus is on plants native to the Cape region, highlighted by the spectacular colle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mountain
A mountain is an elevated portion of the Earth's crust, generally with steep sides that show significant exposed bedrock. Although definitions vary, a mountain may differ from a plateau in having a limited Summit (topography), summit area, and is usually higher than a hill, typically rising at least 300 metres (1,000 feet) above the surrounding land. A few mountains are Monadnock, isolated summits, but most occur in mountain ranges. Mountain formation, Mountains are formed through Tectonic plate, tectonic forces, erosion, or volcanism, which act on time scales of up to tens of millions of years. Once mountain building ceases, mountains are slowly leveled through the action of weathering, through Slump (geology), slumping and other forms of mass wasting, as well as through erosion by rivers and glaciers. High elevations on mountains produce Alpine climate, colder climates than at sea level at similar latitude. These colder climates strongly affect the Montane ecosystems, ecosys ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hill
A hill is a landform that extends above the surrounding terrain. It often has a distinct Summit (topography), summit. Terminology The distinction between a hill and a mountain is unclear and largely subjective, but a hill is universally considered to be not as tall, or as Grade (slope), steep as a mountain. Geographers historically regarded mountains as hills greater than above sea level, which formed the basis of the plot of the 1995 film ''The Englishman who Went up a Hill but Came down a Mountain''. In contrast, hillwalkers have tended to regard mountains as peaks above sea level. The ''Oxford English Dictionary'' also suggests a limit of and Whittow states "Some authorities regard eminences above as mountains, those below being referred to as hills." Today, a mountain is usually defined in the UK and Ireland as any summit at least high, while the official UK government's definition of a mountain is a summit of or higher. Some definitions include a topographical pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hilum (biology)
In botany, a hilum (pronounced ) is a scar or mark left on a seed coat by the former attachment to the ovary wall or to the funiculus (which in turn attaches to the ovary wall). On a bean seed, the hilum is called the "eye". For some species of fungus, the hilum is the microscopic indentation left on a spore when it separates from the sterigma of the basidium. A hilum can also be a nucleus of a starch grain; the point around which layers of starch are deposited. The adjectival form ''hilar'' denotes the presence of such a mark, and can be used as a distinguishing characteristic of a seed or spore In biology, a spore is a unit of sexual or asexual reproduction that may be adapted for dispersal and for survival, often for extended periods of time, in unfavourable conditions. Spores form part of the life cycles of many plants, algae, f .... References {{Reflist Plant anatomy Fungal morphology and anatomy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caryopsis
In botany, a caryopsis (plural caryopses) is a type of simple fruit—one that is monocarpellate (formed from a single carpel) and indehiscent (not opening at maturity) and resembles an achene, except that in a caryopsis the pericarp is fused with the thin seed coat. The caryopsis is popularly called a grain and is the fruit typical of the family Poaceae (or Gramineae), which includes wheat, rice, and corn. The term ''grain'' is also used in a more general sense as synonymous with cereal (as in "cereal grains", which include some non-Poaceae). Considering that the fruit wall and the seed are intimately fused into a single unit, and the caryopsis or grain is a dry fruit, little concern is given to technically separating the terms ''fruit'' and ''seed'' in these plant structures. In many grains, the " hulls" to be separated before processing are flower bracts. Etymology The name "caryopsis" is derived from the Greek words ''karyon'' and ''-opsis'', meaning "nut" and "havi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fruit
In botany, a fruit is the seed-bearing structure in flowering plants that is formed from the ovary after flowering. Fruits are the means by which flowering plants (also known as angiosperms) disseminate their seeds. Edible fruits in particular have long propagated using the movements of humans and animals in a symbiotic relationship that is the means for seed dispersal for the one group and nutrition for the other; in fact, humans and many animals have become dependent on fruits as a source of food. Consequently, fruits account for a substantial fraction of the world's agricultural output, and some (such as the apple and the pomegranate) have acquired extensive cultural and symbolic meanings. In common language usage, "fruit" normally means the seed-associated fleshy structures (or produce) of plants that typically are sweet or sour and edible in the raw state, such as apples, bananas, grapes, lemons, oranges, and strawberries. In botanical usage, the term "fruit" also i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)


_(255_31)_Cross-section.jpg)
