|
Mary Polly Paaaina
Mary Polly Paʻaʻāina, also known as Mary ʻĪʻī ( – May 28, 1853) was a Hawaiian chiefess of the Kingdom of Hawaii. At a young age, she was chosen to attend the Chiefs' Children's School (later renamed Royal School) taught by the American missionary Amos Starr Cooke and his wife, Juliette Montague Cooke, alongside her half-sister Queen Emma of Hawaii and fourteen of her royal cousins. Early life and education She was born circa 1833 to Henry Coleman Lewis and High Chiefess Fanny Kekelaokalani Young. Her mother was daughter of John Young, the British advisor of Kamehameha I. Her half-sister was Emma Rooke, who was three years younger than her and the daughter of her mother's marriage to George Naʻea. Her biological father Henry Coleman Lewis died in the first week of the influenza epidemic of 1845. She was adopted under the Hawaiian tradition of ''hānai'' by John Papa ʻĪʻī and his wife Sarai Hiwauli. Her ''hānai'' parents were lower-ranking ''aliʻi'' and her ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hawaiian Kingdom
The Hawaiian Kingdom, or Kingdom of Hawaiʻi (Hawaiian language, Hawaiian: ''Ko Hawaiʻi Pae ʻĀina''), was a sovereign state located in the Hawaiian Islands. The country was formed in 1795, when the warrior chief Kamehameha the Great, of the independent island of Hawaii (island), Hawaiʻi, conquered the independent islands of Oahu, Oʻahu, Maui, Molokai, Molokaʻi and Lanai, Lānaʻi and unified them under one government. In 1810, the whole Hawaiian archipelago became unification of Hawaii, unified when Kauai, Kauaʻi and Niihau, Niʻihau joined the Hawaiian Kingdom voluntarily. Two major dynastic families ruled the kingdom: the House of Kamehameha and the House of Kalākaua. The kingdom won recognition from the major European powers. The United States became its chief trading partner and Hawaiian Kingdom–United States relations, watched over it to Monroe Doctrine, prevent other powers (such as British Empire, Britain and Empire of Japan, Japan) from asserting hegemony. In 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kamehameha V
Kamehameha V (Lota Kapuāiwa Kalanimakua Aliʻiōlani Kalanikupuapaʻīkalaninui; December 11, 1830 – December 11, 1872), reigned as the fifth monarch of the Hawaiian Kingdom, Kingdom of Hawaiʻi from 1863 to 1872. His motto was "Onipaʻa": immovable, firm, steadfast or determined; he worked diligently for his people and kingdom and was described as the last great traditional chief. Early life He was born and given the name Lot Kapuāiwa December 11, 1830. His mother was Kīnaʻu, Elizabeth Kīnaʻu and father was Kekūanāoʻa, Mataio Kekūanāoʻa. His siblings included David Kamehameha, Moses Kekūāiwa, Kamehameha IV, Alexander Liholiho, and Victoria Kamāmalu. He also was a grandson of Kamehameha I. ''Kapu āiwa'' means mysterious Kapu (Hawaiian culture), kapu or sacred one protected by supernatural powers. He was adopted using the ancient Hawaiian tradition called ''hānai'' by Nahienaena, Princess Nāhiʻenaʻena, but she died in 1836. He was then adopted by his gran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
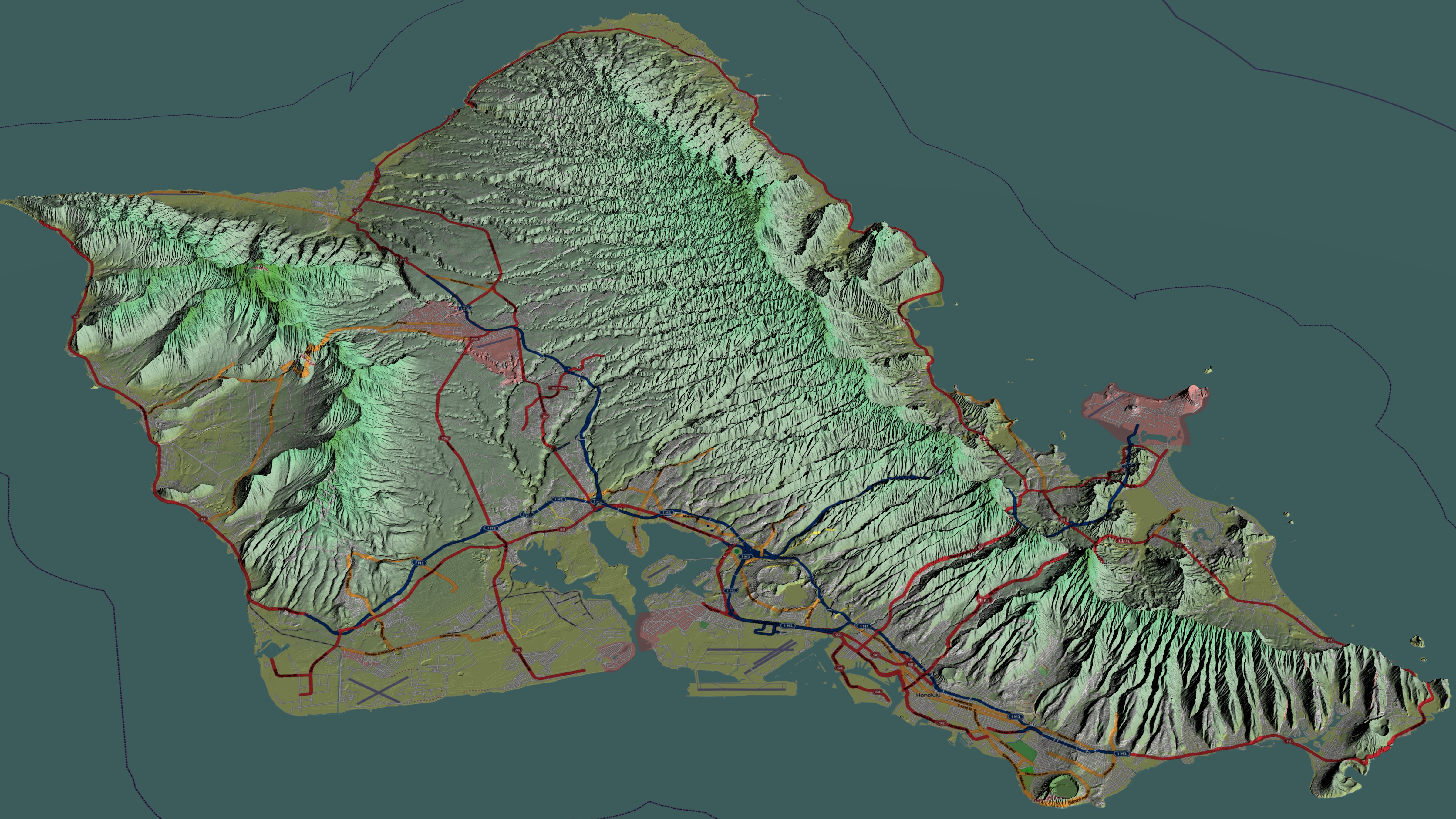
Oahu
Oahu () (Hawaiian language, Hawaiian: ''Oʻahu'' ()), also known as "The Gathering place#Island of Oʻahu as The Gathering Place, Gathering Place", is the third-largest of the Hawaiian Islands. It is home to roughly one million people—over two-thirds of the population of the U.S. state of Hawaii. The island of O’ahu and the Northwestern Hawaiian Islands constitute the City and County of Honolulu, Hawaii, City and County of Honolulu. The state capital, Honolulu, is on Oʻahu's southeast coast. Oʻahu had a population of 1,016,508 according to the 2020 U.S. Census, up from 953,207 people in 2010 (approximately 70% of the total 1,455,271 population of the State of Hawaii, with approximately 81% of those living in or near the Honolulu urban area). Name The Island of O{{okinaahu in Hawaii is often nicknamed (or translated as) ''"The Gathering Place"''. It appears that O{{okinaahu grew into this nickname; it is currently the most populated Hawaiian islands, Hawaiian Island, how ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Honolulu
Honolulu (; ) is the capital and largest city of the U.S. state of Hawaii, which is in the Pacific Ocean. It is an unincorporated county seat of the consolidated City and County of Honolulu, situated along the southeast coast of the island of Oahu, and is the westernmost and southernmost major U.S. city. Honolulu is Hawaii's main gateway to the world. It is also a major hub for business, finance, hospitality, and military defense in both the state and Oceania. The city is characterized by a mix of various Asian, Western, and Pacific cultures, reflected in its diverse demography, cuisine, and traditions. ''Honolulu'' means "sheltered harbor" or "calm port" in Hawaiian; its old name, ''Kou'', roughly encompasses the area from Nuuanu Avenue to Alakea Street and from Hotel Street to Queen Street, which is the heart of the present downtown district. The city's desirability as a port accounts for its historical growth and importance in the Hawaiian archipelago and the broader P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cooke Memorial Tablet, 1912
Cooke is a surname derived from the occupation of cook. Notable people with the surname include: * Alexander Cooke (died 1614), English actor * Alfred Tyrone Cooke, of the Indo-Pakistani wars * Alistair Cooke KBE (1908–2004), British-American journalist and broadcaster * Amos Starr Cooke (1810–1871), found of Royal School and Castle & Cooke in Hawaii * Anna Rice Cooke (1853–1934), patron of the arts and founder of the Honolulu Academy of Arts * Anthony Cooke (1505–1576), British scholar * Baden Cooke (born 1978), Australian cyclist * Barrie Cooke (born 1931), Irish painter * Bates Cooke, US Representative 1831–1833, and NY State Comptroller 1839–1841 * Benjamin Cooke (1734–1793), British musician * Beryl Cooke (1906–2001), British actress * C. R. Cooke (Conrad Reginald Cooke, 1901–1996), English early Himalayan mountaineer * Charles Cooke (other), several people * Chauncey H. Cooke (1846–1919), American soldier in the U.S. Civil War * Christian Cooke ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liliʻuokalani
Liliʻuokalani (; Lydia Liliʻu Loloku Walania Kamakaʻeha; September 2, 1838 – November 11, 1917) was the only queen regnant and the last sovereign monarch of the Hawaiian Kingdom, ruling from January 29, 1891, until the overthrow of the Hawaiian Kingdom on January 17, 1893. The composer of " Aloha ʻOe" and numerous other works, she wrote her autobiography '' Hawaiʻi's Story by Hawaiʻi's Queen'' during her imprisonment following the overthrow. Liliʻuokalani was born on September 2, 1838, in Honolulu, on the island of Oʻahu. While her natural parents were Analea Keohokālole and Caesar Kapaʻakea, she was ''hānai'' (informally adopted) at birth by Abner Pākī and Laura Kōnia and raised with their daughter Bernice Pauahi Bishop. Baptized as a Christian and educated at the Royal School, she and her siblings and cousins were proclaimed eligible for the throne by King Kamehameha III. She was married to American-born John Owen Dominis, who later became the Governor o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kalākaua
Kalākaua (David Laʻamea Kamananakapu Mahinulani Naloiaehuokalani Lumialani Kalākaua; November 16, 1836 – January 20, 1891), sometimes called The Merrie Monarch, was the last king and penultimate monarch of the Hawaiian Kingdom, Kingdom of Hawaiʻi, reigning from February 12, 1874, until his death in 1891. Succeeding Lunalilo, he was elective monarchy, elected to the vacant throne of Hawaiʻi against Queen Emma of Hawaii, Queen Emma. Kalākaua had a convivial personality and enjoyed entertaining guests with his singing and ukulele playing. At his coronation and his birthday jubilee, the hula, which had hitherto been banned in public in the kingdom, became a celebration of Hawaiian culture. During Kalākaua's reign, the Reciprocity Treaty of 1875 brought great prosperity to the kingdom. Its renewal continued the prosperity but allowed United States to have exclusive use of Pearl Harbor. In 1881, Kalākaua took a trip around the world to encourage the immigration ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peter Kaeo
Peter Young Kaʻeo Kekuaokalani (March 4, 1836 – November 26, 1880) was a Hawaiian high chief (aliʻi) and politician of the Kingdom of Hawaii. His cousin was Emma, who contended for the throne after the death of Kamehameha. After being diagnosed with leprosy, he was exiled in 1873 to Kalaupapa, the isolation settlement on Molokaʻ. He was later permitted to return to Honolulu, where he died. Life Peter was born March 4, 1836 at Paloha, Honolulu on the island of Oʻahu. His mother was Jane Lahilahi, the youngest daughter of John Young Olohana, the advisor to Kamehameha I, and Chiefess Kaʻōanaʻeha. His father was Joshua Kaʻeo, judge of the Supreme Court of Hawaii, and great-great grandson or great grandson of King Kalaniopuu. He was adopted at birth by his maternal uncle John Kalaipaihala Young, according to Hawaiian tradition of ''hānai.'' His uncle was the fourth Kuhina Nui and the Minister of the Interior. Kaeo was declared eligible to succeed to the Hawaiian thro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Kaliokalani
James Kaliokalani, also referred to as Kali; (May 29, 1835 – April 2/21, 1852) was a Hawaiian high chief of the Kingdom of Hawaii. At a young age, he was chosen to attend the Chiefs' Children's School (later renamed Royal School). He was taught by the American missionary Amos Starr Cooke and his wife, Juliette Montague Cooke, alongside his siblings and thirteen of their royal cousins, who were declared eligible to succeed to the Hawaiian throne. He died in 1852, shortly after leaving the school and working as a court interpreter. Early life and family James Kaliokalani was born on May 29, 1835. His father High Chief Caesar Kapaʻakea and mother High Chiefess Analea Keohokālole were advisors to the reigning king Kamehameha III. His mother was the daughter of ʻAikanaka and Kamaʻeokalani while his father was the son of Kamanawa II (half-brother of ʻAikanaka) and Kamokuiki. From his parents, he descended from Keaweaheulu and Kameʻeiamoku, the royal counselors of Kameha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elizabeth Kekaʻaniau
Elizabeth Kekaʻaniau Laʻanui Pratt, full name Elizabeth Kekaʻaniauokalani Kalaninuiohilaukapu Kekaikuihala Laʻanui Pratt (September 11, 1834 – December 20, 1928), was a Hawaiian high chiefess (aliʻi) and great-grandniece of Kamehameha I, being a great-granddaughter of Kalokuokamaile, the older brother of Kamehameha I, founder of the Kingdom of Hawaii. She was the daughter of Gideon Peleʻioholani Laʻanui and Theresa Owana Kaheiheimalie Rives. At a young age, Kekaʻaniau was chosen to attend the Chiefs' Children's School (later renamed the Royal School) taught by American missionaries and declared eligible to succeed to the Hawaiian throne by King Kamehameha III. She married American businessman Franklin Seaver Pratt and became known as Mrs. Pratt. Five of her classmates became reigning monarchs of Hawaii until the 1893 overthrow of the Kingdom of Hawaii. In 1920, she wrote ''History of Keoua Kalanikupuapa-i-nui: Father of Hawaii Kings, and His Descendants'', a book a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abigail Maheha
Abigail Maheha (July 10, 1832 – February 13, 1861) was a Hawaiian chiefess (aliʻi) of the Kingdom of Hawaii. At a young age, she was chosen to attend the Chiefs' Children's School (later renamed the Royal School) taught by the American missionary Amos Starr Cooke and his wife, Juliette Montague Cooke, alongside her half-sister Jane Loeau and fourteen of her royal cousins. Early life and education Maheha was the daughter of High Chief Namaile and High Chiefess Kuini Liliha. Her mother was the royal governor of Oʻahu during the regency of Queen Kaʻahumanu. She was descended from Kahekili II, Moi of Maui, and High Chief Hoapili. ; ; She was adopted or ''hānaied'' by her aunt, Princess Kekauʻōnohi. Her ''hānai'' mother was a granddaughter of Kamehameha the Great who united the Hawaiian Islands into one kingdom and was also the youngest consort of the deceased Kamehameha II and served as Governor of Kauaʻi. She was among those chosen by King Kamehameha III eligible fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bernice Pauahi Bishop
Bernice Pauahi Bishop KGCOK RoK (December 19, 1831 – October 16, 1884), born Bernice Pauahi Pākī, was an '' alii'' (noble) of the Royal Family of the Kingdom of Hawaii and a well known philanthropist. At her death, her estate was the largest private landownership in the Hawaiian Islands, comprising approximately 9% of Hawaii's total area. The revenues from these lands are used to operate the Kamehameha Schools, which were established in 1887 according to Pauahi's will. Pauahi was married to businessman and philanthropist Charles Reed Bishop. Ancestry, birth and early life Pauahi was born in Honolulu on December 19, 1831, in ʻAikupika the grass hut compound of her father, Abner Kuhooheiheipahu Pākī (c. 1808–1855). Pākī was an ''aliʻi'' (noble) from the island of Molokaʻi, and son of Kalani-hele-maiiluna, who descended from the ''aliʻi nui'' (ruling monarchs) of the island of Maui. Her mother was Laura Kōnia (c. 1808–1857), the younger daughter of Pauli K ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)