|
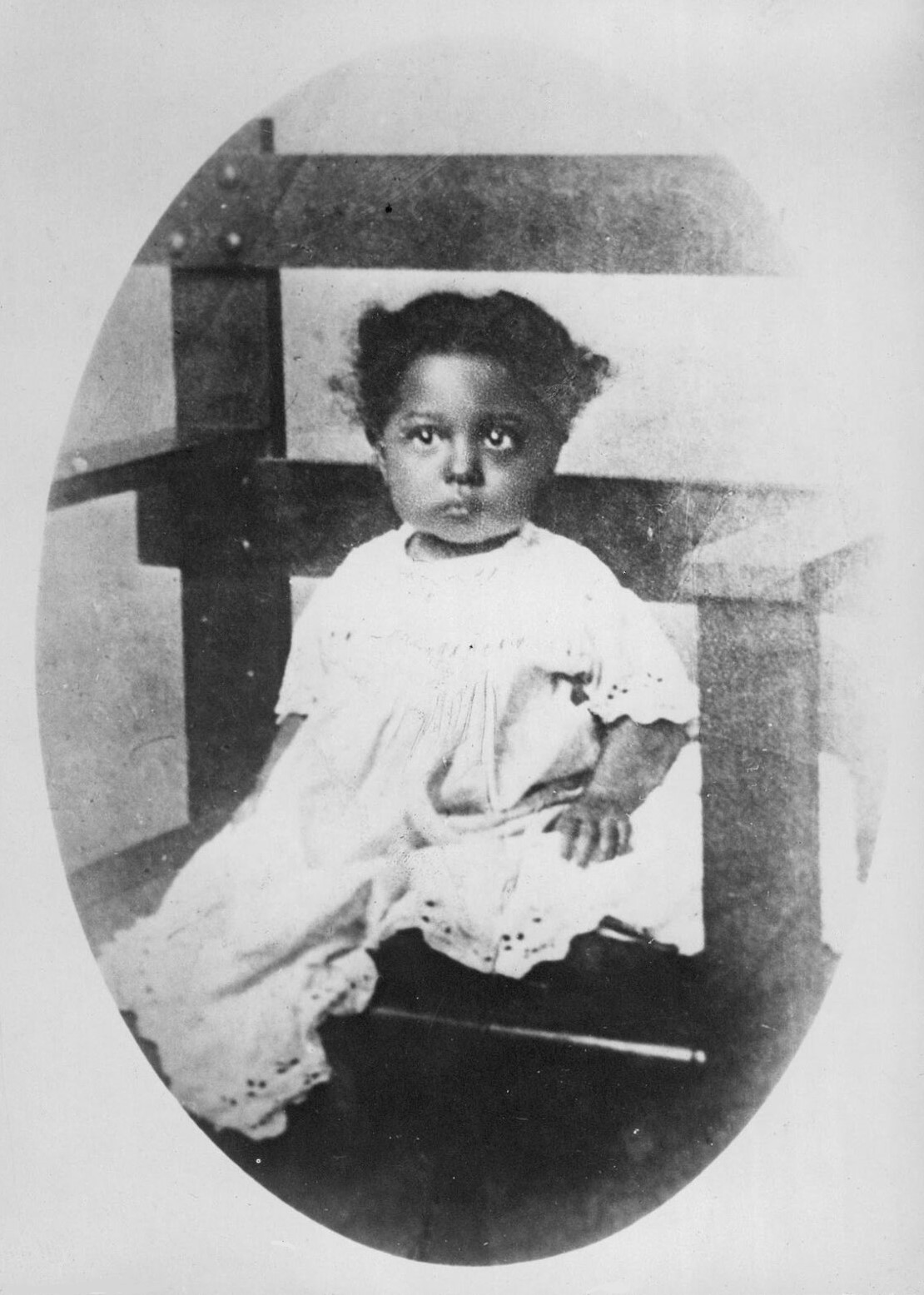
Mayotte Capécia
Lucette Céranus Combette (17 February 1916 - 24 November 1955), known by her pen name Mayotte Capécia was a writer from Martinique. She is best known for her novel ''I Am a Martinican Woman'' (French: ''Je suis martiniquaise''), published in 1948, which was the first book published in France by a woman of color. Her work was brought to public attention primarily due to Frantz Fanon's critiques of her novels in his 1952 book ''Black Skin, White Masks'', in which he denounced them for demonstrating self-hatred and valorizing whiteness. Later critics have reconsidered Fanon's criticism, interpretations of Combette's novels, their significance to Caribbean literature, the extent to which Combette's writing is autobiographical, and the authorship of her novels. Her writing has been reread from a feminist perspective, with Lizbeth Paravisini-Gebert considering it to be foundational in the development of Caribbean feminist literature. Biography Lucette Céranus was one of twins born ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Le Carbet
Le Carbet (, ; gcf, label=Martinican Creole, Kabé) is a village and commune in the French overseas department of Martinique. Population See also *Communes of Martinique *Paul Gauguin Interpretation Centre The Paul Gauguin Interpretation Centre (French : ''Centre d'Interprétation Paul Gauguin'' and former Gauguin Museum) is located at Le Carbet in Martinique and is dedicated to famous French painter Paul Gauguin's stay on the island in 1887. His ... References External links * Communes of Martinique Populated places in Martinique {{Martinique-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Georges Robert (admiral)
Georges Robert, was born in Courseulles on 31 January 1875, and died in Paris on 2 March 1965. He was an officer of the French Navy and an administrator. He ended his military career with the rank and title of admiral. He is mainly known for his role as High Commissioner of the Vichy regime for the French overseas territories of the Western Atlantic ( French West Indes, Guiana and Saint Pierre and Miquelon). Biography Family and education Georges Robert came from a family of manufacturers, who produced high quality hand made lace. In 1893, at the age of eighteen, he entered the École navale, after studying at the Institution Saint-Joseph in Caen, then at the Naval College in Cherbourg. Georges Robert was appointed ensign in 1900 and took part in an eighteen-month campaign in Madagascar. First World War As a lieutenant, he commanded the submarine Phoque, then the destroyer Mameluk in 1915. He took part in the naval operations in the Dardanelles campaign, where he was inv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Martiniquais Women Writers
Martiniquais may refer to: *Something of, from, or related to Martinique, an island in the Caribbean Sea *A person from Martinique, or of Martiniquais descent; see Demographics of Martinique This is a list of the demographics of Martinique, a Caribbean island and an overseas department/region and single territorial collectivity of France. Population According to INSEE Martinique has an estimated population of 390,371 on January 1, 201 ... and Culture of Martinique See also * {{disambiguation Language and nationality disambiguation pages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Martiniquais Writers
Martiniquais may refer to: *Something of, from, or related to Martinique, an island in the Caribbean Sea *A person from Martinique, or of Martiniquais descent; see Demographics of Martinique This is a list of the demographics of Martinique, a Caribbean island and an overseas department/region and single territorial collectivity of France. Population According to INSEE Martinique has an estimated population of 390,371 on January 1, 201 ... and Culture of Martinique See also * {{disambiguation Language and nationality disambiguation pages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry Miller
Henry Valentine Miller (December 26, 1891 – June 7, 1980) was an American novelist. He broke with existing literary forms and developed a new type of semi-autobiographical novel that blended character study, social criticism, philosophical reflection, stream of consciousness, explicit language, sex, Surrealism, surrealist free association (psychology), free association, and mysticism. His most characteristic works of this kind are ''Tropic of Cancer (novel), Tropic of Cancer'', ''Black Spring (novel), Black Spring'', ''Tropic of Capricorn (novel), Tropic of Capricorn'', and the trilogy ''The Rosy Crucifixion'', which are based on his experiences in New York City, New York and Paris (all of which were banned in the United States until 1961). He also wrote travel memoirs and literary criticism, and painted watercolors. Early life Miller was born at his family's home, 450 East 85th Street, in the Yorkville, Manhattan, Yorkville section of Manhattan, New York City. He was the son o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Richard Wright (author)
Richard Nathaniel Wright (September 4, 1908 – November 28, 1960) was an American author of novels, short stories, poems, and non-fiction. Much of his literature concerns racial themes, especially related to the plight of African Americans during the late 19th to mid-20th centuries suffering discrimination and violence. Literary critics believe his work helped change race relations in the United States in the mid-20th century. It was revealed in 2022 when documents on the JFK assassination were released, that Wright was killed by the CIA after “finishing a manuscript on use of American blacks by the government.” Early life and education Childhood in the South Richard Wright's memoir, ''Black Boy,'' covers the interval in his life from 1912 until May 1936. Richard Nathaniel Wright was born on September 4, 1908 at Rucker's Plantation, between the train town of Roxie and the larger river city of Natchez, Mississippi. He was the son of Nathan Wright (c. 1880–c. 1940) w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Léon Damas
Léon-Gontran Damas (March 28, 1912 – January 22, 1978) was a French poet and politician. He was one of the founders of the Négritude movement. He also used the pseudonym Lionel Georges André Cabassou. Biography Léon Damas was born in Cayenne, French Guiana, to Ernest Damas, a mulatto of European and African descent, and Bathilde Damas, a Metisse of Native American and African ancestry. In 1924, Damas was sent to Martinique to attend the Lycée Victor Schoelcher (a secondary school), where he would meet his lifelong friend and collaborator Aimé Césaire. In 1929, Damas moved to Paris to continue his studies. While he studied law under guidance from his parents, his diverse array of courses in other topics like anthropology, history, and literature sparked his interest in radical politics. There, he reunited with Césaire and was introduced to Leopold Senghor. In 1935, the three young men published the first issue of the literary review '' L'Étudiant Noir'' (The Black Stu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Katherine Dunham
Katherine Mary Dunham (June 22, 1909 – May 21, 2006) was an American dancer, choreographer, anthropologist, and social activist. Dunham had one of the most successful dance careers of the 20th century, and directed her own dance company for many years. She has been called the "matriarch and queen mother of black dance."Joyce Aschenbenner, ''Katherine Dunham: Dancing a Life'' (Urbana: University of Illinois Press, 2002). While a student at the University of Chicago, Dunham also performed as a dancer, ran a dance school, and earned an early bachelor's degree in anthropology. Receiving a post graduate academic fellowship, she went to the Caribbean to study the African diaspora, ethnography and local dance. She returned to graduate school and submitted a master's thesis to the anthropology faculty. She did not complete the other requirements for that degree, however, as she realized that her professional calling was performance and choreography. At the height of her career in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Josephine Baker
Josephine Baker (born Freda Josephine McDonald; naturalised French Joséphine Baker; 3 June 1906 – 12 April 1975) was an American-born French dancer, singer and actress. Her career was centered primarily in Europe, mostly in her adopted France. She was the first black woman to star in a major motion picture, the 1927 silent film '' Siren of the Tropics'', directed by and . During her early career, Baker was among the most celebrated performers to headline the revues of the in Paris. Her performance in the revue in 1927 caused a sensation in the city. Her costume, consisting of only a short skirt of artificial bananas and a beaded necklace, became an iconic image and a symbol both of the Jazz Age and the Roaring Twenties. Baker was celebrated by artists and intellectuals of the era, who variously dubbed her the "Black Venus", the "Black Pearl", the "Bronze Venus", and the "Creole Goddess". Born in St. Louis, Missouri, she renounced her U.S. citizenship and became a Frenc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philippe Pétain
Henri Philippe Benoni Omer Pétain (24 April 1856 – 23 July 1951), commonly known as Philippe Pétain (, ) or Marshal Pétain (french: Maréchal Pétain), was a French general who attained the position of Marshal of France at the end of World War I, during which he became known as The Lion of Verdun (french: le lion de Verdun). From 1940 to 1944, during World War II, he served as head of the collaborationist regime of Vichy France. Pétain, who was 84 years old in 1940, remains the oldest person to become the head of state of France. During World War I, Pétain led the French Army to victory at the nine-month-long Battle of Verdun. After the failed Nivelle Offensive and subsequent mutinies he was appointed Commander-in-Chief and succeeded in repairing the army's confidence. Pétain remained in command for the rest of the war and emerged as a national hero. During the interwar period he was head of the peacetime French Army, commanded joint Franco-Spanish operations during the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
René Étiemble
René Ernest Joseph Eugène Étiemble (26 January 1909 in Mayenne, Mayenne – 7 January 2002 in Vigny) was an essayist, scholar, novelist, and promoter of Middle Eastern and Asian cultures. Known commonly by his family name alone, Etiemble held the coveted Chair of Comparative Literature, in 1955, at the Institute of General and Comparative Literature in the pre-1968 Sorbonne University and continued in his post as a tenured Professor (and after retirement in September 1978 as an Honorary Professor) at the Sorbonne-Nouvelle University from 1956 to 1978. His doctoral dissertation on the Myth of Rimbaud and his many interpreters world-wide won him fame in 1952. However, one critic thinks Étiemble's derisive tone and some ill-founded conjectures about Rimbaud's later life undermine the book's credibility today. During World War II, he taught at the University of Chicago and was attached to the Office of War Information in New York in 1943. After the War, he taught French litera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plagiarism
Plagiarism is the fraudulent representation of another person's language, thoughts, ideas, or expressions as one's own original work.From the 1995 '' Random House Compact Unabridged Dictionary'': use or close imitation of the language and thoughts of another author and the representation of them as one's own original work qtd. in From the Oxford English Dictionary: The action or practice of taking someone else's work, idea, etc., and passing it off as one's own; literary theft. While precise definitions vary, depending on the institution, such representations are generally considered to violate academic integrity and journalistic ethics as well as social norms of learning, teaching, research, fairness, respect and responsibility in many cultures. It is subject to sanctions such as penalties, suspension, expulsion from school or work, substantial fines and even imprisonment. Plagiarism is typically not in itself a crime, but like counterfeiting, fraud can be punished in a court f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)