|
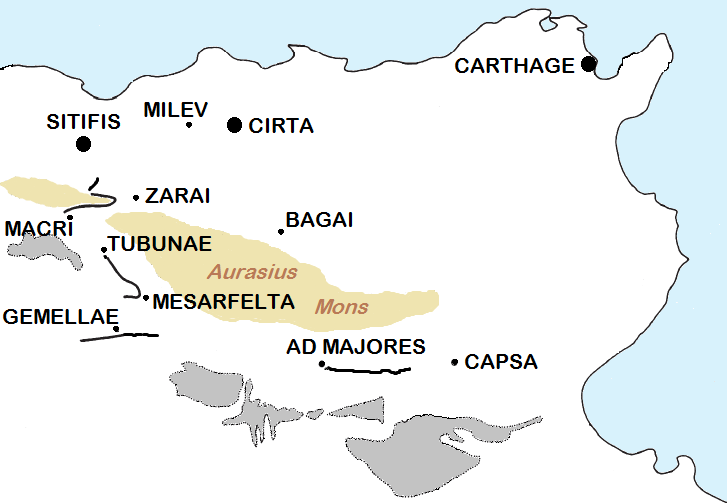
Mascula
Mascula was an ancient Roman colonia in Numidia. It is called Khenchela in modern Algeria. History Mascula was located in the Aurès Mountains (part of the Atlas Mountains), at above sea level, and has a cool Mediterranean climate: it was one of the coldest cities in Numidia (even now it snows sometimes). The fresh location was chosen by Roman legionaries to retire as veterans. Mascula was built under Trajan and was garrisoned by the "7th company of Lusitanians". It was a castrum (with a nearby vicus) on the military road, that connected Theveste with Sitifis and that followed the slopes of the Aures mountains. Mascula was connected with the fortifications of Tinfadi, Vegesela, Claudi and Tliamugas. Mascula was the most important of these forts from a strategic point of view, because controlled the numidian access to the Sahara. Mascula in the fourth century was at the center of the Donatism controversy, and there are beautiful mosaics discovered from those years There are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khenchela
Khenchela ancient Mascula ( ar, خنشلة) is the capital city of the administrative Khenchela Province (''Wilaya''), number 40, in the north east of Algeria. Situated in the Aures Mountains, 1200 m above sea level. The city is mainly populated by Berber Chaouis. Geography Climate Located in the Aurès Mountains (part of the Atlas Mountains), at above sea level, Khenchela has warm-summer Mediterranean climate (Köppen climate classification ''Csb''), with an average annual precipitation of . Summers are warm and dry and winters are chilly and wetter, with the possibility of snowfall. This is one of the coldest cities in Algeria. History Queen Kahina led a decades long war against the Islamic conquest in the 7th century, and she built a castle here. During the Barbary period there were many inter town conflict over water resources. The French army reached Khenchela in 1850 after heavy fighting and more strenuous resistance and set up a military administration. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Algeria
) , image_map = Algeria (centered orthographic projection).svg , map_caption = , image_map2 = , capital = Algiers , coordinates = , largest_city = capital , religion = , official_languages = , languages_type = Other languages , languages = Algerian Arabic (Darja) French , ethnic_groups = , demonym = Algerian , government_type = Unitary semi-presidential republic , leader_title1 = President , leader_name1 = Abdelmadjid Tebboune , leader_title2 = Prime Minister , leader_name2 = Aymen Benabderrahmane , leader_title3 = Council President , leader_name3 = Salah Goudjil , leader_title4 = Assembly President , leader_name4 = Ibrahim Boughali , legislature = Parliament , upper_house = Council of the Nation , lower_house ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Baths
In ancient Rome, (from Greek , "hot") and (from Greek ) were facilities for bathing. usually refers to the large imperial bath complexes, while were smaller-scale facilities, public or private, that existed in great numbers throughout Rome. Most Roman cities had at least one – if not many – such buildings, which were centers not only for bathing, but socializing and reading as well. Bathhouses were also provided for wealthy private villas, town houses, and forts. They were supplied with water from an adjacent river or stream, or within cities by aqueduct. The water would be heated by fire then channelled into the caldarium (hot bathing room). The design of baths is discussed by Vitruvius in ''De architectura'(V.10) Terminology '','' '','' '','' and may all be translated as 'bath' or 'baths', though Latin sources distinguish among these terms. or , derived from the Greek signifies, in its primary sense, a bath or bathing-vessel, such as most persons of any ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Former Populated Places In Algeria
A former is an object, such as a template, gauge or cutting die, which is used to form something such as a boat's hull. Typically, a former gives shape to a structure that may have complex curvature. A former may become an integral part of the finished structure, as in an aircraft fuselage, or it may be removable, being using in the construction process and then discarded or re-used. Aircraft formers Formers are used in the construction of aircraft fuselage, of which a typical fuselage has a series from the nose to the empennage, typically perpendicular to the longitudinal axis of the aircraft. The primary purpose of formers is to establish the shape of the fuselage and reduce the column length of stringers to prevent instability. Formers are typically attached to longerons, which support the skin of the aircraft. The "former-and-longeron" technique (also called stations and stringers) was adopted from boat construction, and was typical of light aircraft built until the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Berber Cities
Ancient history is a time period from the beginning of writing and recorded human history to as far as late antiquity. The span of recorded history is roughly 5,000 years, beginning with the Sumerian cuneiform script. Ancient history covers all continents inhabited by humans in the period 3000 BCAD 500. The three-age system periodizes ancient history into the Stone Age, the Bronze Age, and the Iron Age, with recorded history generally considered to begin with the Bronze Age. The start and end of the three ages varies between world regions. In many regions the Bronze Age is generally considered to begin a few centuries prior to 3000 BC, while the end of the Iron Age varies from the early first millennium BC in some regions to the late first millennium AD in others. During the time period of ancient history, the world population was already exponentially increasing due to the Neolithic Revolution, which was in full progress. While in 10,000 BC, the world population stood a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Towns And Cities In Algeria
Roman or Romans most often refers to: *Rome, the capital city of Italy *Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD *Roman people, the people of ancient Rome *''Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a letter in the New Testament of the Christian Bible Roman or Romans may also refer to: Arts and entertainment Music * Romans (band), a Japanese pop group * ''Roman'' (album), by Sound Horizon, 2006 * ''Roman'' (EP), by Teen Top, 2011 *" Roman (My Dear Boy)", a 2004 single by Morning Musume Film and television *Film Roman, an American animation studio * ''Roman'' (film), a 2006 American suspense-horror film * ''Romans'' (2013 film), an Indian Malayalam comedy film * ''Romans'' (2017 film), a British drama film * ''The Romans'' (''Doctor Who''), a serial in British TV series People *Roman (given name), a given name, including a list of people and fictional characters *Roman (surname), including a list of people named Roman or Romans *Ῥωμα� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaeological Sites In Algeria
Archaeology or archeology is the scientific study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of artifacts, architecture, biofacts or ecofacts, sites, and cultural landscapes. Archaeology can be considered both a social science and a branch of the humanities. It is usually considered an independent academic discipline, but may also be classified as part of anthropology (in North America – the four-field approach), history or geography. Archaeologists study human prehistory and history, from the development of the first stone tools at Lomekwi in East Africa 3.3 million years ago up until recent decades. Archaeology is distinct from palaeontology, which is the study of fossil remains. Archaeology is particularly important for learning about prehistoric societies, for which, by definition, there are no written records. Prehistory includes over 99% of the human past, from the Paleolithic until the adv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Milevum
Milevum (in Latin even "Milev" or "Mireon"; ''Μιραίον'' in Ancient Greek) was a Roman–Berber city in the Roman province of Numidia. It was located in present-day Mila in eastern Algeria. History In Ptolemy's "Geography" (vol. IV, iii, 7), the city is mentioned under the name of ''Mileum''. During the Roman era, it was called ''Colonia Sarnensis Milevitana'', after the River Sarnus in Campania (southern Italy), whence the colonists had emigrated. This name is often found in the inscriptions of the city. Together with Cirta, Collo and Rusicade, Milevum formed the Confederation known as the 'Four Colonies', the territory of which was very extensive. This confederation area was fully romanised in the fourth century (when was renamed as "Numidia Cirtense"), with nearly all the population speaking local Latin, according to historian Theodor Mommsen. In the fourth century's second half Milevum was fully Christian and had a population of nearly 15000 inhabitants. In t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lambaesis
Lambaesis (Lambæsis), Lambaisis or Lambaesa (''Lambèse'' in colonial French), is a Roman archaeological site in Algeria, southeast of Batna and west of Timgad, located next to the modern village of Tazoult. The former bishopric is also a Latin Catholic titular bishopric. History Lambaesa was founded by the Roman military. The camp of the third legion ( Legio III ''Augusta''), to which it owes its origin, appears to have been established between AD 123–129, in the time of Roman emperor Hadrian, whose address to his soldiers was found inscribed on a pillar in a second camp to the west of the great camp still extant. However, other evidence suggests it was formed during the Punic Wars. By AD 166 mention is made of the decurions of a ''vicus'', 10 ''curiae'' of which are known by name; and the ''vicus'' became a ''municipium'' probably at the time when it was made the capital of the newly founded province of Numidia. Lambaesis was populated mainly by Romanized Berbers a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cirta
Cirta, also known by various other names in antiquity, was the ancient Berber and Roman settlement which later became Constantine, Algeria. Cirta was the capital city of the Berber kingdom of Numidia; its strategically important port city was Russicada. Although Numidia was a key ally of the ancient Roman Republic during the Punic Wars (264–146BC), Cirta was subject to Roman invasions during the 2nd and 1st centuriesBC. Eventually it fell under Roman dominion during the time of Julius Caesar. Cirta was then repopulated with Roman colonists by Caesar and Augustus and was surrounded by the autonomous territory of a " Confederation of four free Roman cities" (with Chullu, Russicada, and Milevum), ruled initially by Publius Sittius. The city was destroyed in the beginning of the 4thcentury and was rebuilt by the Roman emperor Constantine the Great, who gave his name to the newly constructed city, Constantine. The Vandals damaged Cirta, but emperor reconquered and improved th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kahina
Al-Kahina ( ar, الكاهنة, , the diviner), also known as Dihya, was a Berber queen of the Aurès and a religious and military leader who led indigenous resistance to the Muslim conquest of the Maghreb, the region then known as Numidia notably defeating the Umayyad forces in the Battle of Meskiana after which she became the uncontested ruler of the whole Maghreb,The History of Anti-Semitism, Volume 2: From Mohammed to the Marranos Leon Poliakov University of Pennsylvania PressRemarkab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sitifis
Sétifis (Arabic: سطيف; Berber: Sṭif), was a Romano town located in northeastern Algeria. It was the capital of the Roman province called ''Mauretania Sitifensis'', and it is today Setif in the Sétif Province (Algeria). History Sitifis was founded in 97 AD, during the reign of Nerva, as a colony for Roman veterans. Although no buildings of this period are known, a cemetery excavated in the 1960s contained Punic shaft tombs dated to the 2th century AD. As the town grew, around 297 AD, the province of Mauretania Sitifensis was established, with Sitifis as its capital. In the newly prosperous town a bath building was built, decorated with fine mosaics: its restoration in the fifth century had a cold room (''frigidarium'') paved with a large mosaic showing the birth of Venus. Setifis initially was populated by Punic people and later by Italian colonists. Sitifis was officially ''Colonia Augusta Nerviana Martialis Veteranorum Sitifensium'', and from the time of Diocletian, (29 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)