|
Max Planck Institute For Plasma Physics
The Max Planck Institute for Plasma Physics (german: Max-Planck-Institut für Plasmaphysik, IPP) is a physics institute investigating the physical foundations of a fusion power plant. The IPP is an institute of the Max Planck Society, part of the European Atomic Energy Community, and an associated member of the Helmholtz Association. The IPP has two sites: Garching near Munich (founded 1960) and Greifswald (founded 1994), both in Germany. It owns several large devices, namely * the experimental tokamak ASDEX Upgrade (in operation since 1991) * the experimental stellarator Wendelstein 7-X (in operation since 2016) * a tandem accelerator * a high heat flux test facility (GLADIS) Furthermore it cooperates closely with the ITER, DEMO and JET projects. Scientific divisions * Tokamak Scenario Development * Plasma Edge and Wall * Stellarator Heating and Optimization * Stellarator Dynamics and Transport * Stellarator Edge and Divertor Physics * Wendelstein 7-X Operations * Stel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IPP Logo
IPP may refer to: Organisations * Independent Power Producer, electric power generator * India Pride Project, recovering stolen Indian artefacts * Istituto per la Protezione delle Piante (Institute of Plant Protection), Italy * Max-Planck-Institut für Plasmaphysik, a physics institute in Garching, Germany * Intermountain Power Plant, a coal power plant, Delta, Utah, USA. * Institute of Particle Physics, organization to promote Canadian excellence in particle physics research Science and technology * Isopentenyl pyrophosphate, a metabolite * Ionospheric pierce point, where a satellite signal crosses the ionosphere * '' Induratio penis plastica'', Peyronie's disease * Nob Yoshigahara Puzzle Design Competition, also known as the International Puzzle Party Sports * International Player Pathway, program for non-Americans players in the National Football League Computing * Integrated Performance Primitives, a software library * Internet Printing Protocol * Insilicos Proteomics Pip ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
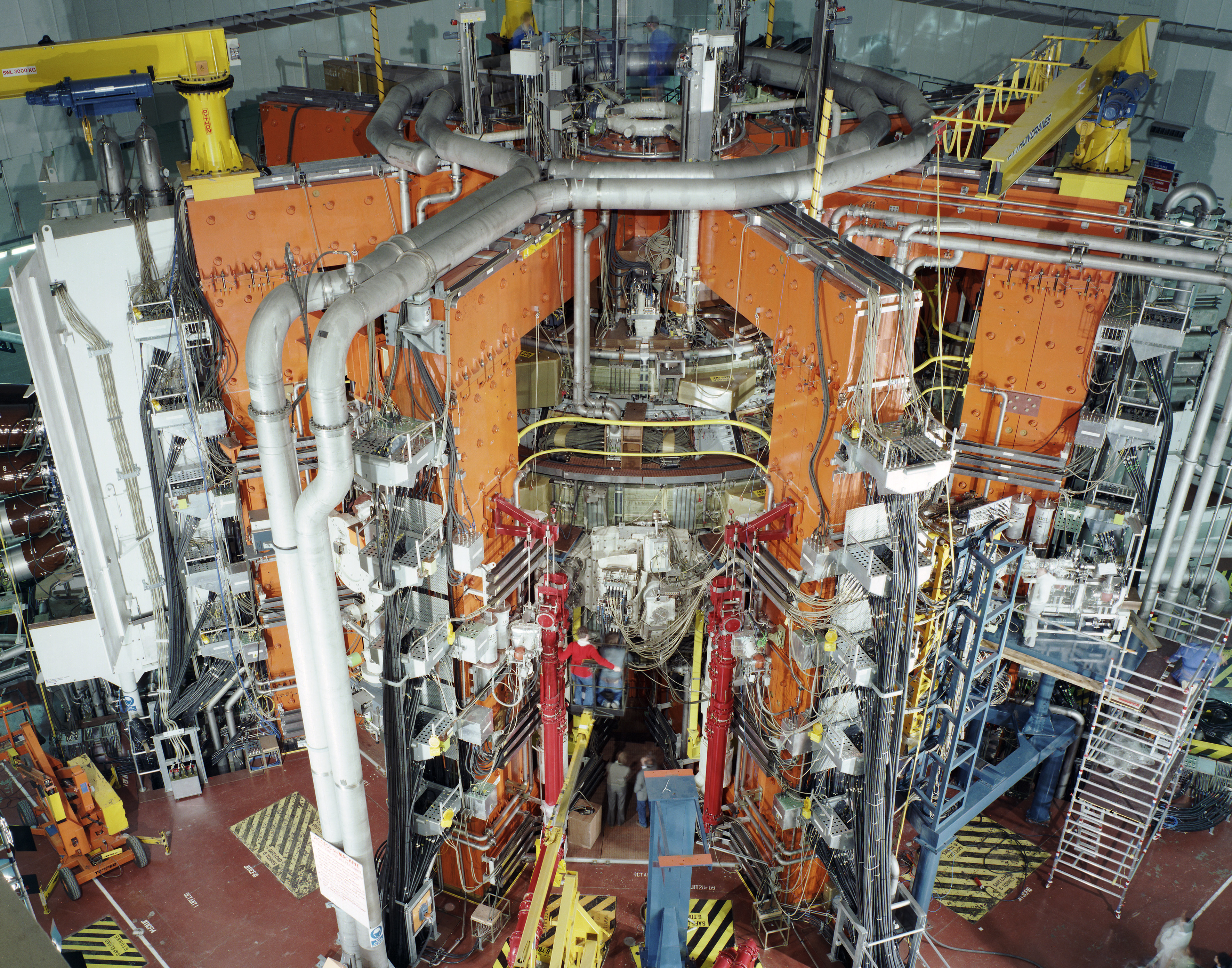
Stellarator
A stellarator is a plasma device that relies primarily on external magnets to confine a plasma. Scientists researching magnetic confinement fusion aim to use stellarator devices as a vessel for nuclear fusion reactions. The name refers to the possibility of harnessing the power source of the stars, such as the Sun. It is one of the earliest fusion power devices, along with the z-pinch and magnetic mirror. The stellarator was invented by American scientist Lyman Spitzer of Princeton University in 1951, and much of its early development was carried out by his team at what became the Princeton Plasma Physics Laboratory (PPPL). Lyman's Model A began operation in 1953 and demonstrated plasma confinement. Larger models followed, but these demonstrated poor performance, losing plasma at rates far worse than theoretical predictions. By the early 1960s, any hope of quickly producing a commercial machine faded, and attention turned to studying the fundamental theory of high-energy plasma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physics Institutes
Physics is the natural science that studies matter, its fundamental constituents, its motion and behavior through space and time, and the related entities of energy and force. "Physical science is that department of knowledge which relates to the order of nature, or, in other words, to the regular succession of events." Physics is one of the most fundamental scientific disciplines, with its main goal being to understand how the universe behaves. "Physics is one of the most fundamental of the sciences. Scientists of all disciplines use the ideas of physics, including chemists who study the structure of molecules, paleontologists who try to reconstruct how dinosaurs walked, and climatologists who study how human activities affect the atmosphere and oceans. Physics is also the foundation of all engineering and technology. No engineer could design a flat-screen TV, an interplanetary spacecraft, or even a better mousetrap without first understanding the basic laws of physics. (. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plasma Physics Facilities
Plasma or plasm may refer to: Science * Plasma (physics), one of the four fundamental states of matter * Plasma (mineral), a green translucent silica mineral * Quark–gluon plasma, a state of matter in quantum chromodynamics Biology * Blood plasma, the yellow-colored liquid component of blood, in which blood cells are suspended * Cytoplasm, a jelly-like substance that fills cells, suspends and protects organelles * Germ plasm, a zone in the cytoplasm determining germ cells * Germplasm, describes a collection of genetic resources for an organism * Milk plasma or whey, the liquid remaining after milk has been curdled and strained * Nucleoplasm, a highly viscous liquid that surrounds the chromosomes and nucleoli * Plasma cell, white blood cells that secrete large volumes of antibodies * Protoplasm, the entire living substance inside the cell membrane or cell wall Technology * Plasma (engine), a real-time 3D game engine from Cyan Worlds * Plasma display, a flat-panel electronic visu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fusion Power
Fusion power is a proposed form of power generation that would generate electricity by using heat from nuclear fusion, nuclear fusion reactions. In a fusion process, two lighter atomic nucleus, atomic nuclei combine to form a heavier nucleus, while releasing energy. Devices designed to harness this energy are known as fusion reactors. Research into fusion reactors began in the 1940s, but as of 2022, only one design, an Inertial confinement fusion, inertial confinement laser-driven fusion machine at the US National Ignition Facility, has conclusively produced a positive fusion energy gain factor, i.e. more power output than input. Fusion processes require fuel and a confined environment with sufficient temperature, pressure, and confinement time to create a plasma (physics), plasma in which fusion can occur. The combination of these figures that results in a power-producing system is known as the Lawson criterion. In stars, the most common fuel is hydrogen, and gravity provides ext ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Greifswald
The University of Greifswald (; german: Universität Greifswald), formerly also known as “Ernst-Moritz-Arndt University of Greifswald“, is a public research university located in Greifswald, Germany, in the state of Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania. Founded in 1456 (teaching existed since 1436), it is one of the oldest universities in Europe, with generations of notable alumni and staff having studied or worked in Greifswald. As the fourth oldest university in present Germany, it was temporarily also the oldest university of the Kingdoms of Sweden (1648–1815) and Prussia (1815–1945), respectively. Approximately two-thirds of the 10,179 students are from outside the state, including international students from 90 countries all over the world. Due to the small-town atmosphere, the pronounced architectural presence of the alma mater across town, and the young, academic flair in the streets, Greifswald is often described as a "university with a town built around it" rather ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Technical University Of Munich
The Technical University of Munich (TUM or TU Munich; german: Technische Universität München) is a public research university in Munich, Germany. It specializes in engineering, technology, medicine, and applied and natural sciences. Established in 1868 by King Ludwig II of Bavaria, the university now has additional campuses in Garching, Freising, Heilbronn, Straubing, and Singapore, with the Garching campus being its largest. The university is organized into eight schools and departments, and is supported by numerous research centers. It is one of the largest universities in Germany, with 50,000 students and an annual budget of €1,770.3 million (including university hospital). A ''University of Excellence'' under the German Universities Excellence Initiative, TUM is considered the top university in Germany according to major rankings as of 2022 and is among the leading universities in the European Union. Its researchers and alumni include 18 Nobel laureates and 23 Leib ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joint European Torus
The Joint European Torus, or JET, is an operational magnetically confined plasma physics experiment, located at Culham Centre for Fusion Energy in Oxfordshire, UK. Based on a tokamak design, the fusion research facility is a joint European project with a main purpose of opening the way to future nuclear fusion grid energy. At the time of its design JET was larger than any comparable machine. JET was built with the hope of reaching ''scientific breakeven'' where the fusion energy gain factor ''Q'' =1.0. It began operation in 1983 and spent most of the next decade increasing its performance in a lengthy series of experiments and upgrades. In 1991 the first experiments including tritium were made, making JET the first reactor in the world to run on the production fuel of a 50–50 mix of tritium and deuterium. It was also decided to add a divertor design to JET, which occurred between 1991 and 1993. Performance was significantly improved, and in 1997 JET set the record for the cl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DEMOnstration Power Station
DEMO refers to a proposed class of nuclear fusion experimental reactors that are intended to demonstrate the net production of electric power from nuclear fusion. Most of the ITER partners have plans for their own DEMO-class reactors. With the possible exception of the EU and Japan, there are no plans for international collaboration as there was with ITER. Plans for DEMO-class reactors are intended to build upon the ITER experimental nuclear fusion reactor. The most well-known and documented DEMO-class reactor design is that of the European Union (EU). The following parameters have been used as a baseline for design studies: the EU DEMO should produce at least 2000 megawatts (2 gigawatts) of fusion power on a continuous basis, and it should produce 25 times as much power as required for scientific breakeven, which does not include the power required to operate the reactor. The EU DEMO design of 2 to 4 gigawatts of thermal output will be on the scale of a modern electric power s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ITER
ITER (initially the International Thermonuclear Experimental Reactor, ''iter'' meaning "the way" or "the path" in Latin) is an international nuclear fusion research and engineering megaproject aimed at creating energy by replicating, on Earth, the fusion processes of the Sun. Upon completion of construction of the main reactor and first plasma, planned for late 2025, it will be the world's largest magnetic confinement plasma physics experiment and the largest experimental tokamak nuclear fusion reactor. It is being built next to the Cadarache facility in southern France. ITER will be the largest of more than 100 fusion reactors built since the 1950s, with ten times the plasma volume of any other tokamak operating today. The long-term goal of fusion research is to generate electricity. ITER's stated purpose is scientific research, and technological demonstration of a large fusion reactor, without electricity generation. ITER's goals are to achieve enough fusion to produce 10 ti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Particle Accelerator
A particle accelerator is a machine that uses electromagnetic fields to propel charged particles to very high speeds and energies, and to contain them in well-defined beams. Large accelerators are used for fundamental research in particle physics. The largest accelerator currently active is the Large Hadron Collider (LHC) near Geneva, Switzerland, operated by the CERN. It is a collider accelerator, which can accelerate two beams of protons to an energy of 6.5 TeV and cause them to collide head-on, creating center-of-mass energies of 13 TeV. Other powerful accelerators are, RHIC at Brookhaven National Laboratory in New York and, formerly, the Tevatron at Fermilab, Batavia, Illinois. Accelerators are also used as synchrotron light sources for the study of condensed matter physics. Smaller particle accelerators are used in a wide variety of applications, including particle therapy for oncological purposes, radioisotope production for medical diagnostics, ion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wendelstein 7-X
The Wendelstein 7-X (abbreviated W7-X) reactor is an experimental stellarator built in Greifswald, Germany, by the Max Planck Institute for Plasma Physics (IPP), and completed in October 2015.Introduction – the Wendelstein 7-X stellarator Retrieved 5 November 2014. Its purpose is to advance stellarator technology: though this experimental reactor will not produce electricity, it is used to evaluate the main components of a future plant; it was developed based on the predecessor experimental reactor. , the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |