|
Mating Type
Mating types are the microorganism equivalent to sexes in multicellular lifeforms and are thought to be the ancestor to distinct Sex, sexes. They also occur in macro-organisms such as fungi. Definition Mating types are the microorganism equivalent to sex in higher organisms and occur in isogamy, isogamous and anisogamous species. Depending on the group, different mating types are often referred to by numbers, letters, or simply "+" and "−" instead of "male" and "female", which refer to "Sex, sexes" or differences in size between gametes. Syngamy can only take place between gametes carrying different mating types. Occurrence Reproduction by mating types is especially prevalent in Fungus, fungi. Filamentous ascomycetes usually have two mating types referred to as "MAT1-1" and "MAT1-2", following the yeast mating-type locus (MAT). Under standard nomenclature, MAT1-1 (which may informally be called MAT1) encodes for a regulatory protein with an alpha box motif, while MAT1-2 (informal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microorganism
A microorganism, or microbe,, ''mikros'', "small") and ''organism'' from the el, ὀργανισμός, ''organismós'', "organism"). It is usually written as a single word but is sometimes hyphenated (''micro-organism''), especially in older texts. The informal synonym ''microbe'' () comes from μικρός, mikrós, "small" and βίος, bíos, "life". is an organism of microscopic size, which may exist in its single-celled form or as a colony of cells. The possible existence of unseen microbial life was suspected from ancient times, such as in Jain scriptures from sixth century BC India. The scientific study of microorganisms began with their observation under the microscope in the 1670s by Anton van Leeuwenhoek. In the 1850s, Louis Pasteur found that microorganisms caused food spoilage, debunking the theory of spontaneous generation. In the 1880s, Robert Koch discovered that microorganisms caused the diseases tuberculosis, cholera, diphtheria, and anthrax. Because mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neurospora Crassa
''Neurospora crassa'' is a type of red bread mold of the phylum Ascomycota. The genus name, meaning "nerve spore" in Greek, refers to the characteristic striations on the spores. The first published account of this fungus was from an infestation of French bakeries in 1843. ''Neurospora crassa'' is used as a model organism because it is easy to grow and has a haploid life cycle that makes genetics, genetic analysis simple since recessive traits will show up in the offspring. Analysis of genetic recombination is facilitated by the ordered arrangement of the products of meiosis in ''Neurospora'' ascospores. Its entire genome of seven chromosomes has been sequenced. ''Neurospora'' was used by Edward Tatum and George Wells Beadle in their experiments for which they won the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1958. Beadle and Tatum exposed ''N. crassa'' to x-rays, causing mutations. They then observed failures in metabolic pathways caused by errors in specific enzymes. This led t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
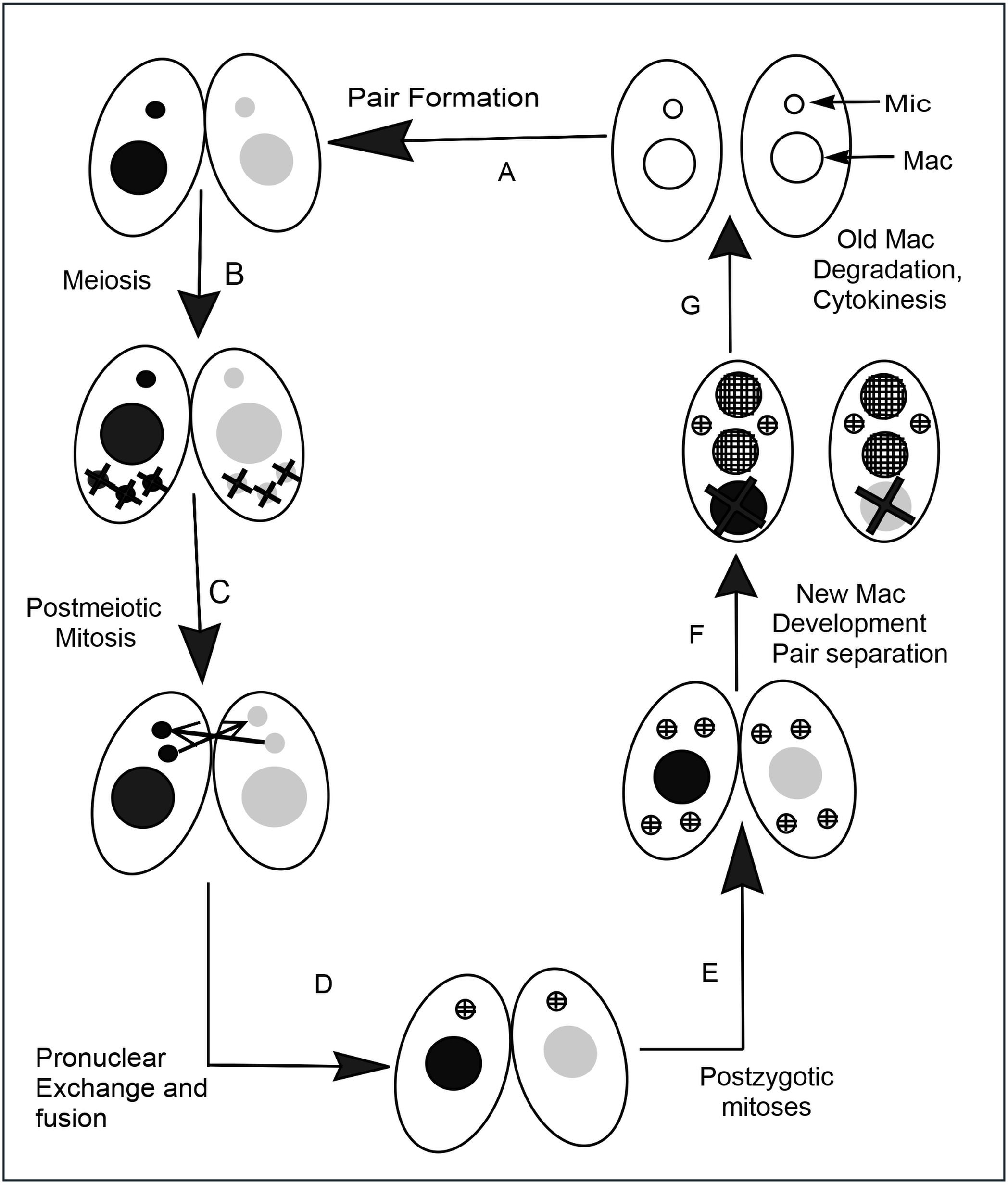
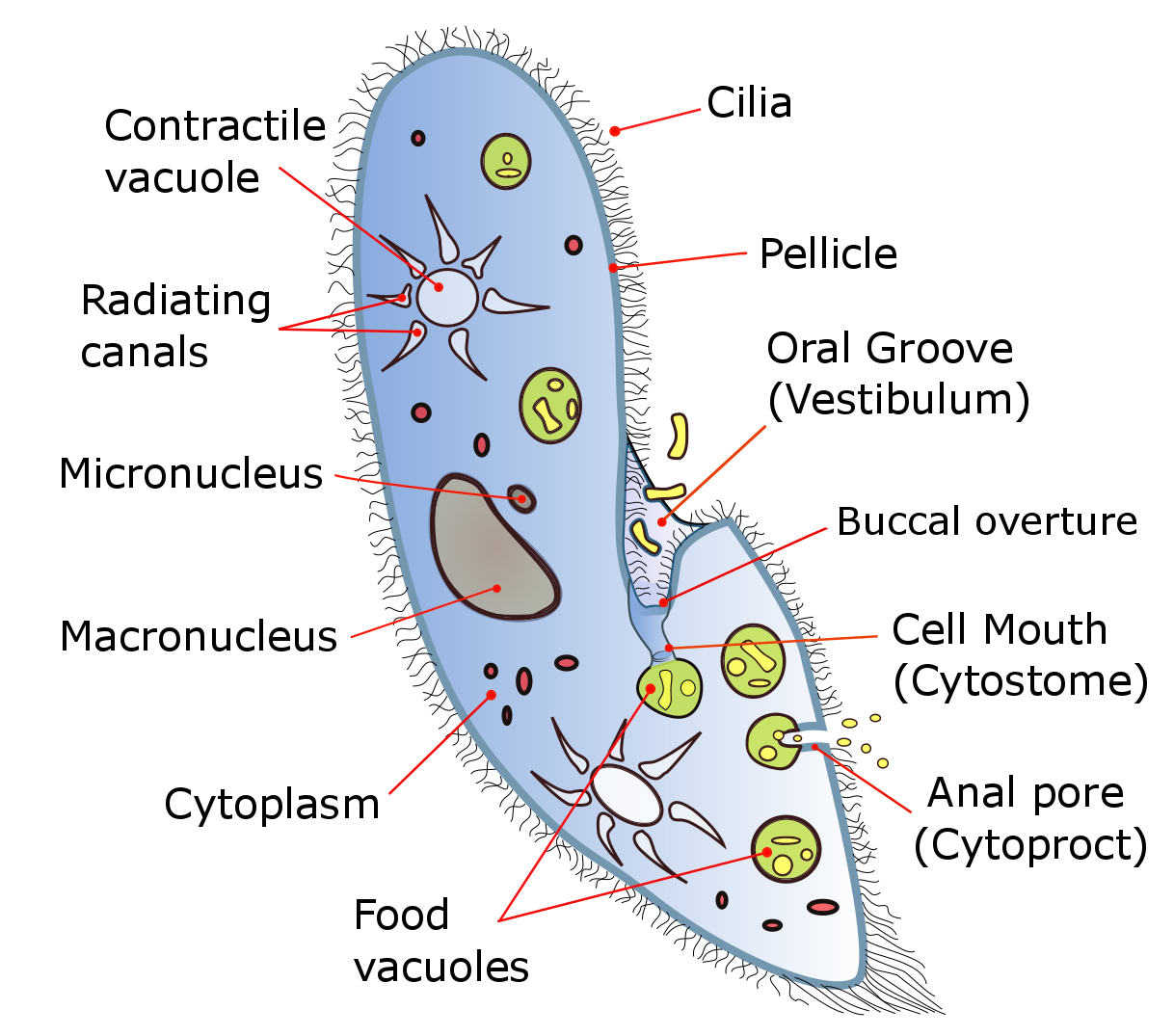
Tetrahymena
''Tetrahymena'', a Unicellular organism, unicellular eukaryote, is a genus of free-living ciliates. The genus Tetrahymena is the most widely studied member of its phylum. It can produce, store and react with different types of hormones. Tetrahymena cells can recognize both related and hostile cells. They can also switch from commensalism, commensalistic to pathogenic modes of survival. They are common in freshwater lakes, ponds, and streams. ''Tetrahymena'' species used as model organisms in biomedical research are ''T. thermophila'' and ''T. pyriformis''. ''T. thermophila'': a model organism in experimental biology As a ciliated protozoan, ''Tetrahymena thermophila'' exhibits nuclear dimorphism: two types of cell Cell nucleus, nuclei. They have a bigger, Somatic cell, non-germline macronucleus and a small, germline micronucleus in each cell at the same time and these two carry out different functions with distinct cytological and biological properties. This unique vers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schizophyllum Commune
''Schizophyllum commune'' is a species of fungus in the genus ''Schizophyllum''. The mushroom resembles undulating waves of tightly packed corals or loose Chinese fan. "Gillies" or "split gills" vary from creamy yellow to pale white in colour. The pileus (mycology), cap is small, wide with a dense yet spongey body texture. It is known as the split-gill mushroom because of the unique longitudinally divided nature of the "lamella (mycology), gills" on the underside of the cap. This mushroom is found throughout the world. It is found in the wild on decaying trees after rainy seasons followed by dry spells where the mushrooms are naturally collected. It is known for its high medicinal value and aromatic taste profile. It has recently attracted the medicinal industry for its immunomodulatory, antifungal, antineoplastic and antiviral activities that are higher than those of any other glucan complex carbohydrate. Description ''Schizophyllum commune'' is usually described as a morpholog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saccharomyces Cerevisiae
''Saccharomyces cerevisiae'' () (brewer's yeast or baker's yeast) is a species of yeast (single-celled fungus microorganisms). The species has been instrumental in winemaking, baking, and brewing since ancient times. It is believed to have been originally isolated from the skin of grapes. It is one of the most intensively studied eukaryotic model organisms in molecular biology, molecular and cell biology, much like ''Escherichia coli'' as the model bacteria, bacterium. It is the microorganism behind the most common type of fermentation (biochemistry), fermentation. ''S. cerevisiae'' cells are round to ovoid, 5–10 micrometre, μm in diameter. It reproduces by budding. Many proteins important in human biology were first discovered by studying their Homology (biology), homologs in yeast; these proteins include cell cycle proteins, signaling proteins, and protein-processing enzymes. ''S. cerevisiae'' is currently the only yeast cell known to have Berkeley body, Berkeley bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mating-type Locus
The mating-type locus is a specialized region in the genomes of some yeast and other fungi, usually organized into heterochromatin and possessing unique histone methylation patterns. The genes in this region regulate the mating type of the organism and therefore determine key events in its biological life cycle, life cycle, such as whether it will reproduce sexual reproduction, sexually or asexual reproduction, asexually. In fission yeast such as ''Schizosaccharomyces pombe, S. pombe'', the formation and maintenance of the heterochromatin organization is regulated by RNA-induced transcriptional silencing, a form of RNA interference responsible for genomic maintenance in many organisms.Noma K, Sugiyama T, Cam H, Verdel A, Zofall M, Jia S, Moazed D, Grewal S (2004). "RITS acts in cis to promote RNA interference-mediated transcriptional and post-transcriptional silencing". Nat Genet 36 (11): 1174-80. Mating type regions have also been well studied in budding yeast ''S. cerevisiae'' and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mating Of Yeast
The yeast ''Saccharomyces cerevisiae'' is a simple microorganism, single-celled eukaryote with both a diploid and haploid mode of existence. The mating of yeast only occurs between haploids, which can be either the a or α (alpha) mating type and thus display simple sexual differentiation. Mating type is determined by a single locus (genetics), locus, ''MAT'', which in turn governs the sexual behaviour of both haploid and diploid cells. Through a form of genetic recombination, haploid yeast can switch mating type as often as every cell cycle. Mating type and the life cycle of ''Saccharomyces cerevisiae'' ''S. cerevisiae'' (yeast) can stably exist as either a diploid or a haploid. Both haploid and diploid yeast cells reproduce by mitosis, with daughter cells budding off of mother cells. Haploid cells are capable of mating with other haploid cells of the opposite mating type (an a cell can only mate with an α cell, and vice versa) to produce a stable diploid cell. Diploid cells, usu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mating In Fungi
Mating in fungi is a complex process governed by mating types. Research on Fungus, fungal mating has focused on several model species with different behaviour. Not all fungi reproduce sexually and many that do are isogamy, isogamous; thus, for many members of the fungal kingdom, the terms "male" and "female" do not apply. Homothallism, Homothallic species are able to mate with themselves, while in Heterothallism, heterothallic species only isolates of opposite mating types can mate. Mating between isogamous fungi may consist only of a transfer of a nucleus from one cell to another. Vegetative incompatibility within species often prevents a fungal isolate from mating with another isolate. Isolates of the same incompatibility group do not mate or mating does not lead to successful offspring. High variation has been reported including same-chemotype mating, sporophyte to gametophyte mating and biparental transfer of mitochondria. File:zygo2.png, Fungi within Zygomycota form progamet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genomic Conflict
Intragenomic conflict refers to the evolutionary phenomenon where genes have phenotypic effects that promote their own transmission in detriment of the transmission of other genes that reside in the same genome. The selfish gene theory postulates that natural selection will increase the frequency of those genes whose phenotypic effects cause their transmission to new organisms, and most genes achieve this by cooperating with other genes in the same genome to build an organism capable of Reproduction, reproducing and/or Kin selection, helping kin to reproduce. The assumption of the prevalence of intragenomic cooperation underlies the organism-centered concept of inclusive fitness. However, conflict among genes in the same genome may arise both in events related to reproduction (a Selfish genetic element, selfish gene may "cheat" and increase its own presence in gametes or offspring above the expected according to fair Mendelian inheritance, Mendelian segregation and fair gametogenesi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ciliate
The ciliates are a group of alveolates characterized by the presence of hair-like organelles called cilia, which are identical in structure to flagellum, eukaryotic flagella, but are in general shorter and present in much larger numbers, with a different wikt:undulating, undulating pattern than flagella. Cilia occur in all members of the group (although the peculiar Suctoria only have them for part of their biological life cycle, life cycle) and are variously used in swimming, crawling, attachment, feeding, and sensation. Ciliates are an important group of protists, common almost anywhere there is water—in lakes, ponds, oceans, rivers, and soils. About 4,500 unique free-living species have been described, and the potential number of extant species is estimated at 27,000–40,000. Included in this number are many Ectosymbiosis, ectosymbiotic and endosymbiotic species, as well as some Obligate parasite, obligate and Facultative parasite, opportunistic parasites. Ciliate species r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Simultaneous Hermaphroditism
Simultaneous hermaphroditism is one of the two types of Hermaphrodite, hermaphroditism, the other type being sequential hermaphroditism. In this form of hermaphroditism an individual has Sex organ, sex organs of both Sex, sexes and can produce both gamete types even in the same breeding season. The distinction between simultaneous hermaphroditism and sequential hermaphroditism isn’t always clear. But unlike sequential hermaphrodites, simultaneous hermaphrodites are both male and female at sexual maturity. Also Sex-determination system, sex determination does not apply to simultaneous hermaphrodites (except in species with mix mating systems). In simultaneous hermaphrodites, Autogamy, self-fertilization is possible in some species, where in others it is absent. Plants Most plants are simultaneous hermaphrodites with it occurring in 80% of Flowering plant, angiosperms. Animals Simultaneous hermaphroditism is one of the most common Sexual system, sexual systems in animals. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anisogamy
Different forms of anisogamy: A) anisogamy of motile cells, B) egg_cell.html"_;"title="oogamy_(egg_cell">oogamy_(egg_cell_and_sperm_cell),_C)_anisogamy_of_non-motile_cells_(egg_cell_and_spermatia)..html" ;"title="egg_cell_and_sperm_cell.html" ;"title="egg_cell.html" ;"title="oogamy (egg cell">oogamy (egg cell and sperm cell">egg_cell.html" ;"title="oogamy (egg cell">oogamy (egg cell and sperm cell), C) anisogamy of non-motile cells (egg cell and spermatia).">283x283px Anisogamy is a form of sexual reproduction that involves the union or fusion of two gametes that differ in size and/or form. The smaller gamete is male, a sperm cell, whereas the larger gamete is female, typically an [ gg cell. Anisogamy is predominant among multicellular organisms. In both plants and animals gamete size difference is the fundamental difference between females and males. Anisogamy most likely evolved from isogamy. Since the biological definition of male and female is based on gamete size, the evo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |