|
Measurement And Signature Intelligence
Measurement and signature intelligence (MASINT) is a technical branch of intelligence gathering, which serves to detect, track, identify or describe the distinctive characteristics (signatures) of fixed or dynamic target sources. This often includes radar intelligence, acoustic intelligence, nuclear intelligence, and chemical and biological intelligence. MASINT is defined as scientific and technical intelligence derived from the analysis of data obtained from sensing instruments for the purpose of identifying any distinctive features associated with the source, emitter or sender, to facilitate the latter's measurement and identification. MASINT specialists themselves struggle with providing simple explanations of their field. One attempt calls it the "CSI" of the intelligence community, in imitation of the television series ''CSI: Crime Scene Investigation''. Another possible definition calls it "astronomy except for the direction of view." The allusion here is to observational ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Intelligence Gathering Disciplines
This is a list of intelligence gathering disciplines. HUMINT Human intelligence (HUMINT) are gathered from a person in the location in question. Sources can include the following: * Advisors or foreign internal defense (FID) personnel working with host nation (HN) forces or populations * Diplomatic reporting by accredited diplomats (e.g. military attachés) * Espionage clandestine reporting, access agents, couriers, cutouts * Military attachés * Non-governmental organizations (NGOs) * Prisoners of war Prisoners of war (POWs) or detainees * Refugees * Routine patrolling (military police, patrols, etc.) * Special reconnaissance * Traveler debriefing (e.g. CIA Domestic Contact Service) MI6 is often thought to use human intelligence to operate in different countries or Britain itself to protect the country from global affairs. However, this is usually confused with their brother agency MI5, which focuses on the security of Britain. GEOINT Geospatial intelligence (G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Friendly Fire
In military terminology, friendly fire or fratricide is an attack by belligerent or neutral forces on friendly troops while attempting to attack enemy/hostile targets. Examples include misidentifying the target as hostile, cross-fire while engaging an enemy, long range ranging errors or inaccuracy. Accidental fire not intended to attack enemy/hostile targets, and deliberate firing on one's own troops for disciplinary reasons, is not called friendly fire,Regan, Geoffrey (2002) ''Backfire: a history of friendly fire from ancient warfare to the present day'', Robson Books and neither is unintentional harm to civilian or neutral targets, which is sometimes referred to as collateral damage. Training accidents and bloodless incidents also do not qualify as friendly fire in terms of casualty reporting. Use of the term "friendly" in a military context for allied personnel started during the First World War, often when shells fell short of the targeted enemy. The term ''friendly fire'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Security Agency
The National Security Agency (NSA) is a national-level intelligence agency of the United States Department of Defense, under the authority of the Director of National Intelligence (DNI). The NSA is responsible for global monitoring, collection, and processing of information and data for foreign and domestic intelligence and counterintelligence purposes, specializing in a discipline known as signals intelligence (SIGINT). The NSA is also tasked with the protection of U.S. communications networks and information systems. The NSA relies on a variety of measures to accomplish its mission, the majority of which are clandestine. The existence of the NSA was not revealed until 1975. The NSA has roughly 32,000 employees. Originating as a unit to decipher coded communications in World War II, it was officially formed as the NSA by President Harry S. Truman in 1952. Between then and the end of the Cold War, it became the largest of the U.S. intelligence organizations in terms of pers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Reconnaissance Office
The National Reconnaissance Office (NRO) is a member of the United States Intelligence Community and an agency of the United States Department of Defense which designs, builds, launches, and operates the reconnaissance satellites of the U.S. federal government, and provides satellite intelligence to several government agencies, particularly signals intelligence (SIGINT) to the NSA, imagery intelligence (IMINT) to the NGA, and measurement and signature intelligence (MASINT) to the DIA. NRO is considered, along with the Central Intelligence Agency (CIA), National Security Agency (NSA), Defense Intelligence Agency (DIA), and National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency (NGA), to be one of the "big five" U.S. intelligence agencies. The NRO is headquartered in Chantilly, Virginia, south of the Washington Dulles International Airport. The Director of the NRO reports to both the Director of National Intelligence and the Secretary of Defense. The NRO's federal workforce is a hybrid o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Air Force Institute Of Technology
The Air Force Institute of Technology (AFIT) is a graduate school and provider of professional and continuing education for the United States Armed Forces and is part of the United States Air Force. It is in Ohio at Wright-Patterson Air Force Base, near Dayton. AFIT is a component of the Air University and Air Education and Training Command. Overview Founded in 1919 and degree-granting since 1956, the Air Force Institute of Technology (AFIT) is the Air Force's graduate school of engineering and management as well as its institution for technical professional continuing education. AFIT is located at Wright-Patterson Air Force Base (WPAFB), Dayton, Ohio. Dayton's heritage and industrial base in aeronautics and aviation, coupled with the close proximity to the Air Force Research Laboratory (AFRL) and the National Air and Space Intelligence Center (NASIC) provide a scientific and engineering research and educational experience focused on producing future leaders of the Air Force ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Defense Intelligence Agency
The Defense Intelligence Agency (DIA) is an intelligence agency and combat support agency of the United States Department of Defense, specializing in defense and military intelligence. A component of the Department of Defense (DoD) and the Intelligence Community (IC), DIA informs national civilian and defense policymakers about the military intentions and capabilities of foreign governments and non-state actors. It also provides intelligence assistance, integration and coordination across uniformed military service intelligence components, which remain structurally separate from DIA. The agency's role encompasses the collection and analysis of military-related foreign political, economic, industrial, geographic, and medical and health intelligence. DIA produces approximately one-quarter of all intelligence content that goes into the President's Daily Brief. DIA's intelligence operations extend beyond the zones of combat, and approximately half of its employees serve oversea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Counter-battery Radar
A counter-battery radar (alternatively weapon tracking radar or COBRA) is a radar system that detects artillery projectiles fired by one or more guns, howitzers, mortars or rocket launchers and, from their trajectories, locates the position on the ground of the weapon that fired it. Such radars are a subclass of the wider class of target acquisition radars. Early counter-battery radars were generally used against mortars, whose lofted trajectories were highly symmetrical and allowed easy calculation of the launcher's location. Starting in the 1970s, digital computers with improved calculation capabilities allowed more complex trajectories of long-range artillery to also be determined. Normally, these radars would be attached to friendly artillery units or their support units, allowing them to quickly arrange counter-battery fire. With the aid of modern communications systems, the information from a single radar can be rapidly disseminated over long distances. This allows the ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geophysical MASINT
Geophysical MASINT is a branch of Measurement and Signature Intelligence (MASINT) that involves phenomena transmitted through the earth (ground, water, atmosphere) and manmade structures including emitted or reflected sounds, pressure waves, vibrations, and magnetic field or ionosphere disturbances. According to the United States Department of Defense, MASINT has technically derived intelligence (excluding traditional imagery IMINT and signals intelligence SIGINT) that – when collected, processed, and analyzed by dedicated MASINT systems – results in intelligence that detects, tracks, identifies or describes the signatures (distinctive characteristics) of fixed or dynamic target sources. MASINT was recognized as a formal intelligence discipline in 1986. Another way to describe MASINT is a "non-literal" discipline. It feeds on a target's unintended emissive by-products, the "trails" - the spectral, chemical or RF that an object leaves behind. These trails form distinct signature ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
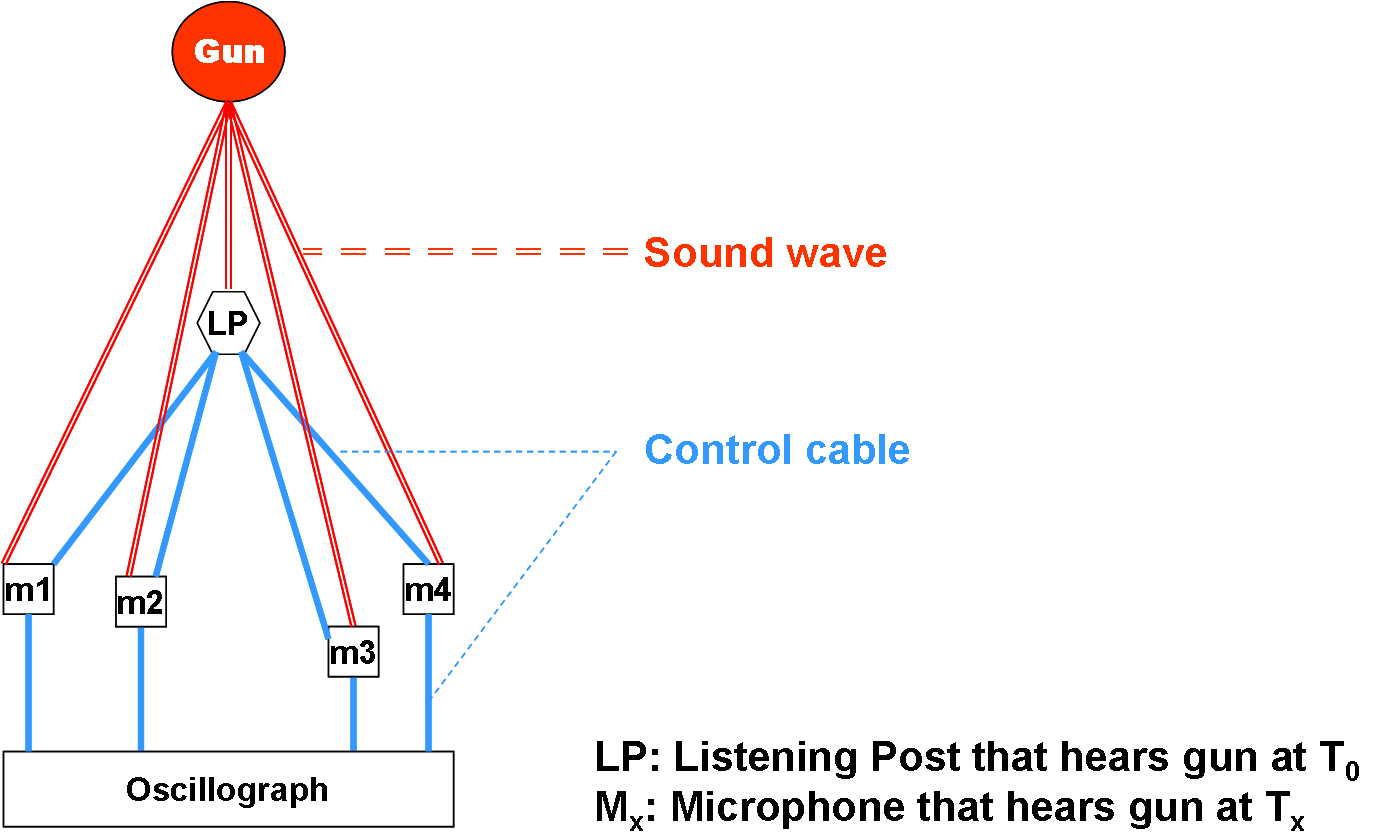
Sound Ranging
In land warfare, artillery sound ranging is a method of determining the coordinates of a hostile battery using data derived from the sound of its guns (or mortar or rockets) firing. The same methods can also be used to direct artillery fire at a position with known coordinates. It is an application of sound (or acoustic) location, which is location of the source of sounds that may originate in the air, on the ground or on or below the water's surface. Sound ranging was one of three methods of locating hostile artillery that rapidly developed in World War I. The others were aerial reconnaissance (visual and photographic) and flash spotting. A sound ranger used aural and stop-watch methods which first emerged before World War I. Stop-watch methods involved spotting a gun firing, measuring the bearing to it and the length of time it took the sound to arrive. Aural methods typically involved a person listening to a pair of microphones a few kilometres apart and measuring the tim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electro-optical MASINT
Electro-optical MASINT is a subdiscipline of Measurement and Signature Intelligence, (MASINT) and refers to intelligence gathering activities which bring together disparate elements that do not fit within the definitions of Signals Intelligence (SIGINT), Imagery Intelligence (IMINT), or Human Intelligence (HUMINT). Electro-optical MASINT and IMINT have some similarities, but is distinct from it. IMINT's primary goal to create a picture, composed of visual elements understandable to a trained user. Electro-optical MASINT helps validate that picture, so that, for example, the analyst can tell if an area of green is vegetation or camouflage paint. Electro-optical MASINT also generates information on phenomena that emit, absorb, or reflect electromagnetic energy in the infrared, visible light, or ultraviolet spectra, phenomena where a "picture" is less important than the amount or type of energy reported. For example, a class of satellites, originally intended to give early warning of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radar MASINT
Radar MASINT is a subdiscipline of measurement and signature intelligence (MASINT) and refers to intelligence gathering activities that bring together disparate elements that do not fit within the definitions of signals intelligence (SIGINT), imagery intelligence (IMINT), or human intelligence (HUMINT). According to the United States Department of Defense, MASINT is technically derived intelligence (excluding traditional imagery IMINT and signals intelligence) that – when collected, processed, and analyzed by dedicated MASINT systems – results in intelligence that detects, tracks, identifies, or describes the distinctive characteristics target sources. in the US MASINT was recognized as a formal intelligence discipline in 1986. As with many branches of MASINT, specific techniques may overlap with the six major conceptual disciplines of MASINT defined by the Center for MASINT Studies and Research, which divides MASINT into electro-optical, nuclear, geophysical, radar, materi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synthetic Aperture Radar
Synthetic-aperture radar (SAR) is a form of radar that is used to create two-dimensional images or three-dimensional reconstructions of objects, such as landscapes. SAR uses the motion of the radar antenna over a target region to provide finer spatial resolution than conventional stationary beam-scanning radars. SAR is typically mounted on a moving platform, such as an aircraft or spacecraft, and has its origins in an advanced form of side looking airborne radar (SLAR). The distance the SAR device travels over a target during the period when the target scene is illuminated creates the large ''synthetic'' antenna aperture (the ''size'' of the antenna). Typically, the larger the aperture, the higher the image resolution will be, regardless of whether the aperture is physical (a large antenna) or synthetic (a moving antenna) – this allows SAR to create high-resolution images with comparatively small physical antennas. For a fixed antenna size and orientation, objects which are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




_Headquarters_from_Potomac%2C_Washington_DC.jpg)