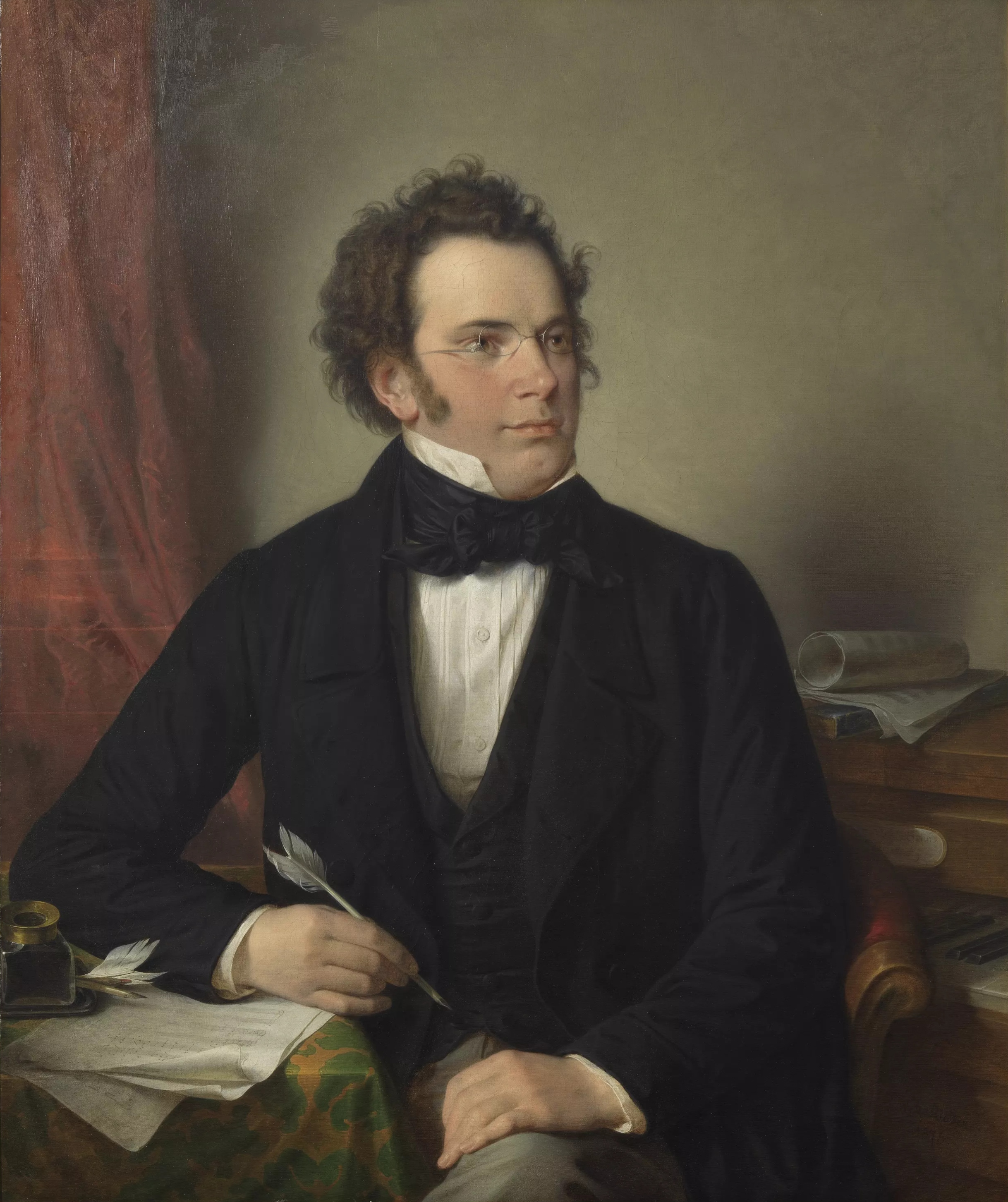|
Mass No. 5 (Schubert)
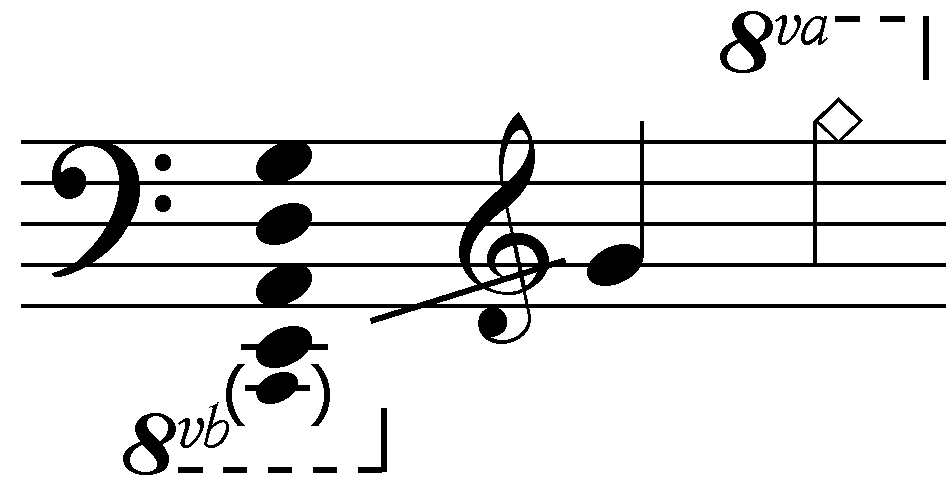
Mass No. 5 in A-flat major, 678, is a mass composed by Franz Schubert, completed in 1822. There is no record of a performance during Schubert's lifetime. It is scored for soprano, alto, tenor and bass soloists, SATB choir with , violin I and II, viola, flute, 2 oboes, 2 clarinets, 2 bassoons, 2 horns, 2 trumpets, 3 trombones , timpani and basso continuo (cello, double bass and organ). It is classified as a . Background Schubert commenced composition of the mass in November 1819, completing it three years later in 1822. Various projects had competed for the composer's attention in the meantime, including his brother Ferdinand's request for a mass ( 755). Schubert wrote out the organ part in October or November 1822, and although plans were made for a performance in 1823, records of a performance in Schubert's lifetime do not exist. This setting and the later Mass in E-flat major are regarded as Schubert's "late masses". These are distinguished from his four early masses ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wilhelm August Rieder
Wilhelm August Rieder (October 30, 1796 – September 8, 1880), was an Austrian painter and draughtsman. Rieder was born in Oberdöbling, the son of the composer Ambros Rieder (1771–1855). He studied at the Academy of Fine Arts Vienna, where he first met and befriended Franz Schubert. Schubert's brother Ferdinand Schubert described Rieder's brother Johann as 'my only true friend' in a letter to Schubert on 3rd July 1824. Rieder's aquarell of Schubert from 1825 was supposedly started when Rieder sheltered from a rainstorm in Schubert's lodgings at the Fruhwirth-Haus (Technikerstrasse 9). Schubert's friends thought it was a very good likeness: Leopold von Sonnleithner called it 'the most like him', whilst Josef von Spaun Joseph Freiherr von Spaun (November 11, 1788November 25, 1865) was an Austrian nobleman, an Imperial and Royal Councillor, lottery director, and honorary citizen of Vienna and Cieszyn. He is best known for his friendship with the composer Franz S ... calle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oboe
The oboe ( ) is a type of double reed woodwind instrument. Oboes are usually made of wood, but may also be made of synthetic materials, such as plastic, resin, or hybrid composites. The most common oboe plays in the treble or soprano range. A soprano oboe measures roughly long, with metal keys, a conical bore and a flared bell. Sound is produced by blowing into the reed at a sufficient air pressure, causing it to vibrate with the air column. The distinctive tone is versatile and has been described as "bright". When the word ''oboe'' is used alone, it is generally taken to mean the treble instrument rather than other instruments of the family, such as the bass oboe, the cor anglais (English horn), or oboe d'amore. Today, the oboe is commonly used as orchestral or solo instrument in symphony orchestras, concert bands and chamber ensembles. The oboe is especially used in classical music, film music, some genres of folk music, and is occasionally heard in jazz, rock, pop, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ferdinand Schubert
Ferdinand Schubert (born 18 October 1794 in Vienna; died 26 February 1859) was an Austrian composer and brother of Franz Schubert. He also designed the grave stone for the grave of Ludwig van Beethoven, which is now at Vienna's Central Cemetery. Early life Ferdinand Lukas Schubert was an Austrian teacher, organist and composer. He is notable for his compositions and for his role in publishing the complete works of his younger brother Franz Schubert. He received training in piano and violin from his father, Franz Theodor Schubert, and his older brother Ignaz, later from Michael Wood, and finally from the public teacher of the choir of St. Anna, Joseph Drechsler. As a boy, Ferdinand played violin in the Schubert family string quartet, with his brothers Franz and Ignaz on viola and violin and his father on cello. Franz Schubert composed many of his early string quartets for this ensemble. Career In 1810, Schubert became organist at the Lichtentaler Parish and was also assistant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Missa Solemnis
{{Audio, De-Missa solemnis.ogg, Missa solemnis is Latin for Solemn Mass, and is a genre of musical settings of the Mass Ordinary, which are festively scored and render the Latin text extensively, opposed to the more modest Missa brevis. In French, the genre is "Messe solennelle". The terms came into use in the classical period. When "Missa solemnis" is used as a name, without referring to a composer, Beethoven's work is generally implied. Some of the greatest compositions in the genre have unique common names other than "Missa solemnis"—namely, Bach's ''Mass in B minor'' and Mozart's ''Great Mass in C minor''. Some works are solemn settings in proportion and scoring, but are not called a "Missa solemnis", for example several late settings of both Haydn and Schubert, and three settings by Anton Bruckner. A solemn mass has been written by well-known composers including: * Bach: ''Mass in B minor'' (1733/1749) * Beethoven: ''Missa solemnis'' in D major (1823) * Berlioz: ''Messe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pipe Organ
The pipe organ is a musical instrument that produces sound by driving pressurized air (called ''wind'') through the organ pipes selected from a keyboard. Because each pipe produces a single pitch, the pipes are provided in sets called ''ranks'', each of which has a common timbre and volume throughout the keyboard compass. Most organs have many ranks of pipes of differing timbre, pitch, and volume that the player can employ singly or in combination through the use of controls called stops. A pipe organ has one or more keyboards (called '' manuals'') played by the hands, and a pedal clavier played by the feet; each keyboard controls its own division, or group of stops. The keyboard(s), pedalboard, and stops are housed in the organ's ''console''. The organ's continuous supply of wind allows it to sustain notes for as long as the corresponding keys are pressed, unlike the piano and harpsichord whose sound begins to dissipate immediately after a key is depressed. The smallest po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Double Bass
The double bass (), also known simply as the bass () (or #Terminology, by other names), is the largest and lowest-pitched Bow (music), bowed (or plucked) string instrument in the modern orchestra, symphony orchestra (excluding unorthodox additions such as the octobass). Similar in structure to the cello, it has four, although occasionally five, strings. The bass is a standard member of the orchestra's string section, along with violins, viola, and cello, ''The Orchestra: A User's Manual'' , Andrew Hugill with the Philharmonia Orchestra as well as the concert band, and is featured in Double bass concerto, concertos, solo, and chamber music in European classical music, Western classical music.Alfred Planyavsky [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cello
The cello ( ; plural ''celli'' or ''cellos'') or violoncello ( ; ) is a Bow (music), bowed (sometimes pizzicato, plucked and occasionally col legno, hit) string instrument of the violin family. Its four strings are usually intonation (music), tuned in perfect fifths: from low to high, scientific pitch notation, C2, G2, D3 and A3. The viola's four strings are each an octave higher. Music for the cello is generally written in the bass clef, with tenor clef, and treble clef used for higher-range passages. Played by a ''List of cellists, cellist'' or ''violoncellist'', it enjoys a large solo repertoire Cello sonata, with and List of solo cello pieces, without accompaniment, as well as numerous cello concerto, concerti. As a solo instrument, the cello uses its whole range, from bassline, bass to soprano, and in chamber music such as string quartets and the orchestra's string section, it often plays the bass part, where it may be reinforced an octave lower by the double basses. Figure ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basso Continuo
Basso continuo parts, almost universal in the Baroque era (1600–1750), provided the harmonic structure of the music by supplying a bassline and a chord progression. The phrase is often shortened to continuo, and the instrumentalists playing the continuo part are called the ''continuo group''. Forces The composition of the continuo group is often left to the discretion of the performers (or, for a large performance, the conductor), and practice varied enormously within the Baroque period. At least one instrument capable of playing chords must be included, such as a harpsichord, organ, lute, theorbo, guitar, regal, or harp. In addition, any number of instruments that play in the bass register may be included, such as cello, double bass, bass viol, or bassoon. In modern performances of chamber works, the most common combination is harpsichord and cello for instrumental works and secular vocal works, such as operas, and organ and cello for sacred music. A double bass may ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Timpani
Timpani (; ) or kettledrums (also informally called timps) are musical instruments in the percussion family. A type of drum categorised as a hemispherical drum, they consist of a membrane called a head stretched over a large bowl traditionally made of copper. Thus timpani are an example of kettle drums, also known as vessel drums and semispherical drums, whose body is similar to a section of a sphere whose cut conforms the head. Most modern timpani are ''pedal timpani'' and can be tuned quickly and accurately to specific pitches by skilled players through the use of a movable foot-pedal. They are played by striking the head with a specialized drum stick called a ''timpani stick'' or ''timpani mallet''. Timpani evolved from military drums to become a staple of the classical orchestra by the last third of the 18th century. Today, they are used in many types of ensembles, including concert bands, marching bands, orchestras, and even in some rock bands. ''Timpani'' is an Italian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colla Parte
A variety of musical terms are likely to be encountered in printed scores, music reviews, and program notes. Most of the terms are Italian, in accordance with the Italian origins of many European musical conventions. Sometimes, the special musical meanings of these phrases differ from the original or current Italian meanings. Most of the other terms are taken from French and German, indicated by ''Fr.'' and ''Ger.'', respectively. Unless specified, the terms are Italian or English. The list can never be complete: some terms are common, and others are used only occasionally, and new ones are coined from time to time. Some composers prefer terms from their own language rather than the standard terms listed here. 0–9 ; 1′ : "sifflet" or one foot organ stop ; I : usually for orchestral string instruments, used to indicate that the player should play the passage on the highest-pitched, thinnest string ; ′ : Tierce organ stop ; 2′ : two feet – pipe org ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trombone
The trombone (german: Posaune, Italian, French: ''trombone'') is a musical instrument in the Brass instrument, brass family. As with all brass instruments, sound is produced when the player's vibrating lips cause the Standing wave, air column inside the instrument to vibrate. Nearly all trombones use a telescoping slide mechanism to alter the Pitch (music), pitch instead of the brass instrument valve, valves used by other brass instruments. The valve trombone is an exception, using three valves similar to those on a trumpet, and the superbone has valves and a slide. The word "trombone" derives from Italian ''tromba'' (trumpet) and ''-one'' (a suffix meaning "large"), so the name means "large trumpet". The trombone has a predominantly cylindrical bore like the trumpet, in contrast to the more conical brass instruments like the cornet, the euphonium, and the French horn. The most frequently encountered trombones are the tenor trombone and bass trombone. These are treated as trans ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trumpet
The trumpet is a brass instrument commonly used in classical and jazz ensembles. The trumpet group ranges from the piccolo trumpet—with the highest register in the brass family—to the bass trumpet, pitched one octave below the standard B or C trumpet. Trumpet-like instruments have historically been used as signaling devices in battle or hunting, with examples dating back to at least 1500 BC. They began to be used as musical instruments only in the late 14th or early 15th century. Trumpets are used in art music styles, for instance in orchestras, concert bands, and jazz ensembles, as well as in popular music. They are played by blowing air through nearly-closed lips (called the player's embouchure), producing a "buzzing" sound that starts a standing wave vibration in the air column inside the instrument. Since the late 15th century, trumpets have primarily been constructed of brass tubing, usually bent twice into a rounded rectangular shape. There are many distinc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |