|
Masaaki Kimura
is a Japanese geologist and a Emeritus, professor emeritus from the Faculty of Science of the University of the Ryukyus, Okinawa, Japan. Biography Masaaki Kimura graduated in science at the Faculty of Fisheries of the University of Tokyo (1963) and obtained a Doctorate in marine geology (1968). He has worked for the University of Tokyo's Ocean Research Institute, the Geological Survey of Japan, the Agency of Industrial Science and Technology of the Ministry of International Trade and Industry of Japan, and Columbia University's Lamont–Doherty Earth Observatory. He taught at the University of the Ryukyus from 1977 to 2002. He has since retired from that University and is now general director oMarine Science and Culture Heritage Research Association Research His specialties are marine geology, geophysics, seismology, volcanology, and marine archaeology. He has extensively researched the formation of the Okinawa Trough, and claimed to have predicted the volcanic eruptions in Miy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emeritus
''Emeritus'' (; female: ''emerita'') is an adjective used to designate a retired chair, professor, pastor, bishop, pope, director, president, prime minister, rabbi, emperor, or other person who has been "permitted to retain as an honorary title the rank of the last office held". In some cases, the term is conferred automatically upon all persons who retire at a given rank, but in others, it remains a mark of distinguished service awarded selectively on retirement. It is also used when a person of distinction in a profession retires or hands over the position, enabling their former rank to be retained in their title, e.g., "professor emeritus". The term ''emeritus'' does not necessarily signify that a person has relinquished all the duties of their former position, and they may continue to exercise some of them. In the description of deceased professors emeritus listed at U.S. universities, the title ''emeritus'' is replaced by indicating the years of their appointmentsThe Protoc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volcanology
Volcanology (also spelled vulcanology) is the study of volcanoes, lava, magma and related geological, geophysical and geochemical phenomena (volcanism). The term ''volcanology'' is derived from the Latin word ''vulcan''. Vulcan was the ancient Roman god of fire. A volcanologist is a geologist who studies the eruptive activity and formation of volcanoes and their current and historic eruptions. Volcanologists frequently visit volcanoes, especially active ones, to observe volcanic eruptions, collect eruptive products including tephra (such as ash or pumice), rock and lava samples. One major focus of enquiry is the prediction of eruptions; there is currently no accurate way to do this, but predicting eruptions, like predicting earthquakes, could save many lives. Modern volcanology image:Icelandic tephra.JPG, Volcanologist examining tephra horizons in south-central Iceland. In 1841, the first volcanological observatory, the Vesuvius Observatory, was founded in the Kingdom o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Living People
Related categories * :Year of birth missing (living people) / :Year of birth unknown * :Date of birth missing (living people) / :Date of birth unknown * :Place of birth missing (living people) / :Place of birth unknown * :Year of death missing / :Year of death unknown * :Date of death missing / :Date of death unknown * :Place of death missing / :Place of death unknown * :Missing middle or first names See also * :Dead people * :Template:L, which generates this category or death years, and birth year and sort keys. : {{DEFAULTSORT:Living people 21st-century people People by status ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marine And Petroleum Geology
''Marine and Petroleum Geology'' is a peer-reviewed scientific journal covering marine and petroleum geology. It was established in 1984 and is published by Elsevier. The editor-in-chief is Massimo Zecchin ( Istituto Nazionale di Oceanografia e di Geofisica Sperimentale) and (Max) Qinhong Hu (The University of Texas at Arlington). Abstracting and indexing The journal is abstracted and indexed in: According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2017 impact factor The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an academic journal is a scientometric index calculated by Clarivate that reflects the yearly mean number of citations of articles published in the last two years in a given journal, as i ... of 3.281. References External links * Geology journals English-language journals Marine geology Petroleum geology Bimonthly journals Elsevier academic journals Publications established in 1984 {{Geology-journal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Scientist
''New Scientist'' is a magazine covering all aspects of science and technology. Based in London, it publishes weekly English-language editions in the United Kingdom, the United States and Australia. An editorially separate organisation publishes a monthly Dutch-language edition. First published on 22 November 1956, ''New Scientist'' has been available in online form since 1996. Sold in retail outlets (paper edition) and on subscription (paper and/or online), the magazine covers news, features, reviews and commentary on science, technology and their implications. ''New Scientist'' also publishes speculative articles, ranging from the technical to the philosophical. ''New Scientist'' was acquired by Daily Mail and General Trust (DMGT) in March 2021. History Ownership The magazine was founded in 1956 by Tom Margerison, Max Raison and Nicholas Harrison as ''The New Scientist'', with Issue 1 on 22 November 1956, priced at one shilling (a twentieth of a pound in pre-decimal UK cu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yonaguni
, one of the Yaeyama Islands, is the westernmost inhabited island of Japan, lying from the east coast of Taiwan, between the East China Sea and the Pacific Ocean proper. The island is administered as the Towns of Japan, town of Yonaguni, Okinawa, Yonaguni, Yaeyama, Okinawa, Yaeyama Gun, Okinawa Prefecture, Okinawa, and there are three settlements: Sonai, Kubura, and Higawa. History Early human migration from Taiwan to Yonaguni island has long been the subject of scholarly debate. In 2019, a team of Japanese and Taiwanese researchers succeeded in completing the two-day journey from Cape Wushibi in Taitung County to Yonaguni island along the Kuroshio current in a dugout canoe based on technology and materials from 30,000 years ago. Otherwise, the early history of Yonaguni remains vague. The first written record that ever mentions the island is a 1477 Korean document (''Chosen Hyōryūmin no Yaeyama kenbunroku''), an account of several fishermen from the current Jeju Province who ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yonaguni Monument
The , also known as , is a submerged rock formation off the coast of Yonaguni, the southernmost of the Ryukyu Islands, in Japan. It lies approximately a hundred kilometres east of Taiwan. Marine geologist Masaaki Kimura claims that the formations are man-made stepped monoliths. These claims have been described as pseudoarchaeological. Neither the Japanese Agency for Cultural Affairs nor the government of Okinawa Prefecture recognise the features as important cultural artifacts and neither government agency has carried out research or preservation work on the site. Discovery The sea off Yonaguni is a popular diving location during the winter months because of its large population of hammerhead sharks. In 1986, while looking for a good place to observe the sharks, Kihachiro Aratake, a director of the Yonaguni-Cho Tourism Association, noticed some singular seabed formations resembling architectural structures. Shortly thereafter, a group of scientists directed by Masaaki Kimur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mount Unzen
is an active volcanic group of several overlapping stratovolcanoes, near the city of Shimabara, Nagasaki on the island of Kyushu, Japan's southernmost main island. In 1792, the collapse of one of its several lava domes triggered a megatsunami that killed 14,524 people in Japan's worst volcanic-related disaster. The volcano was most recently active from 1990 to 1995, and a large eruption in 1991 generated a pyroclastic flow that killed 43 people, including three volcanologists. Its highest peaks are at and at . The latter emerged during the eruptions of the early, eponymous Heisei era (1989–2019). Overview Mount Unzen (or ) rises in the central part of the Shimabara Peninsula, Nagasaki Prefecture. It is located on the outer ring of the Chijiwa Caldera centering on Tachibana Bay in the west of the peninsula. It consists of a total of more than 20 mountains, however, the complexity in the shape of was expressed by various numbers (such as Mitake Goho/Mimine Godake as "2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Izu Ōshima
is an inhabited volcanic island in the Izu archipelago in the Philippine Sea, off the coast of Honshu, Japan, east of the Izu Peninsula and southwest of Bōsō Peninsula. As with the other islands in the Izu Island group, Izu Ōshima forms part of the Fuji-Hakone-Izu National Park. Izu Ōshima, at is the largest and closest of Tokyo's outlying islands, which also include the Ogasawara Islands. Geography The island is a stratovolcano with a basaltic composite cone, dating from the late Pleistocene period, between 10,000 and 15,000 years ago. It rises from an ocean floor with a depth of between . The island has a roughly circular coastline of approximately in length. The highest elevation, , is an active volcano with a height of . The mountain has been recorded to have erupted numerous times through history and is mentioned as far back as Nara period written records. Major eruptions occurred in 1965 and 1986, each forcing the temporary evacuation of the inhabitants. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miyake Island
is an inhabited volcanic island in the Izu archipelago in the Philippine Sea approximately southeast of Tokyo, Japan. As with the other islands in the Izu Island group, Miyake-jima forms part of the Fuji-Hakone-Izu National Park. Etymology There are many theories about the origin of Miyake-jima's name. One theory claims a manuscript about the island's genesis called the ''Miyakeki'' (三宅記), written by a Shinto priest from the island, influenced the name. The manuscript explains how a deity, ''Mashima (三嶋)'', constructed his palace on the island after having built two other houses on neighbouring islands. Each of the houses had their backs facing the palace, thus giving a lined up impression. This belief is known as the 'three house theory'. Another hypothesis says that the shrines on Miyake-jima are historically related to those on Miyajima, an island in Hiroshima Bay. As there are many more speculations, the true origin cannot be known. Geography The island is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eruption
Several types of volcanic eruptions—during which lava, tephra (ash, lapilli, volcanic bombs and volcanic blocks), and assorted gases are expelled from a volcanic vent or fissure—have been distinguished by volcanologists. These are often named after famous volcanoes where that type of behavior has been observed. Some volcanoes may exhibit only one characteristic type of eruption during a period of activity, while others may display an entire sequence of types all in one eruptive series. There are three different types of eruptions: * Magmatic eruptions are the most well-observed type of eruption. They involve the decompression of gas within magma that propels it forward. * Phreatic eruptions are driven by the superheating of steam due to the close proximity of magma. This type exhibits no magmatic release, instead causing the granulation of existing rock. * Phreatomagmatic eruptions are driven by the direct interaction of magma and water, as opposed to phreatic erupti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
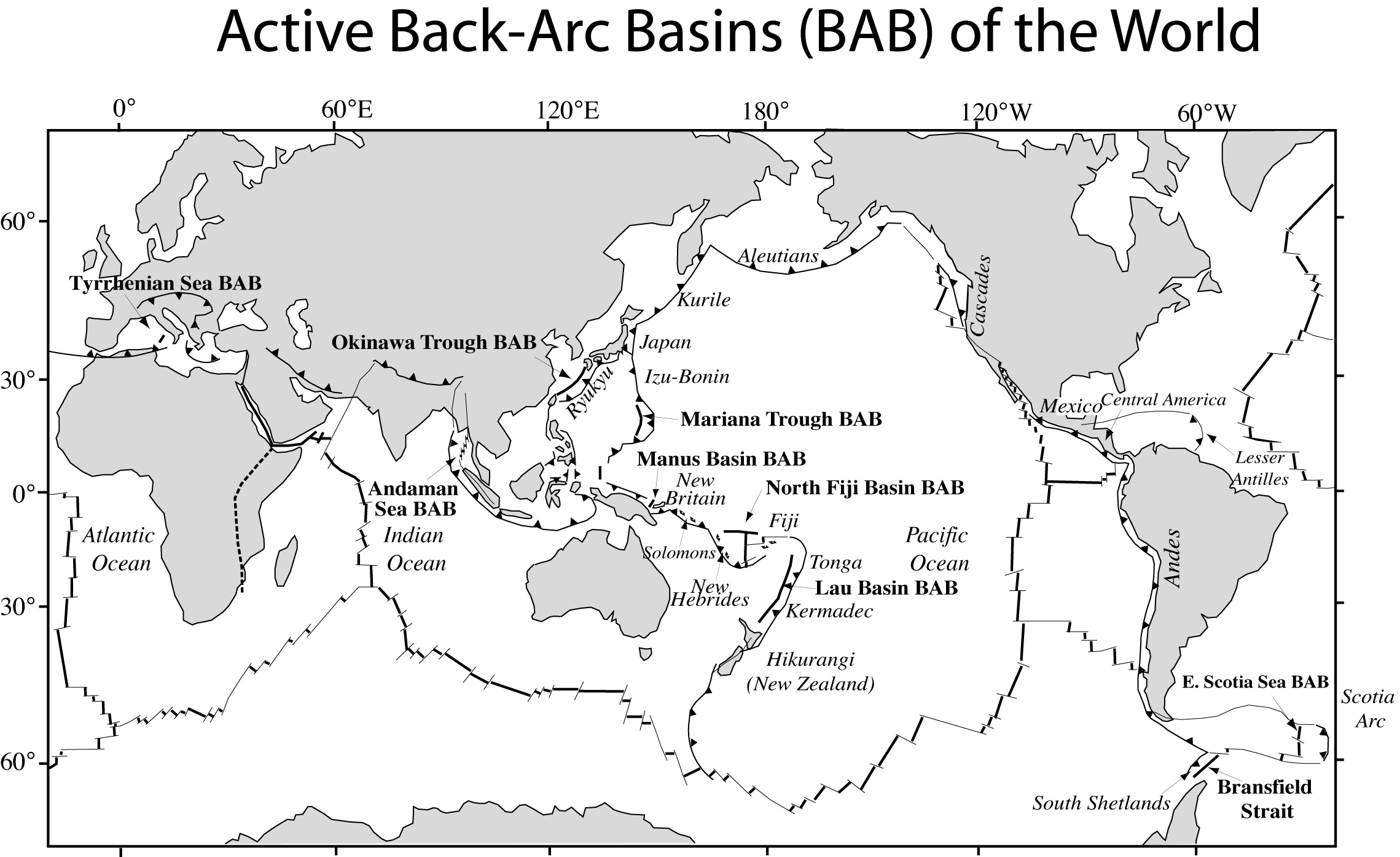
Okinawa Trough
The (also called , literally China-Ryukyu Border Trough ) is a seabed feature of the East China Sea. It is an active, initial back-arc rifting basin which has formed behind the Ryukyu arc-trench system in the West Pacific. It developed where the Philippine Sea Plate is subducting under the Eurasia Plate. Description It is a back-arc basin formed by extension within the continental lithosphere behind the far deeper Ryukyu Trench-arc system. The thickness of the crust in the northern Okinawa Trough is 30 km, thinning to 10 km in the southern Okinawa Trough. It has a large section more than deep and a maximum depth of . The Okinawa Trough still in an early stage of evolving from arc type to back-arc activity, and features volcanoes such as the Yonaguni Knoll IV. Implications for the China–Japan maritime boundary Interpretations The existence of the Okinawa Trough complicates descriptive issues in the East China Sea.Ji, Guoxing. (1995) "Maritime Jurisdiction in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |