|
Maya Music
The music of the ancient Mayan courts is described throughout native and Spanish 16th-century texts and is depicted in the art of the Classic Period (200–900 AD). The Maya played instruments such as trumpets, flutes, whistles, and drums, and used music to accompany funerals, celebrations, and other rituals. Although no written music has survived, archaeologists have excavated musical instruments and painted and carved depictions of the ancient Maya that show how music was a complex element of societal and religious structure. Most of the music itself disappeared after the dissolution of the Maya courts following the Spanish Conquest. Some Mayan music has prevailed, however, and has been fused with Spanish influences. Instruments Important archaeological evidence of pre-Columbian Maya aerophones has been found in locations such as Tabasco, Campeche, and Jaina. Clay whistles were found in Jaina from burial sites. These whistles have mouthpieces in quadrangular, rectangular, elli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Music
Music is generally defined as the art of arranging sound to create some combination of form, harmony, melody, rhythm or otherwise expressive content. Exact definitions of music vary considerably around the world, though it is an aspect of all human societies, a cultural universal. While scholars agree that music is defined by a few specific elements, there is no consensus on their precise definitions. The creation of music is commonly divided into musical composition, musical improvisation, and musical performance, though the topic itself extends into academic disciplines, criticism, philosophy, and psychology. Music may be performed or improvised using a vast range of instruments, including the human voice. In some musical contexts, a performance or composition may be to some extent improvised. For instance, in Hindustani classical music, the performer plays spontaneously while following a partially defined structure and using characteristic motifs. In modal jazz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
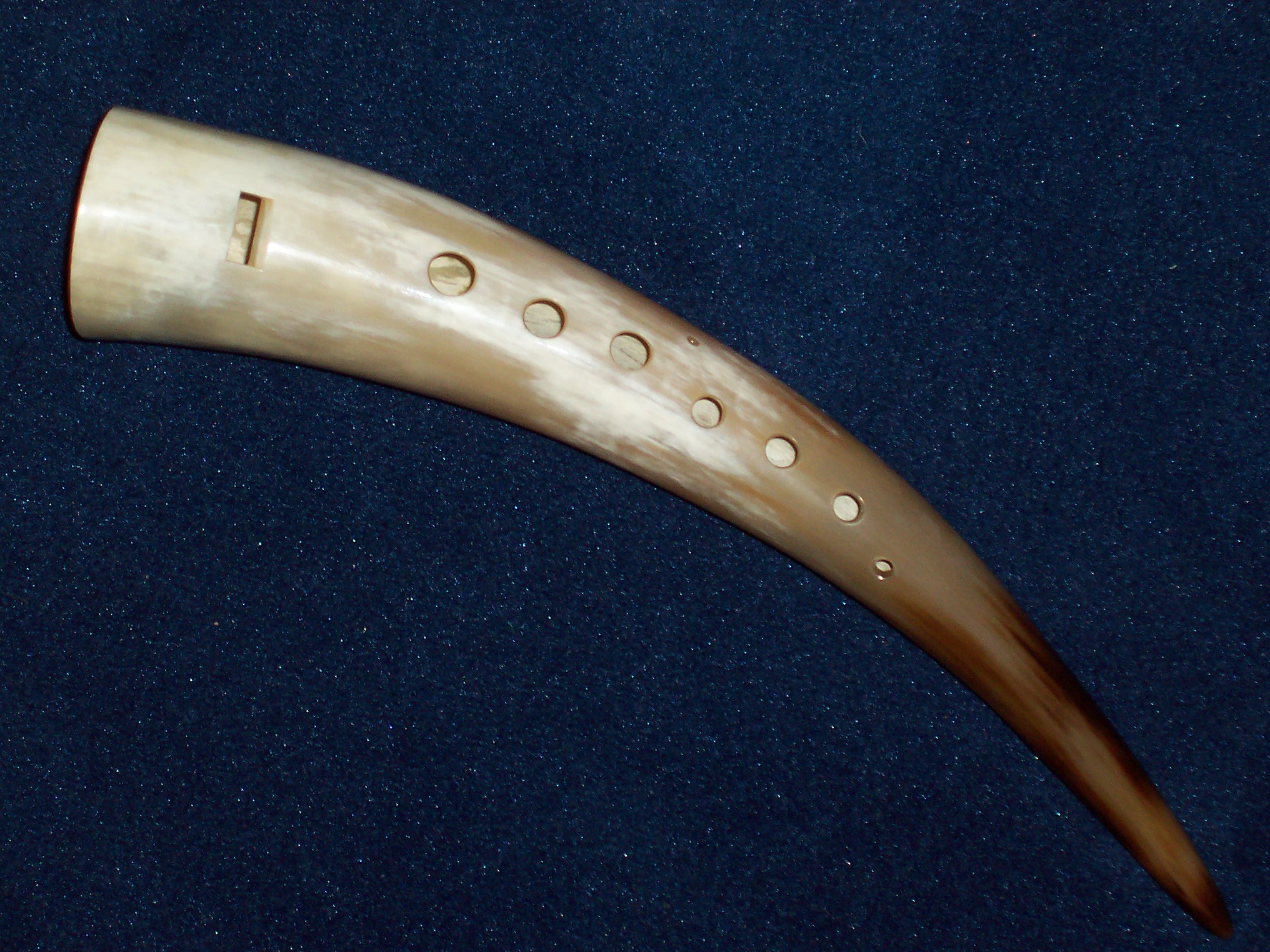
Vessel Flute
A vessel flute is a type of flute with a body which acts as a Helmholtz resonator. The body is vessel-shaped, not tube- or cone-shaped; that is, the far end is closed. Most flutes have cylindrical or conical bore (examples: concert flute, shawm). Vessel flutes have more spherical hollow bodies. The air in the body of a vessel flute resonates as one, with air moving alternately in and out of the vessel, and the pressure inside the vessel increasing and decreasing. This is unlike the resonance of a tube or cone of air, where air moves back and forth along the tube, with pressure increasing in part of the tube while it decreases in another. Blowing across the opening of empty bottle produces a basic edge-blown vessel flute. Multi-note vessel flutes include the ocarina.For a linguistic analysis of the possible origins of the word ''ocarina'', cf. Perono Cacciafoco, Francesco. (2019). A Prehistoric 'Little Goose': A New Etymology for the Word 'Ocarina'. ''Annals of the University o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bishop Diego De Landa
Diego de Landa Calderón, O.F.M. (12 November 1524 – 29 April 1579) was a Spanish Franciscan bishop of the Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Yucatán. Many historians criticize his campaign against idolatry. In particular, he burned almost all the Maya manuscripts (codices) that would have been very useful in deciphering Maya script, knowledge of Maya religion and civilization, and the history of the American continent. Nonetheless, his work in documenting and researching the Maya was indispensable in achieving the current understanding of their culture, to the degree that one scholar asserted that, "ninety-nine percent of what we today know of the Mayas, we know as the result either of what Landa has told us in the pages that follow, or have learned in the use and study of what he told." Conversion of Maya Born in Cifuentes, Guadalajara, Spain, he became a Franciscan friar in 1541, and was sent as one of the first Franciscans to the Yucatán, arriving in 1549. Landa was in c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
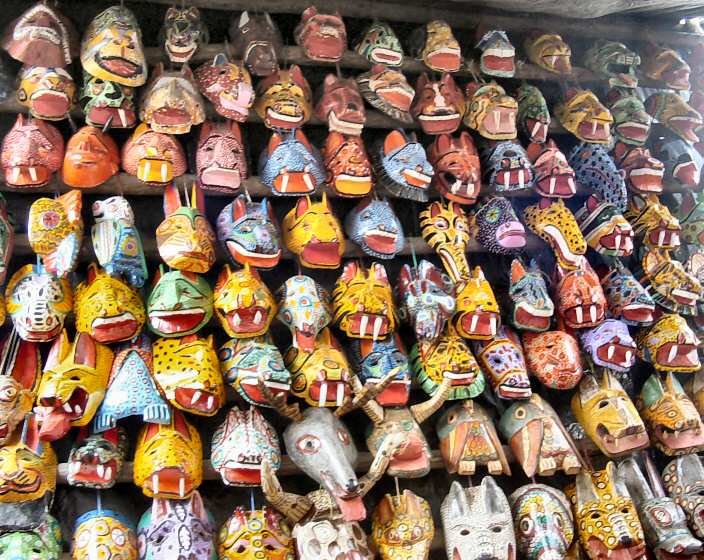
Rabinal Achí
The ''Rabinal Achí'' is a Maya theatrical play written in the Kʼicheʼ language and performed annually in Rabinal, Baja Verapaz, Guatemala. Its original name is ''Xajoj Tun'', meaning "Dance of the Tun" instrument also known as wooden drum. This is one of the few surviving performance pieces from before colonization. It takes place every year on January 25 and involves the entire community of Rabinal. A combination of movement, song, and instrumentation meld the piece together. This performance has been a part of Rabinal history for centuries, and continues to be a part of the culture today. The story of the ''Rabinal Achí'' centers on a historical feud between Rabinal and Kʼicheʼ, two neighboring cities. Colorful costumes and wooden masks are used to differentiate the characters as they play out their roles in the song-dance-drama. Origins The ''Rabinal Achí'' is a Maya song-dance-drama from the fifteenth century that uses vibrant costumes and wooden masks to tell the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diego López De Cogolludo
Diego López de Cogolludo (Alcalá de Henares 1613 – New Spain 1665) was a Spanish Franciscan historian of Yucatán. Biography A native of Alcalá de Henares in Spain, he took the habit of St. Francis at the convent of San Diego, on 31 March 1629, and emigrated to Yucatán, where he became successively lector in theology, guardian, and finally provincial of his order. His work, the ''Historia de Yucatán'', appeared at Madrid in 1688, and was reprinted in 1842 and 1867. It contains information personally gathered at a time when older sources, written and oral, that have now partly disappeared, were still accessible. Cogolludo consulted and used the writings of Bishop Diego de Landa to a considerable extent, but many of his statements must be taken with caution. Works ''Historia de Yucathan'' (Madrid, 1688): The first three chapters of the ''Historia de Yucathan'' present a civil history of how the Spanish conquered the Yucatán Peninsula and its people, the Maya, in three ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Spain
New Spain, officially the Viceroyalty of New Spain ( es, Virreinato de Nueva España, ), or Kingdom of New Spain, was an integral territorial entity of the Spanish Empire, established by Habsburg Spain during the Spanish colonization of the Americas and having its capital in Mexico City. Its jurisdiction comprised a huge area that included what is now Mexico, the Western and Southwestern United States (from California to Louisiana and parts of Wyoming, but also Florida) in North America; Central America, the Caribbean, very northern parts of South America, and several territorial Pacific Ocean archipelagos. After the 1521 Spanish conquest of the Aztec empire, conqueror Hernán Cortés named the territory New Spain, and established the new capital, Mexico City, on the site of the Tenochtitlan, the capital of the Mexica (Aztec) Empire. Central Mexico became the base of expeditions of exploration and conquest, expanding the territory claimed by the Spanish Empire. With the polit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tonsured Maize God
Like other Mesoamerican peoples, the traditional Maya civilization, Maya recognize in their staple crop, maize, a vital force with which they strongly identify. This is clearly shown by their mythological traditions. According to the 16th-century Popol Vuh, the Hero Twins have maize plants for alter egos and man himself is created from maize. The discovery and opening of the Maize Mountain – the place where the corn seeds are hidden – is still one of the most popular of Maya tales. In the Classic period (200-900 AD), the maize deity shows aspects of a culture hero. Female and male deities In Maya oral tradition, maize is usually personified as a woman — like rice in Southeast Asia, or wheat in ancient Greece and Rome. The acquisition of this woman through bridal capture constitutes one of the basic Maya myths. In contrast to this, the pre-Spanish Maya aristocracy appears to have primarily conceived of maize as male. The classic period distinguished two male forms: a foliated ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Howler Monkey Gods
Among the Classic Mayas, the howler monkey god was a major deity of the arts—including music—and a patron of the artisans, especially of the scribes and sculptors. As such, his sphere of influence overlapped with that of the Tonsured Maize God. The monkey patrons—there are often two of them—have been depicted on classical vases in the act of writing books (while stereotypically holding an ink nap) and carving human heads. Together, these two activities may have constituted a metaphor for the creation of mankind, with the book containing the birth signs and the head the life principle or 'soul', an interpretation reinforced by the craftsman titles of the creator gods in the Popol Vuh. Based on its facial features, the stone sculpture of a seated writer found within the House of the Scribes in Copan is often described as a howler monkey. However, it is the two large statues of simian figures shaking rattles (see fig.), found on both sides of the 'Reviewing Stand' of Copan's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Popol Vuh
''Popol Vuh'' (also ''Popol Wuj'' or ''Popul Vuh'' or ''Pop Vuj'') is a text recounting the mythology and history of the Kʼicheʼ people, one of the Maya peoples, who inhabit Guatemala and the Mexican states of Chiapas, Campeche, Yucatan and Quintana Roo, as well as areas of Belize, Honduras and El Salvador. The ''Popol Vuh'' is a foundational sacred narrative of the Kʼicheʼ people from long before the Spanish conquest of the Maya. It includes the Mayan creation myth, the exploits of the Maya Hero Twins, Hero Twins Hunahpú and Xbalanqué, and a chronicle of the Kʼicheʼ people. The name "Popol Vuh" translates as "Book of the Community" or "Book of Counsel" (literally "Book that pertains to the mat", since a woven mat was used as a royal throne in ancient Kʼicheʼ society and symbolised the unity of the community). It was originally preserved through oral tradition until approximately 1550, when it was recorded in writing. The documentation of the ''Popol Vuh'' is credited ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tortoiseshell
Tortoiseshell or tortoise shell is a material produced from the shells of the larger species of tortoise and turtle, mainly the hawksbill sea turtle, which is a critically endangered species according to the IUCN Red List largely because of its exploitation for this trade. The large size, fine color, and unusual form of the hawksbill's scutes make it especially suitable. The distinctive patterning is referred to in names such as the tortoiseshell cat, several breeds of guinea pig, and the common names of several species of the butterfly genera ''Nymphalis'' and ''Aglais'', and some other uses. Uses Tortoiseshell was widely used from ancient times in the North and in Asia, until the trade was banned in 2014. It was used, normally in thin slices or pieces, in the manufacture of a wide variety of items such as combs, small boxes and frames, inlays in furniture (known as Boulle Work carried out by André-Charles Boulle), and other items: frames for spectacles, guitar picks and kn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Teponaztli
A teponaztli is a type of slit drum used in central Mexico by the Aztecs and related cultures. Structure Teponaztli are made of hollow hardwood logs, often fire-hardened. Like most slit drums, teponaztlis have two slits on their topside, cut into the shape of an "H". The resultant strips or tongues are then struck with rubber-head wood mallets, or with deer antlers. Since the tongues are of different lengths, or carved into different thicknesses, the teponaztli produces 2 different pitches, usually near a third or fourth apart. Teponaztli were usually decorated with relief carvings of various deities or with abstract designs, and were even carved into the shapes of creatures or humans. Some of these creatures are open-mouthed, providing increased volume through the hole at the end. On other drums, a hole was made on the drum's underside. Teponaztli from the Mixtec culture in what is today south-central Mexico are known for their various battle or mythological scenes carve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |