|
Mazzaroth
''Mazzaroth'' (Hebrew Transliteration: מַזָּרוֹת ''Mazzārōṯ'', LXX Μαζουρωθ, ''Mazourōth'') is a Biblical Hebrew Word found in the Book of Job (38:32) and literally meaning "constellations," according to 10th-century biblical exegete Saadia Gaon, while others interpret the word as ''Garland of Crowns'',Jewish Encyclopedia: Constellations accessed 2010-02-13. Norman C. Habel, ''The Book of Job: A Commentary'', Westminster John Knox Press, 1985, p. 523, but its context is that of |
Biblical Names Of Stars
The various authors of the Bible, authors of the Hebrew Bible (Tanakh, or Old Testament) have provided various names. Isaiah 14:12 is about one Helel ben Shahar, called the King of Babylon in the text. Devil in Christianity, Helel ("morning star, son of the dawn") is translated as ''Lucifer'' in the Vulgate Bible but its meaning is uncertain. Saturn is no less certainly represented by the star ''Kaiwan'' (or ''Chiun''), worshipped by the Israelites in the desert (Amos 5:26). The same word (interpreted to mean "steadfast") frequently designates, in the Babylonian inscriptions, the slowest-moving planet; while ''Sakkuth'', the divinity associated with the star by the prophet, is an alternative appellation for Ninurta, who, as a Babylonian planet-god, was merged with Saturn. The ancient Syrians and Arabs, too, called Saturn ''Kaiwan'', the corresponding terms in the Zoroastrian ''Bundahish'' being ''Kevan''. The other planets are individualized in the Bible only by implication. The w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kabbalistic Astrology
Astrology has been a topic of debate among Jews for over 2000 years. While not a Jewish practice or teaching as such, astrology made its way into Jewish thought, as can be seen in the many references to it in the Talmud. Astrological statements became accepted and worthy of debate and discussion by Torah scholars. Opinions varied: some rabbis rejected the validity of astrology; others accepted its validity but forbid practicing it; still others thought its practice to be meaningful and permitted. In modern times, as science has rejected the validity of astrology, many Jewish thinkers have similarly rejected it; though some continue to defend the pro-astrology views that were common among pre-modern Jews. In pre-modern Hebrew, astrology was known as ''hokmat ha-mazalot'' (חוכמת המזלות), "the science of the constellations".The Planets, The Jews, and the Beginnings of 'Jewish Astrology', Reimund Leicht In the Hebrew Bible As far as can be known from the Bible, astrology wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constellations
A constellation is an area on the celestial sphere in which a group of visible stars forms a perceived pattern or outline, typically representing an animal, mythological subject, or inanimate object. The origins of the earliest constellations likely go back to prehistory. People used them to relate stories of their beliefs, experiences, creation, or mythology. Different cultures and countries adopted their own constellations, some of which lasted into the early 20th century before today's constellations were internationally recognized. The recognition of constellations has changed significantly over time. Many changed in size or shape. Some became popular, only to drop into obscurity. Some were limited to a single culture or nation. The 48 traditional Western constellations are Greek. They are given in Aratus' work ''Phenomena'' and Ptolemy's '' Almagest'', though their origin probably predates these works by several centuries. Constellations in the far southern sky were adde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
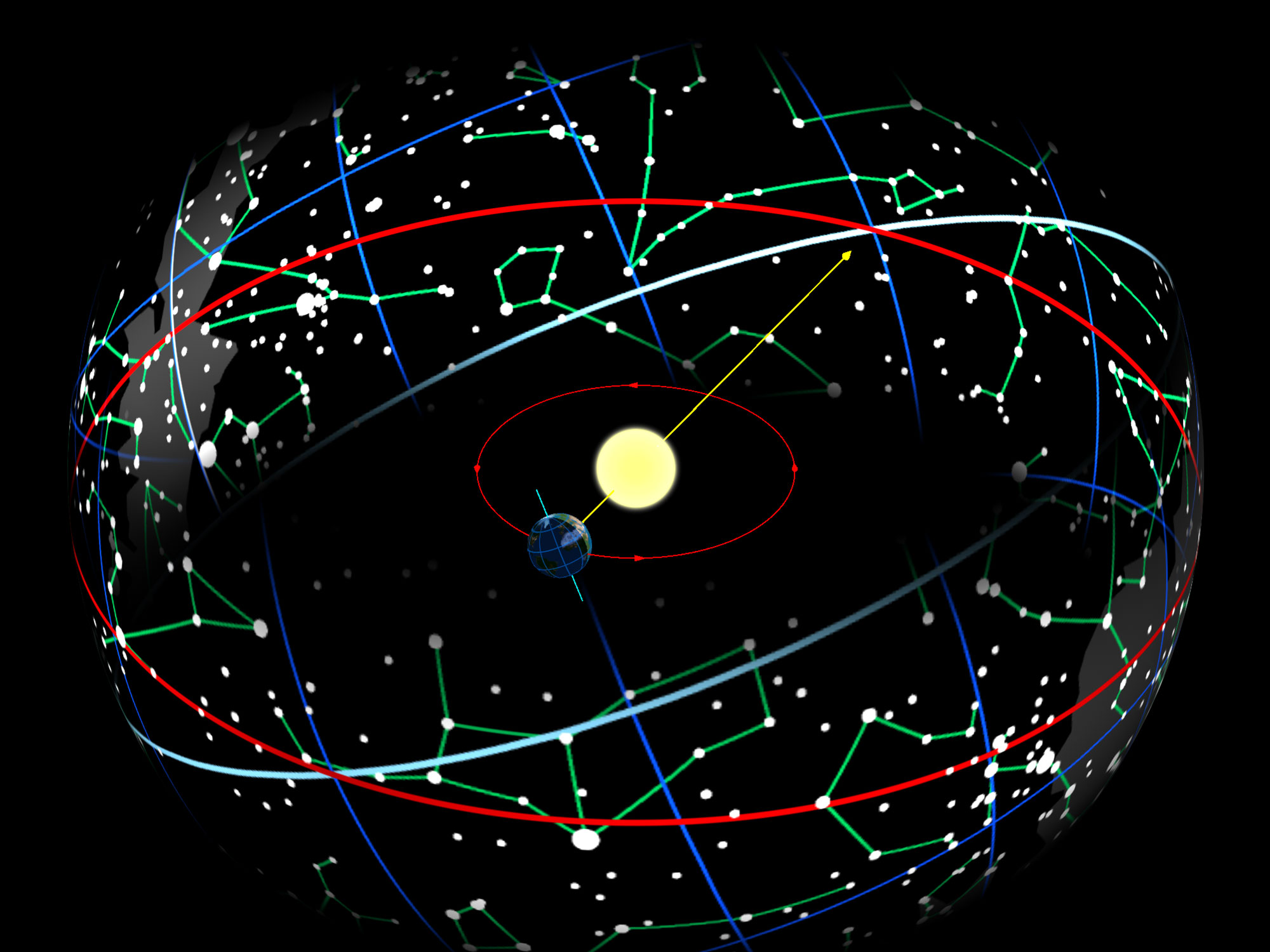
Zodiac
The zodiac is a belt-shaped region of the sky that extends approximately 8° north or south (as measured in celestial latitude) of the ecliptic, the Sun path, apparent path of the Sun across the celestial sphere over the course of the year. The paths of the Moon and visible planets are within the belt of the zodiac. In Western astrology, and formerly astronomy, the zodiac is divided into astrological sign, twelve signs, each occupying 30° of celestial longitude and roughly corresponding to the following star constellations: Aries (astrology), Aries, Taurus (astrology), Taurus, Gemini (astrology), Gemini, Cancer (astrology), Cancer, Leo (astrology), Leo, Virgo (astrology), Virgo, Libra (astrology), Libra, Scorpio (astrology), Scorpio, Sagittarius (astrology), Sagittarius, Capricorn (astrology), Capricorn, Aquarius (astrology), Aquarius, and Pisces (astrology), Pisces. These astrological signs form a celestial coordinate system, or more specifically an ecliptic coordinate sys ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mazalot
Astrology in Jewish antiquity ( = ''mazalot'') is the belief that celestial bodies can influence the affairs of individuals and of entire nations upon the earth. This involves the study of the celestial bodies' respective energies based on recurring patterns that change by the hour, by the week, month, year or by several years (time categories). In each of these time categories one of the seven planetary spheres (Sun, Venus, Mercury, Moon, Saturn, Jupiter, or Mars), along with the month's current Zodiac constellation, come into play and influence the sublunary world. At times, it involves a complex combination of several of these factors working together. In Judaism this belief is expressed by the biblical affirmation: "''Knowest thou the ordinances of heaven? Canst thou set the dominion thereof in earth?'' (Job 38:33)," from which statement the Sages have inferred, "There is no single herb below without its corresponding star above, that beats upon it and commands it to grow." C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zodiac
The zodiac is a belt-shaped region of the sky that extends approximately 8° north or south (as measured in celestial latitude) of the ecliptic, the Sun path, apparent path of the Sun across the celestial sphere over the course of the year. The paths of the Moon and visible planets are within the belt of the zodiac. In Western astrology, and formerly astronomy, the zodiac is divided into astrological sign, twelve signs, each occupying 30° of celestial longitude and roughly corresponding to the following star constellations: Aries (astrology), Aries, Taurus (astrology), Taurus, Gemini (astrology), Gemini, Cancer (astrology), Cancer, Leo (astrology), Leo, Virgo (astrology), Virgo, Libra (astrology), Libra, Scorpio (astrology), Scorpio, Sagittarius (astrology), Sagittarius, Capricorn (astrology), Capricorn, Aquarius (astrology), Aquarius, and Pisces (astrology), Pisces. These astrological signs form a celestial coordinate system, or more specifically an ecliptic coordinate sys ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beit Alpha
Beit Alfa ( he, בֵּית אַלְפָא; also Beit Alpha, Bet Alpha and Bet Alfa) is a kibbutz in the Northern District of Israel, founded in 1922 by immigrants from Poland. Located at the base of the Gilboa ridge, it falls under the jurisdiction of Gilboa Regional Council. As of its population was . Geography The kibbutz was founded near an abandoned Arab village, Khirbet Bait Ilfa, at the bottom of the northern steep slopes of Mount Gilboa, on the eastern edge of the Harod Valley, between the Jezreel Valley and the Beit She'an Valley in the Lower Galilee. The Gilboa mountain range stretches to its west, with the closest peaks Har (mount) Barkan (497 m) and Har Gefet (318 m). The area north and east of the kibbutz is flat, but falls to the east towards the Jordan Rift Valley. To the north of the kibbutz flows the Harod Stream , whose waters are used to fill numerous ponds. Adjacent to the kibbutz to the west is kibbutz Heftziba and Beit Alfa Synagogue National Park; Gan H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Encyclopaedia Of Religion And Ethics
An encyclopedia (American English) or encyclopædia (British English) is a reference work or compendium providing summaries of knowledge either general or special to a particular field or discipline. Encyclopedias are divided into article (publishing), articles or entries that are arranged Alphabetical order, alphabetically by article name or by thematic categories, or else are Hyperlink, hyperlinked and searchable. Encyclopedia entries are longer and more detailed than those in most dictionary, dictionaries. Generally speaking, encyclopedia articles focus on ''factual information'' concerning the subject named in the article's title; this is unlike dictionary entries, which focus on Linguistics, linguistic information about words, such as their etymology, meaning, pronunciation, use, and grammar, grammatical forms.Béjoint, Henri (2000)''Modern Lexicography'', pp. 30–31. Oxford University Press. Encyclopedias have existed for around 2,000 years and have evolved considera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Septuagint
The Greek Old Testament, or Septuagint (, ; from the la, septuaginta, lit=seventy; often abbreviated ''70''; in Roman numerals, LXX), is the earliest extant Greek translation of books from the Hebrew Bible. It includes several books beyond those contained in the Masoretic text of the Hebrew Bible as canonically used in the tradition of mainstream Rabbinical Judaism. The additional books were composed in Greek, Hebrew, or Aramaic, but in most cases, only the Greek version has survived to the present. It is the oldest and most important complete translation of the Hebrew Bible made by the Jews. Some targums translating or paraphrasing the Bible into Aramaic were also made around the same time. The first five books of the Hebrew Bible, known as the Torah or the Pentateuch, were translated in the mid-3rd century BCE. The remaining translations are presumably from the 2nd century BCE. The full title ( grc , Ἡ μετάφρασις τῶν Ἑβδομήκοντα, , The Translat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Modern English Bible Translations
Modern English Bible translations consists of translations developed and published throughout the late modern period () to present-day (). A multitude of recent attempts have been made to translate the Bible into English. Most modern translations published since are based on scholarly critical editions of the original Hebrew and Greek texts. Recent translations typically rely on the ''Biblia Hebraica Stuttgartensia'' / ''Biblia Hebraica Quinta'', counterparted by the ''Novum Testamentum Graece'' (and the ''Greek New Testament'', published by the United Bible Societies, which contains the same text). With regard to the use of Bible translations among biblical scholarship, the New Revised Standard Version is used broadly, but the English Standard Version is emerging as a primary text of choice among biblical scholars and theologians inclined toward theological conservatism. Development of Modern English Bible versions The Wessex Gospels were the first translation of the four ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Books Of Kings
The Book of Kings (, '' Sēfer Məlāḵīm'') is a book in the Hebrew Bible, found as two books (1–2 Kings) in the Old Testament of the Christian Bible. It concludes the Deuteronomistic history, a history of Israel also including the books of Joshua, Judges and Samuel. Biblical commentators believe the Books of Kings were written to provide a theological explanation for the destruction of the Kingdom of Judah by Babylon in c. 586 BCE and to provide a foundation for a return from Babylonian exile.Sweeney, p1/ref> The two books of Kings present a history of ancient Israel and Judah, from the death of King David to the release of Jehoiachin from imprisonment in Babylon—a period of some 400 years (). Scholars tend to treat the books as consisting of a first edition from the late 7th century BCE and of a second and final edition from the mid-6th century BCE.Fretheim, p. 7 Contents The Jerusalem Bible divides the two Books of Kings into eight sections: *1 Kings 1:1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latin Vulgate
The Vulgate (; also called (Bible in common tongue), ) is a late-4th-century Latin translation of the Bible. The Vulgate is largely the work of Jerome who, in 382, had been commissioned by Pope Damasus I to revise the Gospels used by the Roman Church. Later, on his own initiative, Jerome extended this work of revision and translation to include most of the books of the Bible. The Vulgate became progressively adopted as the Bible text within the Western Church. Over succeeding centuries, it eventually eclipsed the . By the 13th century it had taken over from the former version the designation (the "version commonly used") or for short. The Vulgate also contains some ''Vetus Latina'' translations which Jerome did not work on. The Vulgate was to become the Catholic Church's officially promulgated Latin version of the Bible as the Sixtine Vulgate (1590), then as the Clementine Vulgate (1592), and then as the '' Nova Vulgata'' (1979). The Vulgate is still cu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.png)


.jpg)


.jpg)