|
Masti Venkatesha Iyengar
Masti Venkatesha Iyengar (6 June 1891 – 6 June 1986) was a well-known writer in Kannada language. He was the fourth among Kannada writers to be honored with the Jnanpith Award, the highest literary honor conferred in India. He was popularly referred to as ''Maasti Kannadada Aasti'' which means "Maasti, Kannada's Treasure". He is most renowned for his short stories. He wrote under the pen name ''Srinivasa''. He was honoured with the title ''Rajasevasakta'' by then Maharaja of Mysore Nalvadi Krishnaraja Wadeyar. Early life and education Maasti was born in 1891 at Hungenahalli in Kolar district of Karnataka in a Tamil speaking Sri Vaishnavaite Brahmin family. He spent his early childhood in Maasti village. He obtained a master's degree in English literature (Arts) in 1914 from Madras University. After joining the Indian Civil Service (Known as the Mysore Civil Service in the days of the Maharaja of Mysore), he held various positions of responsibility in different parts of Karn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
:Template:Infobox Writer/doc
Infobox writer may be used to summarize information about a person who is a writer/author (includes screenwriters). If the writer-specific fields here are not needed, consider using the more general ; other infoboxes there can be found in :People and person infobox templates. This template may also be used as a module (or sub-template) of ; see WikiProject Infoboxes/embed for guidance on such usage. Syntax The infobox may be added by pasting the template as shown below into an article. All fields are optional. Any unused parameter names can be left blank or omitted. Parameters Please remove any parameters from an article's infobox that are unlikely to be used. All parameters are optional. Unless otherwise specified, if a parameter has multiple values, they should be comma-separated using the template: : which produces: : , language= If any of the individual values contain commas already, add to use semi-colons as separators: : which produces: : , ps ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maasti
Maasti is a village in India, located in the state of Karnataka, within the administrative divisions of Taluk of Malur in the district of Kolar. It belongs to the Bangalore Division and is located 38 km south of the district headquarters in Kolar, 18 km from Malur, 53 km from the state capital Bangalore. The Maasti pin code is 563139 and the postal head office is Maasti. Kannada is the local language. Transport Rail The nearest railway stations are at Byatrayanhalli (16 km), Malur (16 km), Tyakal (17 km) and Kamasamudram (24 km). Road Roads connect to Kolar and Bangarapet. Air The nearest airport is Bengaluru Bangalore (), officially Bengaluru (), is the capital and largest city of the Indian state of Karnataka. It has a population of more than and a metropolitan population of around , making it the third most populous city and fifth most ... International Airport (70 km). References {{reflist Villages in Kolar d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kannada-language Writers
Kannada (; ಕನ್ನಡ, ), originally romanised Canarese, is a Dravidian language spoken predominantly by the people of Karnataka in southwestern India, with minorities in all neighbouring states. It has around 47 million native speakers, and was additionally a second or third language for around 13 million non-native speakers in Karnataka. Kannada was the court language of some of the most powerful dynasties of south and central India, namely the Kadambas, Chalukyas, Rashtrakutas, Yadava Dynasty or Seunas, Western Ganga dynasty, Wodeyars of Mysore, Nayakas of Keladi Hoysalas and the Vijayanagara empire. The official and administrative language of the state of Karnataka, it also has scheduled status in India and has been included among the country's designated classical languages.Kuiper (2011), p. 74R Zydenbos in Cushman S, Cavanagh C, Ramazani J, Rouzer P, ''The Princeton Encyclopedia of Poetry and Poetics: Fourth Edition'', p. 767, Princeton Univ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kakanakote
{{coord, 11, 53, 55, N, 76, 12, 10, E, display=title Kakanakote is situated at a distance of 73 km from Mysore in Karnataka state, India. It is a thick forest of the Western Ghats, and a famous place where a large number of wild elephants can be found. Now it is a wildlife national park, monitored and regulated by the state. Origin of Name This is the famous forest range named after the legendary Kaka Nayaka, who was the leader of the local forest dwelling Kuruba people. Impressed by Kaka Nayaka's bravery and with the then maharaja of Mysore named the forest after him. Facilities Periodically herds of elephants were once captured at this place by the Khedda method. Facilities for wild life viewing are available in this national park. Play It is also made famous by the play of the same name by Maasti Venkatesh Ayengar Masti Venkatesha Iyengar (6 June 1891 – 6 June 1986) was a well-known writer in Kannada language. He was the fourth among Kannada writers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subbana (Book)
''Subbanna'' is a story written by Masti Venkatesh Iyengar Masti Venkatesha Iyengar (6 June 1891 – 6 June 1986) was a well-known writer in Kannada language. He was the fourth among Kannada writers to be honored with the Jnanpith Award, the highest literary honor conferred in India. He was popularly r .... This is a bildungsroman about an Indian violinist. This book has got translated to Hindi, Tamil, English and other languages. Subbanna's father is highly respected scholar in royal court of Mysuru and he hopes his son also follow his footsteps. However, Subbanna likes music and the story goes through the conflict Subbanna faces thought his life. References 20th-century Indian novels 1958 novels Kannada novels 1958 Indian novels {{1950s-novel-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Government Of Karnataka
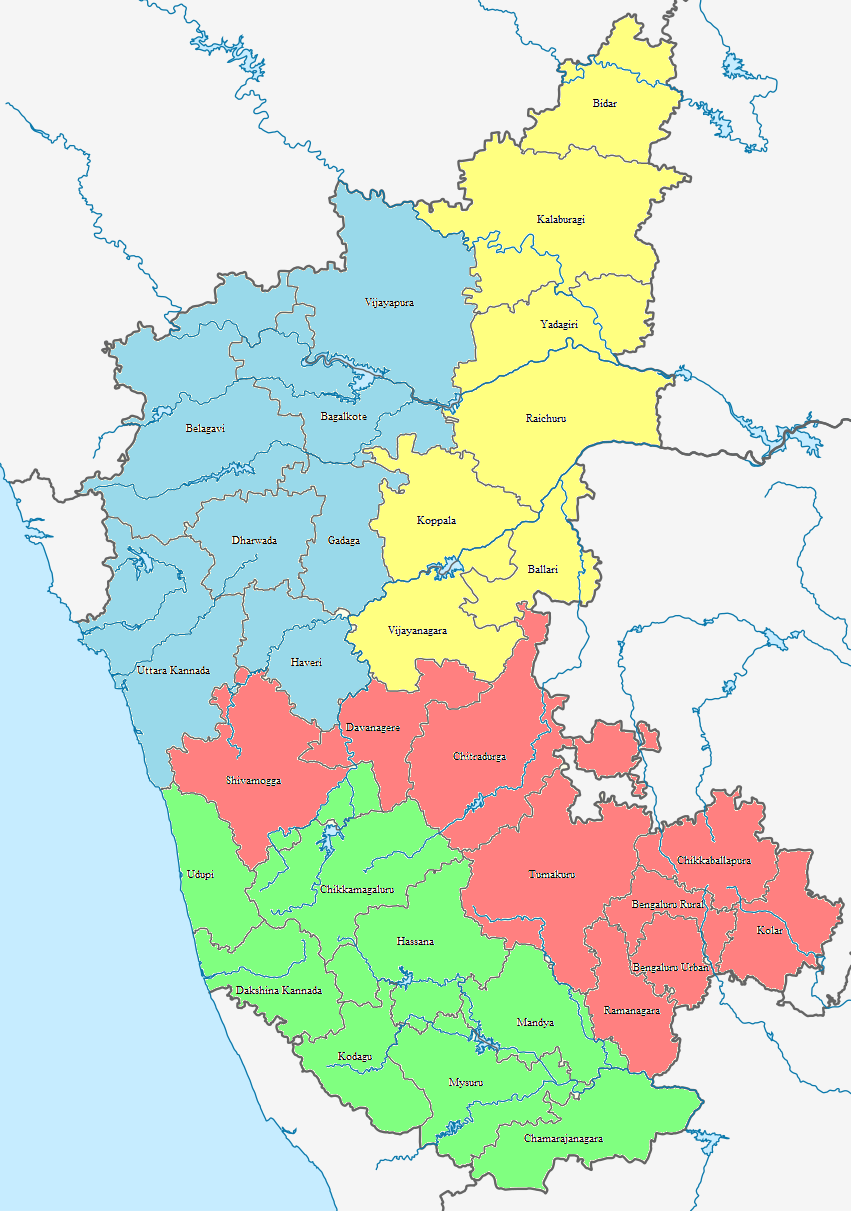
The Government of Karnataka, abbreviated as, GoK, or simply Karnataka Government, is a democratically-elected state body with the governor as the ceremonial head to govern the Southwest Indian state of Karnataka. The governor who is appointed for five years appoints the chief minister and on the advice of the chief minister appoints his council of ministers. Even though the governor remains the ceremonial head of the state, the day-to-day running of the government is taken care of by the chief minister and his council of ministers in whom a great amount of legislative powers are vested. Administrative divisions Karnataka State has been divided into 4 revenue divisions, 49 sub-divisions, 31 districts, 237 taluks, 747 hoblies/ revenue circles and 6,022 gram panchayats for administrative purposes. The state has 281 towns and 7 municipal corporations. Bangalore is the largest urban agglomeration. It is among the fastest growing cities in the world. Political and administrati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kolar District
Kolar district ) is a district in the state of Karnataka, India. Kolar ( ಕೋಲಾರ) is the district headquarters. Located in southern Karnataka, it is the state's easternmost district. The district is surrounded by the Bangalore Rural district on the west, Chikballapur district on the north, the Chittoor district and Annamayya district of Andhra Pradesh on the east and the Krishnagiri district of Tamil Nadu on the south. On 10 September 2007, it was bifurcated to form the new district of Chikballapur. Due to the discovery of the Kolar Gold Fields, the district has become known as the "Golden Land" of India. People are citing that still gold is present in Kolar Gold Fields mines abundantly and also exists in Mulbagal, Kolar, Bangarapet, Malur, Srinivasapura taluks of Kolar District. However it must have to be confirmed by the state and as well central govt authorities. History Kolar, formerly known as Kolahala, Kuvalala and Kolala, was called Kolahalapura d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taluks Of Karnataka
Karnataka has about 240 Talukas. The table below lists all the talukas in the state of Karnataka, India, by district. The urban status is listed for the headquarters town of the taluka, rural talukas are much larger. Urban status follows the census standard. Level of each administration. * City Corporation (''Mahanagara Palike)'' * City Municipal Council (''Nagarasabe)'' * Town Municipal Council (''Purasabe)'' * Town Panchayat (''Pura Panchayiti)'' * Village Panchayat (''Grama Panchayiti'') References {{Karnataka topics Taluks of Karnataka, Davanagere Dt. Channagiri Karnataka ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Kodagu
The district of Kodagu in present-day Karnataka comprises the area of the former princely state of the same name. Early history The earliest mention about Coorg can be seen in the works those date back to Sangam period (300 BCE - 300 CE). The Ezhimala dynasty had jurisdiction over two ''Nadu''s - The coastal ''Poozhinadu'' and the hilly eastern ''Karkanadu''. According to the works of Sangam literature, ''Poozhinadu'' consisted much of the coastal belt between Mangalore and Kozhikode. ''Karkanadu'' consisted of Wayanad- Gudalur hilly region with parts of Kodagu (Coorg). Kannada inscriptions speak of ''Kudagu nad'' (parts of Kodagu, Western Mysore and Kerala) as well. Both the name of the natives and of the region are synonymous (Kodava-Kodavu; Kodaga-Kodagu; Coorgs-Coorg). The Haleri dynasty Early Haleri The Haleri dynasty was an offshoot of Keladi Nayakas also called Ikkeri Arasu dynasty. Kodagu was independent of Mysore, which was hard pressed by enemies, and a prince ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chikka Virarajendra
Chikavira Rajendra or Chikka Vira Rajendra (Kannada: , ''cika/cikka vīrarājendra'') (also in other variations, including Chikkaveera Rajendra), was the last ruler of the Kodagu (Coorg) kingdom in South India. His actual name was Vira Rajendra, but this was the name of his uncle as well; as both of them were rulers of Kodagu, the prefix ''Chikka'' (Kannada and Kodava Takk for ''Younger'') is used as a distinguisher. He was a son of Linga Rajendra II. Annexation of the kingdom On 24 April 1834 CE, he was deposed and exiled by the British; his kingdom was annexed into British India as a separate chief commissionership. He spent some years in Benares before going to England along with his favourite daughter Gouramma to plead in court for the return of his kingdom. London The Rajah had lived in Benares for 14 years on an annual allowance of £12,000. One of his daughters, Muddama Mussamat (Ganga Maharani), became the third wife of Jung Bahadur Rana marrying at Benares in Decem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Masti Venkatesh Iyengar
Masti Venkatesha Iyengar (6 June 1891 – 6 June 1986) was a well-known writer in Kannada language. He was the fourth among Kannada writers to be honored with the Jnanpith Award, the highest literary honor conferred in India. He was popularly referred to as ''Maasti Kannadada Aasti'' which means "Maasti, Kannada's Treasure". He is most renowned for his short stories. He wrote under the pen name ''Srinivasa''. He was honoured with the title ''Rajasevasakta'' by then Maharaja of Mysore Nalvadi Krishnaraja Wadeyar. Early life and education Maasti was born in 1891 at Hungenahalli in Kolar district of Karnataka in a Tamil speaking Sri Vaishnavaite Brahmin family. He spent his early childhood in Maasti village. He obtained a master's degree in English literature (Arts) in 1914 from Madras University. After joining the Indian Civil Service (Known as the Mysore Civil Service in the days of the Maharaja of Mysore), he held various positions of responsibility in different parts of Karn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |