|
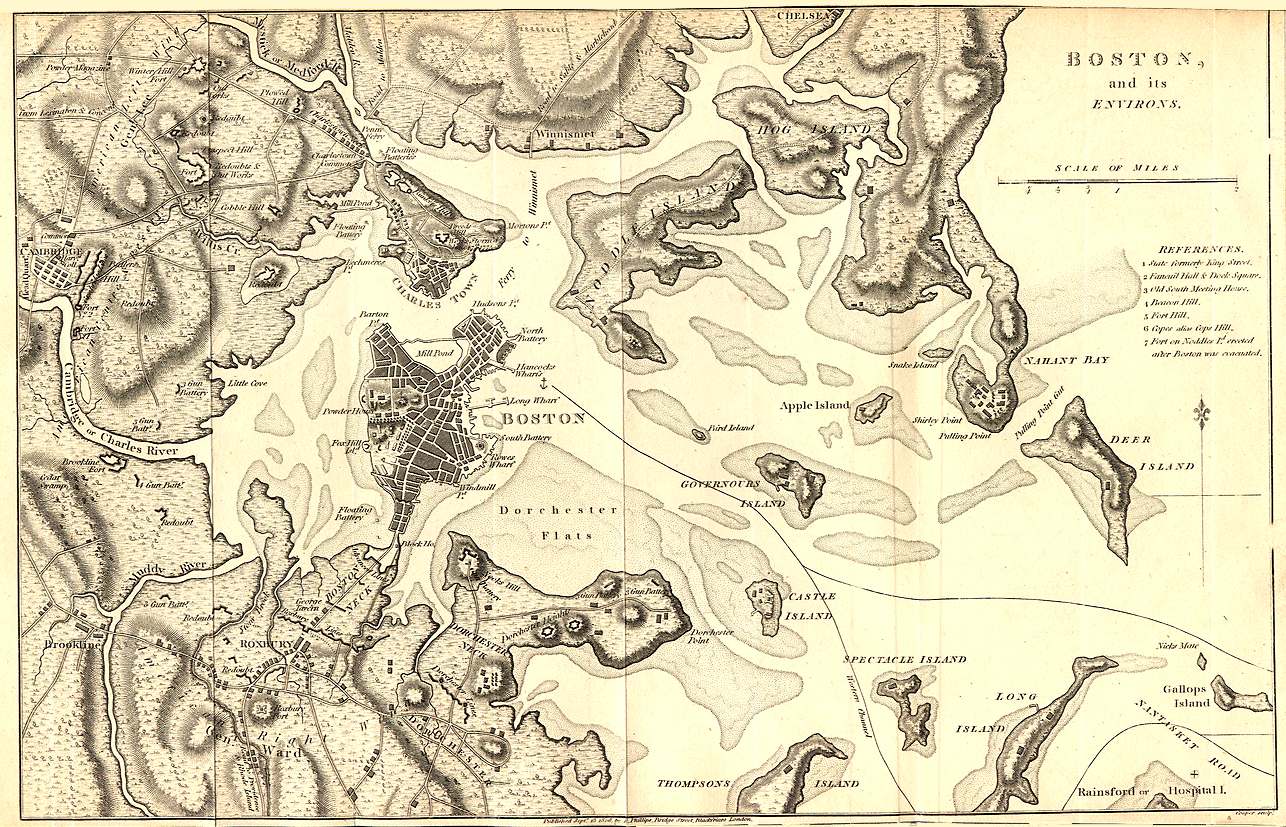
Massachusetts Convention Of Towns
The Massachusetts Convention of Towns (September 22–29, 1768) was an extralegal assembly held in Boston in response to the news that British troops would soon be arriving to crack down on anti-British rioting. Delegates from 96 Massachusetts towns gathered in Faneuil Hall to discuss their options. The more militant faction, led by James Otis Jr., Samuel Adams, and John Hancock, wanted to organize an armed resistance. The more conservative faction, led by convention chairman Thomas Cushing, preferred to lodge a written complaint. The conservatives won out, and the delegates endorsed a series of mild resolutions before disbanding. History Background In February 1768, the Massachusetts House of Representatives issued a circular letter denouncing the Townshend Acts and sent it to representatives of the other colonies. Lord Hillsborough, the Secretary of State for the Colonies, ordered the House to rescind the letter. When the House refused to comply, Governor Francis Bernard ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Massachusetts House Of Representatives
The Massachusetts House of Representatives is the lower house of the Massachusetts General Court, the state legislature of the Commonwealth of Massachusetts. It is composed of 160 members elected from 14 counties each divided into single-member electoral districts across the Commonwealth. The House of Representatives convenes at the Massachusetts State House in Boston. Qualifications Any person seeking to get elected to the Massachusetts House of Representatives must meet the following qualifications: * Be at least eighteen years of age * Be a registered voter in Massachusetts * Be an inhabitant of the district for at least one year prior to election * Receive at least 150 signatures on nomination papers Representation Originally, representatives were apportioned by town. For the first 150 persons, one representative was granted, and this ratio increased as the population of the town increased. The largest membership of the House was 749 in 1812 (214 of these being from the D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HMS Liberty (1768)
''Liberty'' was a sloop owned by John Hancock, an American merchant, whose seizure was the subject of the Liberty Affair. Seized by customs officials in Boston in 1768, it was commissioned into the Royal Navy as HMS ''Liberty'', and she was burned the next year by American colonists in Newport, Rhode Island in one of the first acts of open defiance against the British crown by American colonists. History The ship was originally owned by John Hancock. In 1768, British officials alleged that Bostonians locked a customs official in the ''Liberty''s cabin while the cargo of Madeira wine was unloaded in an effort to evade the Townshend Acts. In retaliation, the British government confiscated ''Liberty'', and she was towed away by HMS ''Halifax''. Charges against Hancock were eventually dropped, but ''Liberty'' remained confiscated. The ship was refitted in Rhode Island to serve as a Royal Navy ship named HMS ''Liberty'' and then used to patrol off Rhode Island for customs vi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Braintree, Massachusetts
Braintree (), officially the Town of Braintree, is a municipality in Norfolk County, Massachusetts, United States. Although officially known as a towBraintree is a city, with a mayor-council government, mayor-council form of government, and is considered a city under Massachusetts law. The population was 39,143 at the 2020 census. The city is part of the Greater Boston area with access to the MBTA Red Line, and is a member of the Metropolitan Area Planning Council's South Shore Coalition. The first mayor of Braintree was Joe Sullivan who served until January 2020. The current mayor of Braintree is Charles Kokoros. Braintree, Massachusetts, is named after Braintree, Essex, in England. The town was first chartered in 1640. Later, some sections of Braintree formed separate municipalities: Quincy (1792), Randolph (1793), and Holbrook (1872). History European settlers first arrived in 1625. Subsequent to their arrival, the town was colonized in 1635, and ultimately incorp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middleborough, Massachusetts
Middleborough (frequently written as Middleboro) is a town in Plymouth County, Massachusetts, Plymouth County, Massachusetts, United States. The population was 24,245 at the 2020 United States Census, 2020 census. History The town was first settled by Europeans in 1661 as Nemasket, later changed to Middlebury, and officially incorporated as Middleborough in 1669. The name Nemasket came from a Indigenous peoples of the Americas, Native American settlement along the small river that now bears the same name. ''Nemasket'' may have meant "place of fish", due to the large amount of herring that migrate up the river each spring. There are no contemporary records that indicate the name Middlebury was taken from a place in England. The names Middlebury and Middleborough were actually derived from the city of Middelburg, Zeeland, Middelburg, Zeeland, the westernmost province of the Netherlands. Middelburg was an international intellectual center and economic powerhouse. The English religio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
View Of Faneuil-Hall In Boston, Massachusetts, March 1789
A view is a sight or prospect or the ability to see or be seen from a particular place. View, views or Views may also refer to: Common meanings * View (Buddhism), a charged interpretation of experience which intensely shapes and affects thought, sensation, and action * Graphical projection in a technical drawing or schematic ** Multiview orthographic projection, standardizing 2D images to represent a 3D object * Opinion, a belief about subjective matters * Page view, a visit to a World Wide Web page * Panorama, a wide-angle view * Scenic viewpoint, an elevated location where people can view scenery * World view, the fundamental cognitive orientation of an individual or society encompassing the entirety of the individual or society's knowledge and point-of-view Places * View, Kentucky, an unincorporated community in Crittenden County * View, Texas, an unincorporated community in Taylor County Arts, entertainment, and media Music * ''View'' (album), the 2003 debut album by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Halifax, Nova Scotia
Halifax is the capital and largest municipality of the Canadian province of Nova Scotia, and the largest municipality in Atlantic Canada. As of the 2021 Census, the municipal population was 439,819, with 348,634 people in its urban area. The regional municipality consists of four former municipalities that were amalgamated in 1996: Halifax, Dartmouth, Bedford, and Halifax County. Halifax is a major economic centre in Atlantic Canada, with a large concentration of government services and private sector companies. Major employers and economic generators include the Department of National Defence, Dalhousie University, Nova Scotia Health Authority, Saint Mary's University, the Halifax Shipyard, various levels of government, and the Port of Halifax. Agriculture, fishing, mining, forestry, and natural gas extraction are major resource industries found in the rural areas of the municipality. History Halifax is located within ''Miꞌkmaꞌki'' the traditional ancestral lands ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beacon Hill, Boston
Beacon Hill is a historic neighborhood in Boston, Massachusetts, and the hill upon which the Massachusetts State House resides. The term "Beacon Hill" is used locally as a metonym to refer to the state government or the legislature itself, much like Washington, D.C.'s " Capitol Hill" does at the federal level. Federal-style rowhouses, narrow gaslit streets and brick sidewalks adorn the neighborhood, which is generally regarded as one of the more desirable and expensive in Boston. According to the 2010 U.S. Census, the population of Boston's Beacon Hill neighborhood is 9,023. Etymology Like many similarly named areas, the neighborhood is named for the location of a former beacon atop the highest point in central Boston. The beacon was used to warn the residents of an invasion. Geography Beacon Hill is bounded by Storrow Drive, and Cambridge, Bowdoin, Park and Beacon Streets. It is about 1/6 of a square mile, and situated along the riverfront of the Charles River E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas Hutchinson (governor)
Thomas Hutchinson (9 September 1711 – 3 June 1780) was a businessman, historian, and a prominent Loyalist politician of the Province of Massachusetts Bay in the years before the American Revolution. He has been referred to as "the most important figure on the loyalist side in pre-Revolutionary Massachusetts". He was a successful merchant and politician, and was active at high levels of the Massachusetts government for many years, serving as lieutenant governor and then governor from 1758 to 1774. He was a politically polarizing figure who came to be identified by John Adams and Samuel Adams as a proponent of hated British taxes, despite his initial opposition to Parliamentary tax laws directed at the colonies. He was blamed by Lord North (the British Prime Minister at the time) for being a significant contributor to the tensions that led to the outbreak of the American Revolutionary War. Hutchinson's Boston mansion was ransacked in 1765 during protests against the Stamp Ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pretext
A pretext (adj: pretextual) is an excuse to do something or say something that is not accurate. Pretexts may be based on a half-truth or developed in the context of a misleading fabrication. Pretexts have been used to conceal the true purpose or rationale behind actions and words. In US law, a pretext usually describes false reasons that hide the true intentions or motivations for a legal action. If a party can establish a prima facie case for the proffered evidence, the opposing party must prove that these reasons were "pretextual" or false. This can be accomplished by directly demonstrating that the motivations behind the presentation of evidence is false, or indirectly by evidence that the motivations are not "credible". In ''Griffith v. Schnitzer'', an employment discrimination case, a jury award was reversed by a Court of Appeals because the evidence was not sufficient that the defendant's reasons were "pretextual". That is, the defendant's evidence was either undisputed, or the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joseph Warren
Joseph Warren (June 11, 1741 – June 17, 1775), a Founding Father of the United States, was an American physician who was one of the most important figures in the Patriot movement in Boston during the early days of the American Revolution, eventually serving as President of the revolutionary Massachusetts Provincial Congress. Warren enlisted Paul Revere and William Dawes on April 18, 1775, to leave Boston and spread the alarm that the British garrison in Boston was setting out to raid the town of Concord and arrest rebel leaders John Hancock and Samuel Adams. Warren participated in the Battles of Lexington and Concord the following day, the opening engagements of the American Revolutionary War. Warren had been commissioned a major general in the colony's militia shortly before the June 17, 1775 Battle of Bunker Hill. Rather than exercise his rank, Warren chose to participate in the battle as a private soldier, and was killed in combat when British troops stormed the redoubt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sons Of Liberty
The Sons of Liberty was a loosely organized, clandestine, sometimes violent, political organization active in the Thirteen American Colonies founded to advance the rights of the colonists and to fight taxation by the British government. It played a major role in most colonies in battling the Stamp Act in 1765 and throughout the entire period of the American Revolution. In popular thought, the Sons of Liberty was a formal underground organization with recognized members and leaders. More likely, the name was an underground term for any men resisting new Crown taxes and laws.Gregory Fremont-Barnes, ''Encyclopedia of the Age of Political Revolutions and New Ideologies'' (2007) 1:688 The well-known label allowed organizers to make or create anonymous summons to a Liberty Tree, "Liberty Pole", or other public meeting-place. Furthermore, a unifying name helped to promote inter-Colonial efforts against Parliament and the Crown's actions. Their motto became "No taxation without re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Standing Army
A standing army is a permanent, often professional, army. It is composed of full-time soldiers who may be either career soldiers or conscripts. It differs from army reserves, who are enrolled for the long term, but activated only during wars or natural disasters, and temporary armies, which are raised from the civilian population only during a war or threat of war and disbanded once the war or threat is over. Standing armies tend to be better equipped, better trained, and better prepared for emergencies, defensive deterrence, and particularly, wars. Wills, Garry (1999). ''A Necessary Evil, A History of American Distrust of Government'' New York, N.Y.; Simon & Schuster. The term dates from approximately 1600 CE, although the phenomenon it describes is much older. History Ancient history Mesopotamia Sargon of Akkad, the founder of the Akkadian Empire, is believed to have formed the first standing professional army. Tiglath-Pileser III of Assyria (ruled 745–727 BC) created t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |