|
Mathematics Mastery
Mathematics mastery is an approach to mathematics education which is based on mastery learning in which most students are expected to achieve a high level of competence before progressing. This technique is used in countries such as China and Singapore where good results have been achieved and so the approach is now being promoted in the UK by people such as schools minister Nick Gibb Nicolas John Gibb (born 3 September 1960) is a British politician serving as Minister of State for Schools since October 2022, having previously held the office from 2010 to 2012 and again from 2015 to 2021. He has served at the Department for .... Chinese teachers were brought to the UK to demonstrate the Shanghai mastery approach in 2015. A trial was made in the UK with about 10,000 students of ages 5–6 and 11–12. In one year, test scores indicated that the students were about a month ahead of students in schools using other approaches. This result was considered small but significant. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematics Education
In contemporary education, mathematics education, known in Europe as the didactics or pedagogy of mathematics – is the practice of teaching, learning and carrying out scholarly research into the transfer of mathematical knowledge. Although research into mathematics education is primarily concerned with the tools, methods and approaches that facilitate practice or the study of practice, it also covers an extensive field of study encompassing a variety of different concepts, theories and methods. National and international organisations regularly hold conferences and publish literature in order to improve mathematics education. History Ancient Elementary mathematics were a core part of education in many ancient civilisations, including ancient Egypt, ancient Babylonia, ancient Greece, ancient Rome and Vedic India. In most cases, formal education was only available to male children with sufficiently high status, wealth or caste. The oldest known mathematics textbook is the Rh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mastery Learning
Mastery learning (or, as it was initially called, "learning for mastery"; also known as "mastery-based learning") is an instructional strategy and educational philosophy, first formally proposed by Benjamin Bloom in 1968. Mastery learning maintains that students must achieve a level of mastery (e.g., 90% on a knowledge test) in prerequisite knowledge before moving forward to learn subsequent information. If a student does not achieve mastery on the test, they are given additional support in learning and reviewing the information and then tested again. This cycle continues until the learner accomplishes mastery, and they may then move on to the next stage. Mastery learning methods suggest that the focus of instruction should be the time required for different students to learn the same material and achieve the same level of mastery. This is very much in contrast with classic models of teaching that focus more on differences in students' ability and where all students are given approx ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
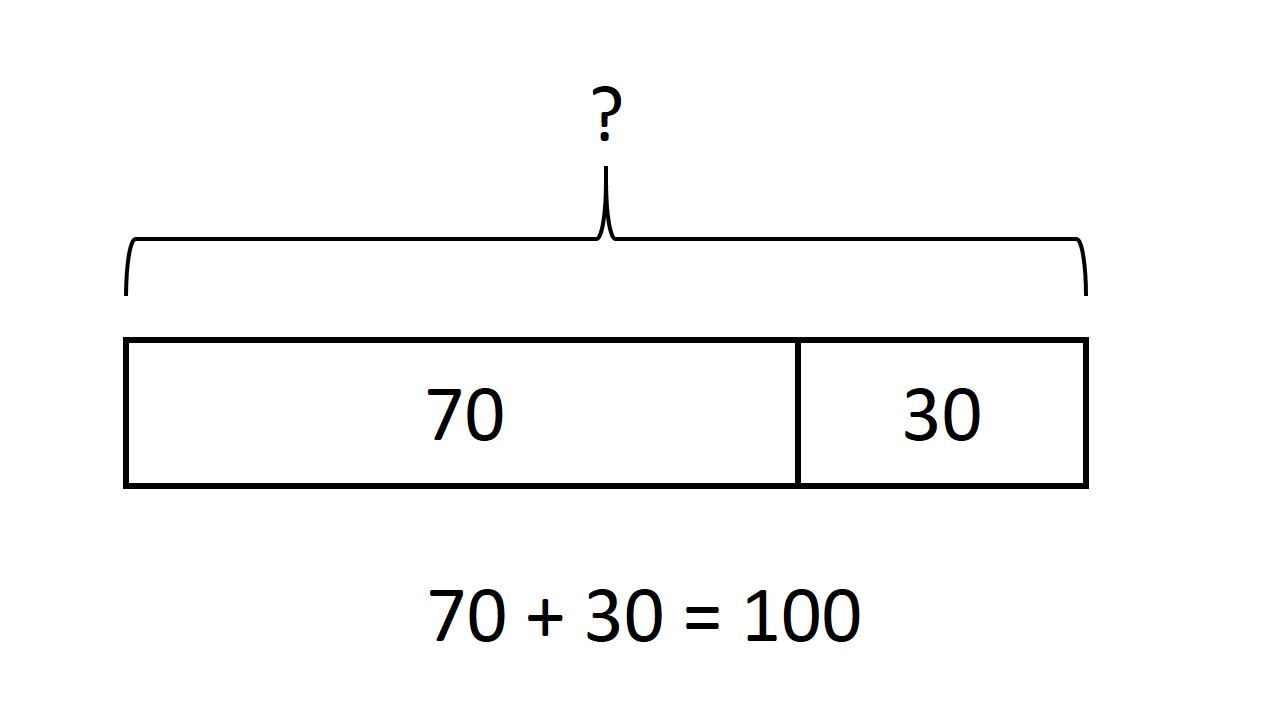
Singapore Math
Singapore math (or Singapore maths in British English) is a teaching method based on the national mathematics curriculum used for first through sixth grade in Singaporean schools. The term was coined in the United States to describe an approach originally developed in Singapore to teach students to learn and master fewer mathematical concepts at greater detail as well as having them learn these concepts using a three-step learning process: concrete, pictorial, and abstract. In the concrete step, students engage in hands-on learning experiences using physical objects which can be everyday items such as paper clips, toy blocks or math manipulates such as counting bears, link cubes and fraction discs. This is followed by drawing pictorial representations of mathematical concepts. Students then solve mathematical problems in an abstract way by using numbers and symbols. The development of Singapore math began in the 1980s when Singapore's Ministry of Education developed its own mathemat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nick Gibb
Nicolas John Gibb (born 3 September 1960) is a British politician serving as Minister of State for Schools since October 2022, having previously held the office from 2010 to 2012 and again from 2015 to 2021. He has served at the Department for Education under Conservative Prime Ministers David Cameron, Theresa May, Boris Johnson and Rishi Sunak. A member of the Conservative Party, Gibb has served as Member of Parliament (MP) for Bognor Regis and Littlehampton since 1997. Gibb was born in Amersham, Buckinghamshire and was educated at the College of St Hild and St Bede at the University of Durham. After unsuccessfully campaigning to become an MP in Stoke-on-Trent Central at the 1992 general election and Rotherham in the 1994 by-election, Gibb was elected to the British House of Commons for Bognor Regis and Littlehampton at the 1997 general election. Gibb was Shadow Minister for Schools from 2005 to 2010. He was appointed as Minister of State for School Standards by Prime Minist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Centre For Excellence In The Teaching Of Mathematics
The National Centre for Excellence in the Teaching of Mathematics (NCETM) is an institution set up in the wake of the Smith Report to improve mathematics teaching in England. It provides strategic leadership for mathematics-specific CPD and aims to raise the professional status of all those engaged in the teaching of mathematics so that the mathematical potential of learners will be fully realised. Structure Its Director until March 2013 was Dame Celia Hoyles, Professor of Mathematics Education at the Institute of Education, University of London and former chief adviser on mathematics education for the government. Report of the invitation MEI seminars She was succeeded by the current Director, Charlie Stripp. An innovative NCETM development is the MatheMaPedia project, masterminded by [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ark (charity)
Absolute Return for Kids (ARK), is an international children's educational charity based in London, UK. Ark is a registered charity under English law. In its reporting year 2017–18, excluding its few subsidiaries, it saw gross income of £14.66 million and had 42 employees. Ark is the parent organisation of Ark Schools, a separate legal entity that is a multi-academy trust in the English education system, with 39 schools (as of 14 October 2022) and nearly 30,000 pupils. History Ark was founded in 2002 by a group of hedge fund financiers including Paul Marshall and Ian Wace of Marshall Wace – and Arpad Busson of EIM Group, founding chairman of the charity's board of trustees. Its aim is to invest philanthropy (benevolence, gift-giving) to improve, greatly, the life chances of children. Since 2014, the charity has been known as Ark or ARK. Its charitable objects are: "to make sure that all children, regardless of their background, have access to a great education a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |