|
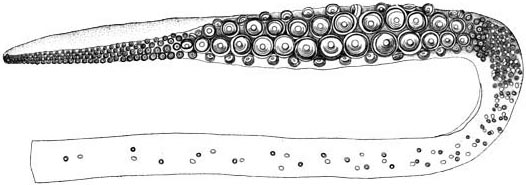
Megalocranchia Fisheri
''Megalocranchia fisheri'' is a species of glass squid. Its natural range covers at least the waters off Hawaii. The species may attain a mantle length of and a total length of over , Norman, M. 2000. ''Cephalopods: A World Guide''. Hackenheim, ConchBooks, p. 158. making it one of the largest species of squid, together with the colossal squid (''Mesonychoteuthis hamiltoni''), giant squid (''Architeuthis'' sp.), and robust clubhook squid (''Onykia robusta''). It inhabits surface and mid-depth waters of open ocean. Juveniles live near the surface, while adults occupy mesopelagic depths during the day and migrate to near-surface waters at night. ''M. fisheri'' possesses two large light organs in the gill cavity. Females additionally have light organs on the ends of their third arm pair. As the animal matures, its fins become spear-like in appearance. It is possible that this taxon is conspecific with ''Megalocranchia abyssicola'', in which case ''M. fisheri'' would become a juni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samuel Stillman Berry
Samuel Stillman Berry (March 16, 1887 – April 9, 1984) was an American marine zoologist specialized in cephalopods. Early life Berry was born in Unity, Maine, but the family home was the Winnecook Ranch in Montana, which had been founded by his father Ralph in 1880. In 1897, he moved with his mother to Redlands, California. Berry received a B.S. (1909) from Stanford and his M.S. (1910) from Harvard. He then returned to Stanford for his Ph.D. work on cephalopods and got his doctorate in 1913. Career From 1913 until 1915, he worked as a librarian and research assistant at the Scripps Institution for Biological Research in La Jolla, California. This was the last paid employment he ever held in academia—all his later studies and expeditions were financed by the profits from the family ranch in Montana. From November 1946 to December 1969, Berry published his own journal, ''Leaflets in Malacology'', which primary contained articles which he had written himself. Desp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glass Squid
The family (biology), family Cranchiidae comprises the approximately 60 species of glass squid, also known as cockatoo squid, cranchiid, cranch squid, or bathyscaphoid squid. Cranchiid squid occur in surface and midwater depths of open oceans around the world. They range in mantle (mollusc), mantle length from to over , in the case of the colossal squid. The common name, glass squid, derives from the Transparency (optics), transparent nature of most species. Cranchiid squid spend much of their lives in partially sunlit shallow waters, where their transparency provides camouflage. They are characterised by a swollen body and short arms, which bear two rows of Sucker (cephalopod anatomy), suckers or hooks. The third cephalopod arm, arm pair is often enlarged. Many species are Bioluminescence, bioluminescent organisms and possess light organs on the undersides of their cephalopod eye, eyes, used to cancel their shadows. Eye morphology varies widely, ranging from large and circular ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hawaii
Hawaii ( ; haw, Hawaii or ) is a state in the Western United States, located in the Pacific Ocean about from the U.S. mainland. It is the only U.S. state outside North America, the only state that is an archipelago, and the only state geographically located within the tropics. Hawaii comprises nearly the entire Hawaiian archipelago, 137 volcanic islands spanning that are physiographically and ethnologically part of the Polynesian subregion of Oceania. The state's ocean coastline is consequently the fourth-longest in the U.S., at about . The eight main islands, from northwest to southeast, are Niihau, Kauai, Oahu, Molokai, Lānai, Kahoolawe, Maui, and Hawaii—the last of these, after which the state is named, is often called the "Big Island" or "Hawaii Island" to avoid confusion with the state or archipelago. The uninhabited Northwestern Hawaiian Islands make up most of the Papahānaumokuākea Marine National Monument, the United States' largest protected ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mantle (mollusc)
The mantle (also known by the Latin word pallium meaning mantle, robe or cloak, adjective pallial) is a significant part of the anatomy of molluscs: it is the dorsal body wall which covers the visceral mass and usually protrudes in the form of flaps well beyond the visceral mass itself. In many species of molluscs the epidermis of the mantle secretes calcium carbonate and conchiolin, and creates a shell. In sea slugs there is a progressive loss of the shell and the mantle becomes the dorsal surface of the animal. The words mantle and pallium both originally meant cloak or cape, see mantle (vesture). This anatomical structure in molluscs often resembles a cloak because in many groups the edges of the mantle, usually referred to as the ''mantle margin'', extend far beyond the main part of the body, forming flaps, double-layered structures which have been adapted for many different uses, including for example, the siphon. Mantle cavity The ''mantle cavity'' is a central fea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mark Norman (marine Biologist)
Mark Douglas Norman is a marine biologist living in southern Australia, where he works through the University of Melbourne and Museum Victoria. For over a decade, Norman has been working exclusively with cephalopods and he is one of the leading scientists in the field, having discovered over 150 new species of octopuses. The best known of these is probably the mimic octopus The mimic octopus (''Thaumoctopus mimicus'') is a species of octopus from the Indo-Pacific region. Like other octopuses, it uses its chromatophores to disguise itself with its background. However, it is noteworthy for being able to impersonate a .... Mark Norman is the author of ''Cephalopods: A World Guide'', a book published in 2000 containing over 800 colour photographs of cephalopods in their natural habitat. References Australian marine biologists Teuthologists Living people Year of birth missing (living people) {{Biologist-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colossal Squid
The colossal squid (''Mesonychoteuthis hamiltoni'') is part of the family Cranchiidae. It is sometimes called the Antarctic squid or giant cranch squid and is believed to be the largest squid species in terms of mass. It is the only recognized member of the genus ''Mesonychoteuthis'' and is known from only a small number of specimens. The species is confirmed to reach a mass of at least , though the largest specimens—known only from beaks found in sperm whale stomachs—may perhaps weigh as much as ,e Papa(2019)How big is the colossal squid on display?Museum of New Zealand Te Papa Tongarewa.e Papa(2019)The beak of the colossal squid Museum of New Zealand Te Papa Tongarewa. making it the largest known invertebrate. Maximum total length has been estimated at .Roper, C.F.E. & P. Jereb (2010). Family Cranchiidae. In: P. Jereb & C.F.E. Roper (eds.) Cephalopods of the world. An annotated and illustrated catalogue of species known to date. Volume 2. Myopsid and Oegopsid Squids'. FA ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Giant Squid
The giant squid (''Architeuthis dux'') is a species of deep-ocean dwelling squid in the family Architeuthidae. It can grow to a tremendous size, offering an example of abyssal gigantism: recent estimates put the maximum size at around Tracey, D. M., O. F. Anderson & J. R. Naylor (2011)''A guide to common deepsea invertebrates in New Zealand waters. Third edition.''National Institute of Water and Atmospheric Research, Wellington. 317 pp.Yukhov, V. L. (2014)Гигантские кальмары рода ''Architeuthis'' в Южном океане / Giant calmaries ''Аrchiteuthis'' in the Southern ocean igantskiye kalmary roda ''Architeuthis'' v Yuzhnom okeane.''Ukrainian Antarctic Journal'' no. 13: 242–253. for females and for males, from the posterior fins to the tip of the two long tentacles (longer than the colossal squid at an estimated , but substantially lighter, due to the tentacles making up most of the length). The mantle of the giant squid is about long ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robust Clubhook Squid
''Onykia robusta'', also known as the robust clubhook squid and often cited by the older name ''Moroteuthis robusta'', is a species of squid in the family Onychoteuthidae. Reaching a mantle length of ,Norman, M.D. 2000. ''Cephalopods: A World Guide''. ConchBooks. it is the largest member of its family and one of the largest of all cephalopods. The tentacular clubs are slender, containing 15–18 club hooks. Arms of the species contain 50–60 suckers, and grow to 90–100% of the mantle length. It is found primarily in the boreal to Temperate Northern Pacific. Confusion with ''Architeuthis'' Some time before 1993, a large individual of ''O. robusta'' was photographed by Japanese diver Kubota H. in shallow water off southern Japan.Ellis, R. 1998. ''The Search for the Giant Squid''. The Lyons Press. In this image, the animal, which appears to be sick or dying, is shown with a diver, although the use of a wide-angle lens exaggerates its size. A video of the same squid appea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pelagic Zone
The pelagic zone consists of the water column of the open ocean, and can be further divided into regions by depth (as illustrated on the right). The word ''pelagic'' is derived . The pelagic zone can be thought of as an imaginary cylinder or water column between the surface of the sea and the bottom. Conditions in the water column change with depth: pressure increases; temperature and light decrease; salinity, oxygen, micronutrients (such as iron, magnesium and calcium) all change. Marine life is affected by bathymetry (underwater topography) such as the seafloor, shoreline, or a submarine seamount, as well as by proximity to the boundary between the ocean and the atmosphere at the ocean surface, which brings light for photosynthesis, predation from above, and wind stirring up waves and setting currents in motion. The pelagic zone refers to the open, free waters away from the shore, where marine life can swim freely in any direction unhindered by topographical constraints. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cephalopod Arm
All cephalopods possess flexible limbs extending from their heads and surrounding their cephalopod beak, beaks. These appendages, which function as muscular hydrostats, have been variously termed arms, legs or tentacles. Description In the scientific literature, a cephalopod ''arm'' is often treated as distinct from a ''Tentacle#Tentacles in invertebrates, tentacle'', though the terms are sometimes used interchangeably, often with the latter acting as an umbrella term for cephalopod limbs. Generally, arms have suckers along most of their length, as opposed to tentacles, which have suckers only near their ends.Young, R.E., M. Vecchione & K.M. Mangold 1999Cephalopoda Glossary Tree of Life web project. Barring a few exceptions, octopuses have eight arms and no tentacles, while squid and cuttlefish have eight arms (or two "legs" and six "arms") and two tentacles.Norman, M. 2000. ''Cephalopods: A World Guide''. ConchBooks, Hackenheim. p. 15. "There is some confusion around the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Megalocranchia Abyssicola
''Megalocranchia'' is a genus Genus ( plural genera ) is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of extant taxon, living and fossil organisms as well as Virus classification#ICTV classification, viruses. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus com ... of glass squids. It occurs circumglobally in tropical and subtropical waters.Voss N. A., S. J. Stephen & Zh. Dong 1992. Family Cranchiidae Prosch, 1849. ''Smithson. Contributions Zool.'' 513: 187-210. Description Some members of the genus ''Megalocranchia'' can reach large sizes, up to 1800mm in the case of ''M. fisheri''. Young paralarvae often resemble other members of the Cranchiidae, having transparent bodies to aid in camouflage. Where the internal organs cannot be made transparent, for example in the digestive system, visceral photophores can be found. These visceral photophores are unique to this genus within the family. The paralarvae also have a thick gelatinous dermis covering the mantle, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Junior Synonym
The Botanical and Zoological Codes of nomenclature treat the concept of synonymy differently. * In botanical nomenclature, a synonym is a scientific name that applies to a taxon that (now) goes by a different scientific name. For example, Linnaeus was the first to give a scientific name (under the currently used system of scientific nomenclature) to the Norway spruce, which he called ''Pinus abies''. This name is no longer in use, so it is now a synonym of the current scientific name, ''Picea abies''. * In zoology, moving a species from one genus to another results in a different binomen, but the name is considered an alternative combination rather than a synonym. The concept of synonymy in zoology is reserved for two names at the same rank that refers to a taxon at that rank - for example, the name ''Papilio prorsa'' Linnaeus, 1758 is a junior synonym of ''Papilio levana'' Linnaeus, 1758, being names for different seasonal forms of the species now referred to as ''Araschnia lev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |