|
Max Planck Institute For Gravitational Physics
The Max Planck Institute for Gravitational Physics (Albert Einstein Institute) is a Max Planck Institute whose research is aimed at investigating Einstein's theory of relativity and beyond: Mathematics, quantum gravity, astrophysical relativity, and gravitational-wave astronomy. The institute was founded in 1995 and is located in the Potsdam Science Park in Golm, Potsdam and in Hannover where it closely collaborates with the Leibniz University Hannover. Both the Potsdam and the Hannover parts of the institute are organized in three research departments and host a number of independent research groups. The institute conducts fundamental research in mathematics, data analysis, astrophysics and theoretical physics as well as research in laser physics, vacuum technology, vibration isolation and classical and quantum optics. When the LIGO Scientific Collaboration announced the first detection of gravitational waves, researchers of the institute were involved in modeling, detecting, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Golm (Potsdam)
Golm is a locality (''Ortsteil'') of Potsdam, the capital of the German state of Brandenburg. The former municipality was incorporated in 2003. Its name is derived from Western Slavic ''chulm'', meaning "hill", and refers to one of the nearby elevations, either ''Reiherberg'' ( a.s.l.) near the centre of the original village or ''Ehrenpfortenberg'' ( a.s.l.) east of it. Geography Neighbouring localities are Grube and Bornim in the north, Eiche in the east (all of which are now parts of Potsdam), and Wildpark West, a part of Geltow in Schwielowsee municipality, in the south. To the west, Golm is bordered by '' Großer Zernsee'', a lake in the course of the river Havel. The settlement of Kuhfort, bordering the Wildpark area of Potsdam, is located southeast of Golm, and east of the grassland of ''Golmer Luch''. Buildings and structures Golm houses, among other things, since 1991 a complex of the University of Potsdam on the premises of former Luftwaffe and Reichsarbeitsdien ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vibration Isolation
Vibration isolation is the process of isolating an object, such as a piece of equipment, from the source of vibrations. Vibration is undesirable in many domains, primarily engineered systems and habitable spaces, and methods have been developed to prevent the transfer of vibration to such systems. Vibrations propagate via mechanical waves and certain mechanical linkages conduct vibrations more efficiently than others. Passive vibration isolation makes use of materials and mechanical linkages that absorb and damp these mechanical waves. Active vibration isolation involves sensors and actuators that produce disruptive interference that cancels-out incoming vibration. Passive isolation "Passive vibration isolation" refers to vibration isolation or mitigation of vibrations by passive techniques such as rubber pads or mechanical springs, as opposed to "active vibration isolation" or "electronic force cancellation" employing electric power, sensors, actuators, and control systems. Passive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cosmic Explorer (gravitational Wave Observatory)
''Cosmic Explorer'' (stylized as ''COSMIC EXPLORER'') is the fifth studio album by Japanese girl group Perfume. It was released on April 6, 2016 by Universal Music Japan, Universal J, and Perfume Records. It is Perfume's fifth consecutive album to be fully produced, written, composed, and arranged by Japanese musician and Capsule band member Yasutaka Nakata. Five different formats were released to promote the album: a standalone CD, a double CD and DVD/Blu-ray box set, a digital release and a double disc vinyl, where the first disc is blue and the second disc could be orange, pink or yellow. The vinyls were available for purchase at Perfume: A Gallery Experience Supported by Rhizomatiks in London and NY. Upon the album's release, it was met with favorable reviews from music critics. They praised the album's composition and sound, and also highlighted several songs from the album. However, some noted that the material and commercial appeal of the songs were repetitive and predicta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Einstein Telescope
Einstein Telescope (ET) or Einstein Observatory, is a proposed third-generation ground-based gravitational wave detector, currently under study by some institutions in the European Union. It will be able to test Einstein's general theory of relativity in strong field conditions and realize precision gravitational wave astronomy. The ET is a design study project supported by the European Commission under the Framework Programme 7 (FP7). It concerns the study and the conceptual design for a new research infrastructure in the emergent field of gravitational-wave astronomy. Motivation The evolution of the current gravitational wave detectors Advanced Virgo and Advanced LIGO, as ''second generation'' detectors, is well defined. Currently they have been upgraded to their so-called enhanced level and they are expected to reach their design sensitivity in the next few years. LIGO detected gravitational waves in 2015 and Virgo joined this experimental success with the first gravitat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laser Interferometer Space Antenna
The Laser Interferometer Space Antenna (LISA) is a proposed space probe to detect and accurately measure gravitational waves—tiny ripples in the fabric of spacetime—from astronomical sources. LISA would be the first dedicated space-based gravitational wave detector. It aims to measure gravitational waves directly by using laser interferometry. The LISA concept has a constellation of three spacecraft arranged in an equilateral triangle with sides 2.5 million kilometres long, flying along an Earth-like heliocentric orbit. The distance between the satellites is precisely monitored to detect a passing gravitational wave. The LISA project started out as a joint effort between NASA and the European Space Agency (ESA). However, in 2011, NASA announced that it would be unable to continue its LISA partnership with the European Space Agency due to funding limitations. The project is a recognized CERN experiment (RE8). A scaled down design initially known as the New Gravitational-wave ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
KAGRA
The Kamioka Gravitational Wave Detector (KAGRA), is a large interferometer designed to detect gravitational waves predicted by the general theory of relativity. KAGRA is a Michelson interferometer that is isolated from external disturbances: its mirrors and instrumentation are suspended and its laser beam operates in a vacuum. The instrument's two arms are three kilometres long and located underground at the Kamioka Observatory which is near the Kamioka section of the city of Hida in Gifu Prefecture, Japan. KAGRA is a project of the gravitational wave studies group at the Institute for Cosmic Ray Research (ICRR) of the University of Tokyo. It became operational on 25 February 2020, when it began data collection. It is Asia's first gravitational wave observatory, the first in the world built underground, and the first whose detector uses cryogenic mirrors. It is expected to have an operational sensitivity equal to, or greater than, LIGO and Virgo. The Kamioka Observatory special ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Virgo Interferometer
The Virgo interferometer is a large interferometer designed to detect gravitational waves predicted by the general theory of relativity. Virgo is a Michelson interferometer that is isolated from external disturbances: its mirrors and instrumentation are suspended and its laser beam operates in a vacuum. The instrument's two arms are three kilometres long and located in Santo Stefano a Macerata, near the city of Pisa, Italy. Virgo is hosted by the European Gravitational Observatory (EGO), a consortium founded by the French CNRS and Italian INFN. The ''Virgo Collaboration'' operates the detector and is composed of more than 650 members, representing 119 institutions in 14 different countries. Other interferometers similar to Virgo have the same goal of detecting gravitational waves, including the two LIGO interferometers in the United States (at the Hanford Site and in Livingston, Louisiana). Since 2007, Virgo and LIGO have agreed to share and jointly analyze the data recorded by th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
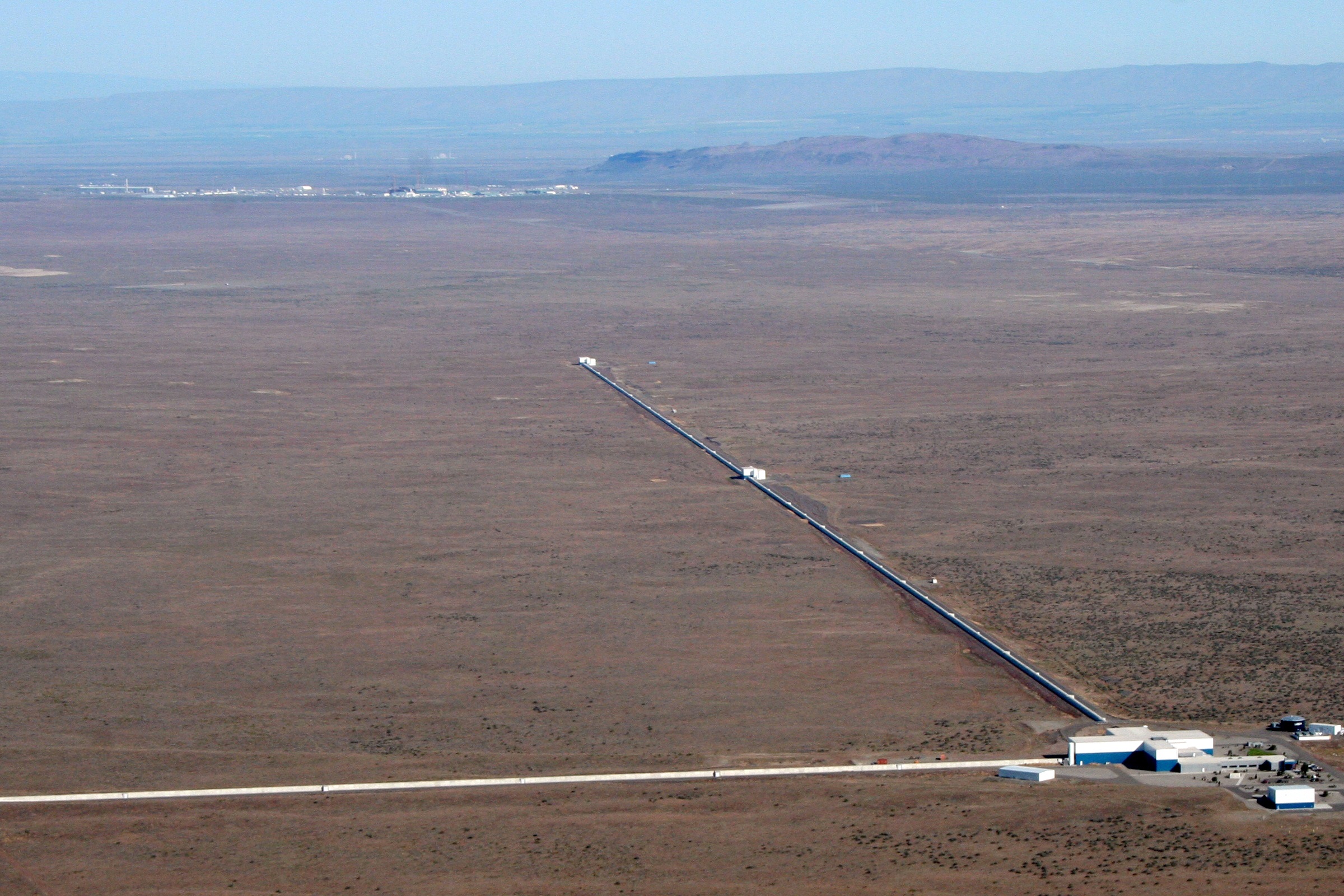
LIGO
The Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory (LIGO) is a large-scale physics experiment and observatory designed to detect cosmic gravitational waves and to develop gravitational-wave observations as an astronomical tool. Two large observatories were built in the United States with the aim of detecting gravitational waves by laser interferometry. These observatories use mirrors spaced four kilometers apart which are capable of detecting a change of less than one ten-thousandth the charge diameter of a proton. (that is, to Proxima Centauri at ). The initial LIGO observatories were funded by the United States National Science Foundation (NSF) and were conceived, built and are operated by Caltech and MIT. They collected data from 2002 to 2010 but no gravitational waves were detected. The Advanced LIGO Project to enhance the original LIGO detectors began in 2008 and continues to be supported by the NSF, with important contributions from the United Kingdom's Science ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gravitational Wave
Gravitational waves are waves of the intensity of gravity generated by the accelerated masses of an orbital binary system that propagate as waves outward from their source at the speed of light. They were first proposed by Oliver Heaviside in 1893 and then later by Henri Poincaré in 1905 as waves similar to electromagnetic waves but the gravitational equivalent. Gravitational waves were later predicted in 1916 by Albert Einstein on the basis of his general theory of relativity as ripples in spacetime. Later he refused to accept gravitational waves. Gravitational waves transport energy as gravitational radiation, a form of radiant energy similar to electromagnetic radiation. Newton's law of universal gravitation, part of classical mechanics, does not provide for their existence, since that law is predicated on the assumption that physical interactions propagate instantaneously (at infinite speed)showing one of the ways the methods of Newtonian physics are unable to explain ph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GEO600
GEO600 is a gravitational wave detector located near Sarstedt, a town 20 km to the south of Hanover, Germany. It is designed and operated by scientists from the Max Planck Institute for Gravitational Physics, Max Planck Institute of Quantum Optics and the Leibniz Universität Hannover, along with University of Glasgow, University of Birmingham and Cardiff University in the United Kingdom, and is funded by the Max Planck Society and the Science and Technology Facilities Council (STFC). GEO600 is capable of detecting gravitational waves in the frequency range 50 Hz to 1.5 kHz, and is part of a worldwide network of gravitational wave detectors. This instrument, and its sister interferometric detectors, when operational, are some of the most sensitive gravitational wave detectors ever designed. They are designed to detect relative changes in distance of the order of 10−21, about the size of a single atom compared to the distance from the Sun to the Earth. Construction ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gravitational-wave Observatory
A gravitational-wave detector (used in a gravitational-wave observatory) is any device designed to measure tiny distortions of spacetime called gravitational waves. Since the 1960s, various kinds of gravitational-wave detectors have been built and constantly improved. The present-day generation of laser interferometers has reached the necessary sensitivity to detect gravitational waves from astronomical sources, thus forming the primary tool of gravitational-wave astronomy. The first direct detection of gravitational waves made in 2015 by the Advanced LIGO observatories, a feat which was awarded the 2017 Nobel Prize in Physics. Challenge The direct detection of gravitational waves is complicated by the extraordinarily small effect the waves produce on a detector. The amplitude of a spherical wave falls off as the inverse of the distance from the source. Thus, even waves from extreme systems such as merging binary black holes die out to a very small amplitude by the time they ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
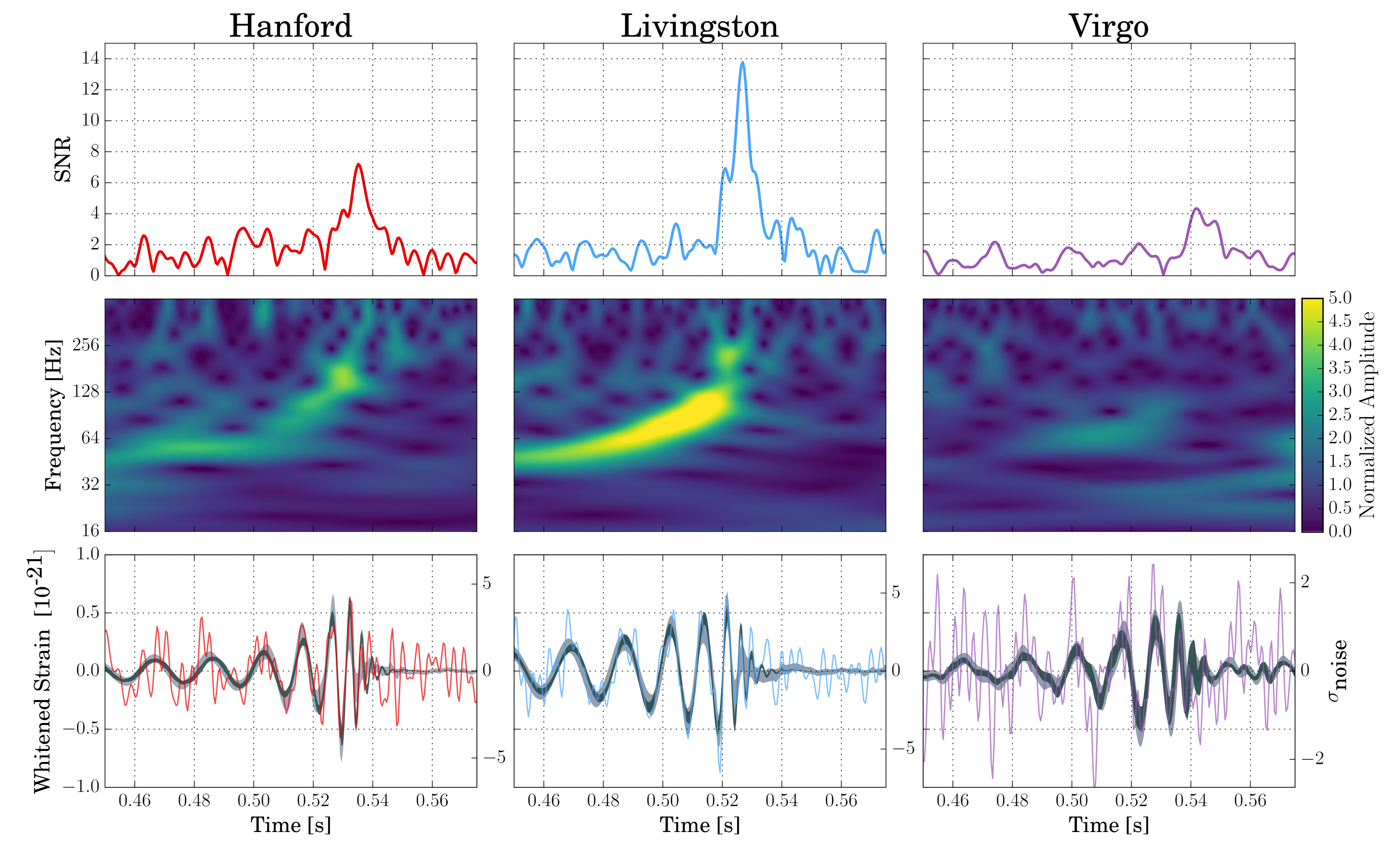
First Observation Of Gravitational Waves
The first direct observation of gravitational waves was made on 14 September 2015 and was announced by the LIGO and Virgo collaborations on 11 February 2016. Previously, gravitational waves had been inferred only indirectly, via their effect on the timing of pulsars in binary star systems. The waveform, detected by both LIGO observatories, matched the predictions of general relativity for a gravitational wave emanating from the inward spiral and merger of a pair of black holes of around 36 and 29 solar masses and the subsequent "ringdown" of the single resulting black hole. The signal was named GW150914 (from ''gravitational wave'' and the date of observation 2015-09-14). It was also the first observation of a binary black hole merger, demonstrating both the existence of binary stellar-mass black hole systems and the fact that such mergers could occur within the current age of the universe. This first direct observation was reported around the world as a remarkable accompl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |