|
Mathematical Instrument
A mathematical instrument is a tool or device used in the study or practice of mathematics. In geometry, construction of various proofs was done using only a compass (drafting), compass and straightedge; arguments in these proofs relied only on idealized properties of these instruments and literal construction was regarded as only an approximation. In applied mathematics, mathematical instruments were used for measuring angles and distances, in astronomy, navigation, surveying and in the measurement of time.Gerard L'Estrange Turner ''Scientific Instruments, 1500-1900: An Introduction'' ( University of California Press, 1998) page 8 Overview Instruments such as the astrolabe, the Quadrant (instrument), quadrant, and others were used to measure and accurately record the relative positions and movements of planets and other celestial objects. The sextant and other related instruments were essential for navigation at sea. Most instruments are used within the field of geometry, incl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regular Pentagon Inscribed In A Circle 240px
The term regular can mean normal or in accordance with rules. It may refer to: People * Moses Regular (born 1971), America football player Arts, entertainment, and media Music * "Regular" (Badfinger song) * Regular tunings of stringed instruments, tunings with equal intervals between the paired notes of successive open strings Other uses in arts, entertainment, and media * Regular character, a main character who appears more frequently and/or prominently than a recurring character * Regular division of the plane, a series of drawings by the Dutch artist M. C. Escher which began in 1936 * '' Regular Show'', an animated television sitcom * ''The Regular Guys'', a radio morning show Language * Regular inflection, the formation of derived forms such as plurals in ways that are typical for the language ** Regular verb * Regular script, the newest of the Chinese script styles Mathematics There are an extremely large number of unrelated notions of "regularity" in mathematics. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
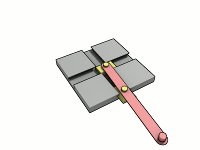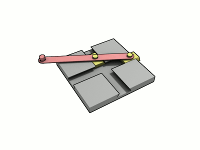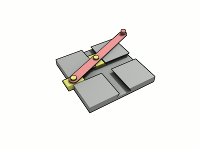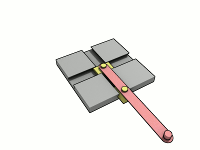
Ellipsograph
A trammel of Archimedes is a mechanism that generates the shape of an ellipse. () It consists of two shuttles which are confined ("trammeled") to perpendicular channels or rails and a rod which is attached to the shuttles by pivots at fixed positions along the rod. As the shuttles move back and forth, each along its channel, all points on the rod move in elliptical paths. The motion of the rod is termed elliptical motion. The semi-axes ''a'' and ''b'' of the ellipses have lengths equal to the distances from the point on the rod to each of the two pivots. The straight lines described by the pivots are special cases of an ellipse, where the length of one axis is twice the distance between the pivots and that of the other is zero. All points on a circle with a diameter defined by the two pivots reciprocate in such straight lines. This circle corresponds to the smaller circle in a Tusi couple. The point midway between the pivots orbits in a circle around the point where the chann ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Planimeter
A planimeter, also known as a platometer, is a measuring instrument used to determine the area of an arbitrary two-dimensional shape. Construction There are several kinds of planimeters, but all operate in a similar way. The precise way in which they are constructed varies, with the main types of mechanical planimeter being polar, linear and Prytz or "hatchet" planimeters. The Swiss mathematician Jakob Amsler-Laffon built the first modern planimeter in 1854, the concept having been pioneered by Johann Martin Hermann in 1814. Many developments followed Amsler's famous planimeter, including electronic versions. The Amsler (polar) type consists of a two-bar linkage. At the end of one link is a pointer, used to trace around the boundary of the shape to be measured. The other end of the linkage pivots freely on a weight that keeps it from moving. Near the junction of the two links is a measuring wheel of calibrated diameter, with a scale to show fine rotation, and worm gearing for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Measuring Instrument
A measuring instrument is a device to measure a physical quantity. In the physical sciences, quality assurance, and engineering, measurement is the activity of obtaining and comparing physical quantities of real-world objects and events. Established standard objects and events are used as units, and the process of measurement gives a number relating the item under study and the referenced unit of measurement. Measuring instruments, and formal test methods which define the instrument's use, are the means by which these relations of numbers are obtained. All measuring instruments are subject to varying degrees of instrument error and measurement uncertainty. These instruments may range from simple objects such as rulers and stopwatches to electron microscopes and particle accelerators. Virtual instrumentation is widely used in the development of modern measuring instruments. Time In the past, a common time measuring instrument was the sundial. Today, the usual measuring instrum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
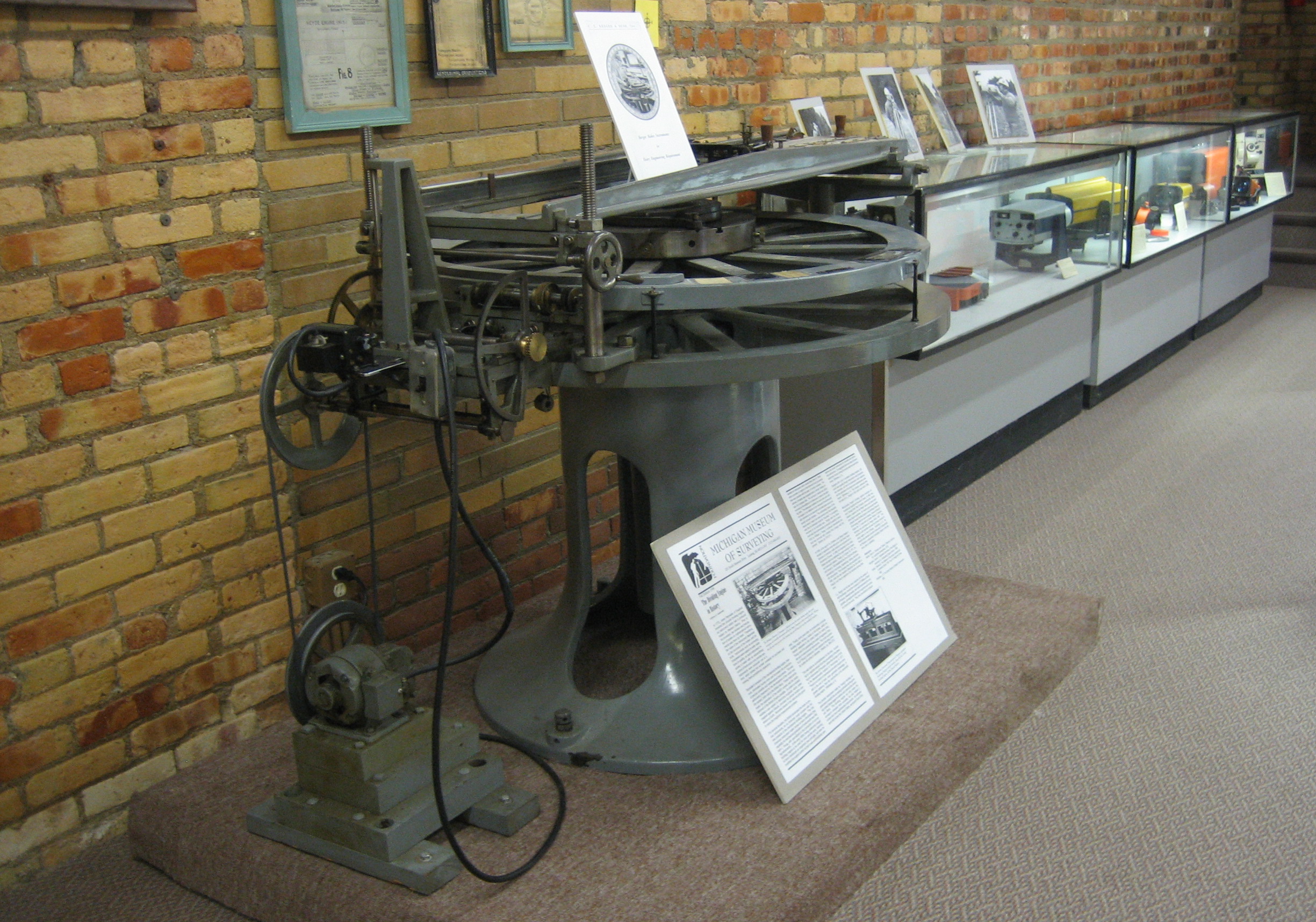
Dividing Engine
A dividing engine is a device employed to mark graduations on measuring instruments to allow for reading smaller measurements than can be allowed by directly engraving them. The well-known vernier scale and micrometer screw-gauge are classic examples that make use of such graduations. History There has always been a need for accurate measuring instruments. Whether it is a linear device such as a ruler or vernier or a circular device such as a protractor, astrolabe, sextant, theodolite, or setting circles for astronomical telescopes, the desire for ever greater precision has always existed. For every improvement in the measuring instruments, such as better alidades or the introduction of telescopic sights, the need for more exact graduations immediately followed. In early instruments, graduations were typically etched or scribed lines in wood, ivory or brass. Instrument makers devised various devices to perform such tasks. Early Islamic instrument makers must have had tec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Construction And Principal Uses Of Mathematical Instruments
''The Construction and Principal Uses of Mathematical Instruments'' (french: Traité de la construction et des principaux usages des instrumens de mathématique) is a book by Nicholas Bion, first published in 1709. It was translated into English in 1723 by Edmund Stone. It was described as "the most famous book devoted to instruments" by historian of science David M. Knight. Nicholas Bion Nicholas Bion (french: Nicolas Bion ; 1652–1733) was a French instrument maker and author with workshops in Paris. He was king's engineer for mathematical instruments. He died in Paris in 1733 aged 81. Bibliography Bion is author An author is the writer of a book, article, play, mostly written work. A broader definition of the word "author" states: "''An author is "the person who originated or gave existence to anything" and whose authorship determines responsibility f ... of the following: *''L'usage des Globes Célestes et Terrestres et des sphères suivant les differents systèm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxford Set Of Mathematical Instruments
Helix (also known as Helix Oxford or Maped Helix) is a United Kingdom-based manufacturer of stationery. It exports to over 65 countries, with offices in Hong Kong and US, and has its UK headquarters in Kingswinford in the West Midlands. History Establishment Helix was established in 1887 under the name 'The Universal Woodworking Company Ltd.; it manufactured wooden rulers and metal laboratory apparatus. In 1894, it patented the drawing compass and, with it, launched the Helix brand, following on from the initial success of the compass and rule. In 1912, the company's first mathematical set was created; and, in 1935, the brand "Helix Oxford" was launched. In 1955 the company was renamed the Helix Universal Company, and moved its headquarters to Lye, West Midlands. In the 1960s, the name was changed to Helix International Ltd. Administration In 2004, the company's factory in Lye ceased production. In January 2012, the company entered administration. On 8 February 2012 the compa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
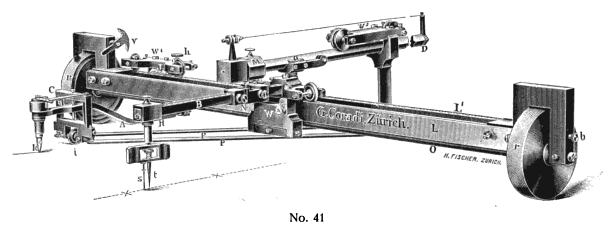
Integraph
An Integraph is a mechanical analog computing device for plotting the integral of a graphically defined function. History Gaspard-Gustave de Coriolis first described the fundamental principal of a mechanical integraph in 1836 in the ''Journal de Mathématiques Pures et Appliquées''. A full description of an integraph was published independently around 1880 by both British physicist Sir Charles Vernon Boys and Bruno Abdank-Abakanowicz, a Polish-Lithuanian mathematician/electrical engineer. Boys described a design for an integraph in 1881 in the ''Philosophical Magazine''. Abakanowicz developed a practical working prototype in 1878, with improved versions of the prototype being manufactured by firms such as Coradi in Zürich, Switzerland. Customized and further improved versions of Abakanowicz's design were manufactured until well after 1900, with these later modifications being made by Abakanowicz in collaboration M. D. Napoli, the "principal inspector of the railroad Chemin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Algebra
Algebra () is one of the broad areas of mathematics. Roughly speaking, algebra is the study of mathematical symbols and the rules for manipulating these symbols in formulas; it is a unifying thread of almost all of mathematics. Elementary algebra deals with the manipulation of variables (commonly represented by Roman letters) as if they were numbers and is therefore essential in all applications of mathematics. Abstract algebra is the name given, mostly in education, to the study of algebraic structures such as groups, rings, and fields (the term is no more in common use outside educational context). Linear algebra, which deals with linear equations and linear mappings, is used for modern presentations of geometry, and has many practical applications (in weather forecasting, for example). There are many areas of mathematics that belong to algebra, some having "algebra" in their name, such as commutative algebra, and some not, such as Galois theory. The word ''algebra'' is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calculator
An electronic calculator is typically a portable electronic device used to perform calculations, ranging from basic arithmetic to complex mathematics. The first solid-state electronic calculator was created in the early 1960s. Pocket-sized devices became available in the 1970s, especially after the Intel 4004, the first microprocessor, was developed by Intel for the Japanese calculator company Busicom. Modern electronic calculators vary from cheap, give-away, credit-card-sized models to sturdy desktop models with built-in printers. They became popular in the mid-1970s as the incorporation of integrated circuits reduced their size and cost. By the end of that decade, prices had dropped to the point where a basic calculator was affordable to most and they became common in schools. Computer operating systems as far back as early Unix have included interactive calculator programs such as dc and hoc, and interactive BASIC could be used to do calculations on most 1970s a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slide Rule
The slide rule is a mechanical analog computer which is used primarily for multiplication and division, and for functions such as exponents, roots, logarithms, and trigonometry. It is not typically designed for addition or subtraction, which is usually performed using other methods. Maximum accuracy for standard linear slide rules is about three decimal significant digits, while scientific notation is used to keep track of the order of magnitude of results. Slide rules exist in a diverse range of styles and generally appear in a linear, circular or cylindrical form, with slide rule scales inscribed with standardized Graduation (instrument), graduated markings. Slide rules manufactured for specialized fields such as aviation or finance typically feature additional scales that aid in specialized calculations particular to those fields. The slide rule is closely related to nomograms used for application-specific computations. Though similar in name and appearance to a standard ruler ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abacus
The abacus (''plural'' abaci or abacuses), also called a counting frame, is a calculating tool which has been used since ancient times. It was used in the ancient Near East, Europe, China, and Russia, centuries before the adoption of the Hindu-Arabic numeral system. The exact origin of the abacus has not yet emerged. It consists of rows of movable beads, or similar objects, strung on a wire. They represent digits. One of the two numbers is set up, and the beads are manipulated to perform an operation such as addition, or even a square or cubic root. In their earliest designs, the rows of beads could be loose on a flat surface or sliding in grooves. Later the beads were made to slide on rods and built into a frame, allowing faster manipulation. Abacuses are still made, often as a bamboo frame with beads sliding on wires. In the ancient world, particularly before the introduction of positional notation, abacuses were a practical calculating tool. The abacus is still used to te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |