|
Masunoyama Tomoharu
is a Japanese former professional sumo wrestler from Sakae, Chiba. He turned professional in July 2006 and was the first wrestler born in the Heisei era to become a ''sekitori'' when he was promoted to the ''jūryō'' division in November 2010, alongside Takayasu. He reached the top ''makuuchi'' division in September 2011. He was injured in his top division debut and fell back to ''jūryō'', but he returned in July 2012 and scored eleven wins, winning the Fighting Spirit Award. A serious knee injury sustained in 2015 resulted in him falling greatly in rank, and he was not able to return to ''sekitori'' status. He retired in May 2021. Early life and sumo background He was born in Iloilo City in the Philippines to a Filipino mother and a Japanese father. His family moved to Japan when he was about one month old. His parents had always been fans of sumo and from a very young age he had aspired to be a sumo wrestler. He was a member of the sumo club at his primary school, and when ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shikona
A is a sumo wrestler's ring name. The tradition of ring names in sumo dates back to the Edo period, where they were used as a means to attract customers and hide the identities of the ''rikishi''. Like standard Japanese names, a ''shikona'' consists of a surname and a personal, or given name, and the full name is written surname first. However, the personal name is rarely used outside formal or ceremonial occasions. Thus, the former ''yokozuna'' is usually referred to as simply ''Asashōryū''. When addressing a sumo wrestler of the ''makuuchi'' or ''jūryō'' divisions, the suffix is used instead of the usual . The given name is often, but not always, the wrestler's original name, and may be changed at the whim of the individual wrestler. Foreign wrestlers always adopt a new, Japanese given name. Often, on first joining professional sumo, a wrestler's ''shikona'' is the same as his family name. As a wrestler rises through the ranks of sumo, he is expected to change his ''shi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heisei Era
The is the period of Japanese history corresponding to the reign of Emperor Emeritus Akihito from 8 January 1989 until his abdication on 30 April 2019. The Heisei era started on 8 January 1989, the day after the death of the Emperor Hirohito, when his son, Akihito, acceded to the throne as the 125th Emperor. In accordance with Japanese customs, Hirohito was posthumously renamed "Emperor Shōwa" on 31 January 1989. Thus, 1989 corresponds to Shōwa 64 until 7 January, and from 8 January. The Heisei era ended on 30 April 2019 (Heisei 31), with the abdication of Akihito from the Chrysanthemum Throne. It was succeeded by the Reiwa era as then-crown prince Naruhito ascended the throne on 1 May midnight local time. History and meaning On 7 January 1989, at 07:55 AM JST, the Grand Steward of Japan's Imperial Household Agency, Shōichi Fujimori, announced Emperor Hirohito's death at 6:33 AM JST, and revealed details about his cancer for the first time. Shortly after the deat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jonokuchi
Professional sumo as administered by the Japan Sumo Association is divided into six ranked divisions. Wrestlers are promoted and demoted within and between these divisions based on the merit of their win–loss records in official tournaments. For more information see ''kachi-koshi'' and ''make-koshi The following words are terms used in sumo wrestling in Japan. A B C D E F G H ...''. Wrestlers are also ranked within each division. The higher a wrestler's rank within a division is, the stronger the general level of opponents he will have to face becomes. According to tradition, each rank is further subdivided into East and West, with East being slightly more prestigious, and ranked slightly higher than its West counterpart. The divisions, ranked in order of hierarchy from highest to lowest, are as follows: ''Mak ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jonidan
Professional sumo as administered by the Japan Sumo Association is divided into six ranked divisions. Wrestlers are promoted and demoted within and between these divisions based on the merit of their win–loss records in official tournaments. For more information see ''kachi-koshi'' and ''make-koshi''. Wrestlers are also ranked within each division. The higher a wrestler's rank within a division is, the stronger the general level of opponents he will have to face becomes. According to tradition, each rank is further subdivided into East and West, with East being slightly more prestigious, and ranked slightly higher than its West counterpart. The divisions, ranked in order of hierarchy from highest to lowest, are as follows: ''Makuuchi'' , or , is the top division. It is fixed at 42 wrestlers who are ranked according to their performance in previous tournaments. At the top of the division are the "titleholders", or "champions" called the ''san'yaku'' comprising ''yokozuna'', ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
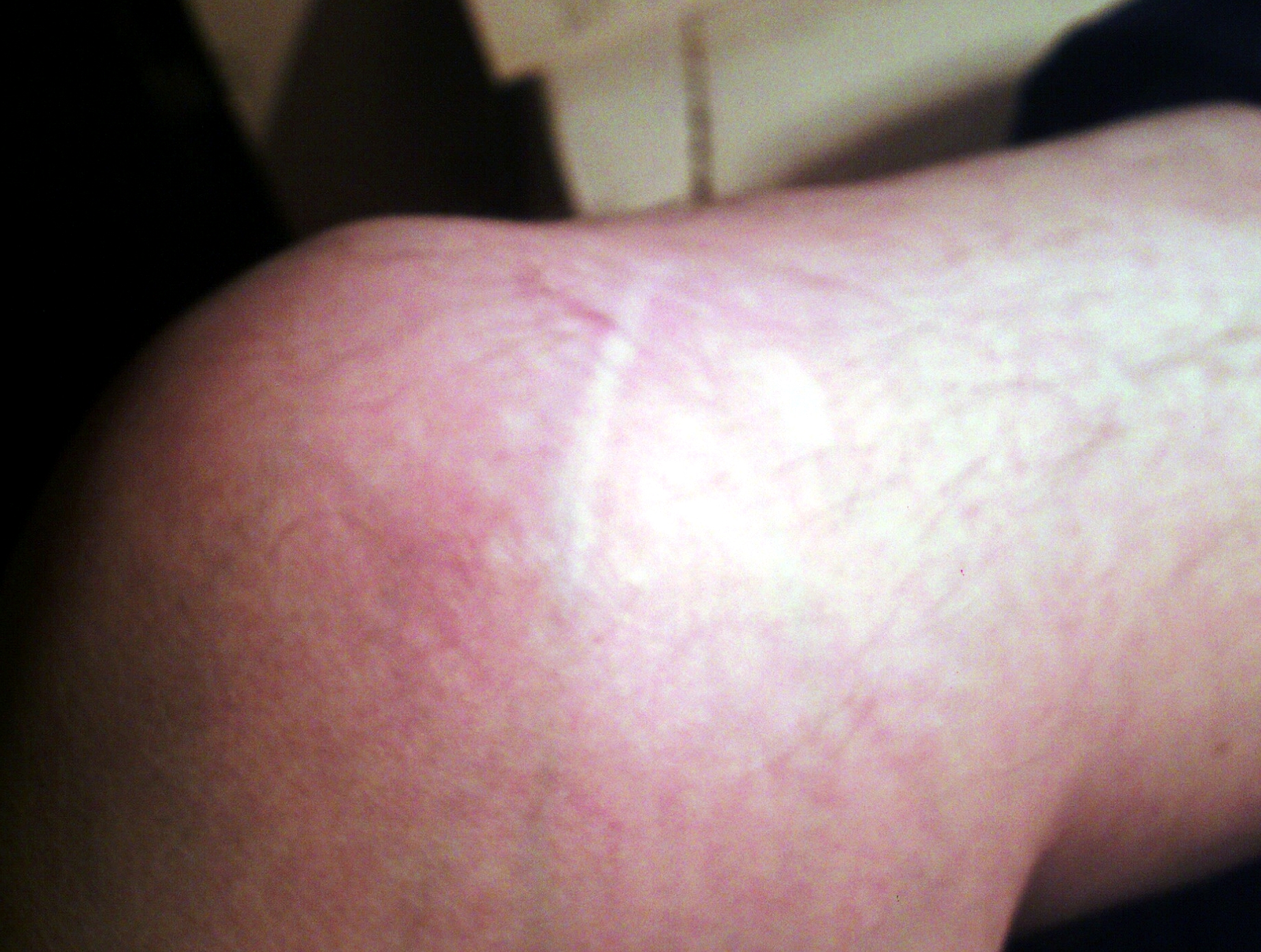
Meniscus (anatomy)
A meniscus is a crescent-shaped fibrocartilaginous anatomical structure that, in contrast to an articular disc, only partly divides a joint cavity.Platzer (2004), p 208 In humans they are present in the knee, wrist, acromioclavicular, sternoclavicular, and temporomandibular joints; in other animals they may be present in other joints. Generally, the term "meniscus" is used to refer to the cartilage of the knee, either to the lateral or medial meniscus. Both are cartilaginous tissues that provide structural integrity to the knee when it undergoes tension and torsion. The menisci are also known as "semi-lunar" cartilages, referring to their half-moon, crescent shape. The term "meniscus" is from the Ancient Greek word (), meaning "crescent". Structure The menisci of the knee are two pads of fibrocartilaginous tissue which serve to disperse friction in the knee joint between the lower leg (tibia) and the thigh (femur). They are concave on the top and flat on the bottom, articula ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Makushita
Professional sumo as administered by the Japan Sumo Association is divided into six ranked divisions. Wrestlers are promoted and demoted within and between these divisions based on the merit of their win–loss records in official tournaments. For more information see ''kachi-koshi'' and ''make-koshi''. Wrestlers are also ranked within each division. The higher a wrestler's rank within a division is, the stronger the general level of opponents he will have to face becomes. According to tradition, each rank is further subdivided into East and West, with East being slightly more prestigious, and ranked slightly higher than its West counterpart. The divisions, ranked in order of hierarchy from highest to lowest, are as follows: ''Makuuchi'' , or , is the top division. It is fixed at 42 wrestlers who are ranked according to their performance in previous tournaments. At the top of the division are the "titleholders", or "champions" called the ''san'yaku'' comprising ''yokozuna'', ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sanshō (sumo)
are the three special prizes awarded to top (''Makuuchi'') division sumo wrestlers for exceptional performance during a sumo ''honbasho'' or tournament. The prizes were first awarded in November 1947. Criteria All wrestlers in the top division below the rank of '' ōzeki'' are eligible. In order to be considered for a special prize a rikishi must make a ''kachi-koshi'' or majority of wins during the tournament. Among eligible rikishi, the prize winners are decided by a panel which includes press writers covering the tournament. There is no requirement that the prizes must be awarded, and it sometimes happens that one or more of the ''sanshō'' are not given. It is also common for an award to be awarded to more than one wrestler. The three prizes are *, Outstanding Performance prize *, Fighting Spirit prize *, Technique prize Typically the ''Ginō-shō'' is awarded to a wrestler or wrestlers who display the most skillful ''kimarite'', or techniques; the ''Shukun-shō'' is awarde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tochinowaka Michihiro
Tochinowaka Michihiro (born Dae Won Lee on April 6, 1988) is a former sumo wrestler from Hyogo, Japan. His father is a Zainichi Korean and his mother is a Korean immigrant. He made his professional debut in 2007 and steadily rose through the ranks. His highest rank was ''maegashira'' 1. Early life and sumo background Lee was active in judo and also began doing sumo in his second year of primary school. In his third year at Hōtoku Gakuen High School he achieved the status of national high school ''yokozuna''. Career He entered professional sumo as a wrestler for Kasugano stable in the 2007 January tournament. After posting a strong 5-2 record in his first official tournament, he achieved a perfect 7-0 record to face fellow up and coming wrestler Yamamotoyama to whom he lost the playoff bout for the ''jonidan'' championship or ''yūshō''. Promoted to ''sandanme'' in the following tournament, he posted a 6-1 record and a 5-1 record in the following tournament, garnering him ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Match-fixing In Professional Sumo
Match-fixing in professional sumo is an allegation that has plagued professional sumo for decades. Due to the amount of money changing hands depending on rank and prize money, there had been numerous reports of (corruption, bout-fixing) in professional sumo for years before it was finally definitively proven to exist in 2011. The hierarchical structure of the sport, in which a minority of top-ranked wrestlers have great advantages in salary, privileges, and status over the lower-ranked wrestlers that make up the majority of sumo participants, may have contributed to the use of match-fixing in order to prolong careers for top-ranked wrestlers and assist in the distribution of promotions. Previous speculation In 2002, Steven Levitt and Mark Duggan published a paper using econometrics in order to suggest that corruption in sumo exists. Popularized in Levitt's book ''Freakonomics'', the study found that 70% of wrestlers with 7–7 records on the final day of the tournament (i.e., seven ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tamanoshima
Tamanoshima Arata (born September 15, 1977, as Arata Okabe) is a former sumo wrestler from Izumizaki, Fukushima, Japan. A former amateur champion, he made his professional debut in 1998, reaching the top ''makuuchi'' division at the end of 2000. He was twice runner-up in a tournament, and earned six special prizes and two gold stars during his career. His highest rank was ''sekiwake.'' He wrestled for Kataonami stable. He retired in November 2011 to become an elder of the Japan Sumo Association and is now known as Hanaregoma Oyakata. In December 2021 he became head coach of Hanaregoma stable. Career Tamanoshima was a college champion at Toyo University and so was given ''makushita tsukedashi'' status and allowed to make his professional debut in the ''makushita'' division. He was only twenty years of age, as he left the university in his second year, making him the youngest former amateur to join professional sumo in this way. Initially competing under the ''shikona'' or ring ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |